Summary
Microsoft is investigating two reported zero-day vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, 2016, and 2019. The first vulnerability, identified as CVE-2022-41040, is a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability, while the second, identified as CVE-2022-41082, allows remote code execution (RCE) when PowerShell is accessible to the attacker.
At this time, Microsoft is aware of limited targeted attacks using the two vulnerabilities to get into users’ systems. In these attacks, CVE-2022-41040 can enable an authenticated attacker to remotely trigger CVE-2022-41082. It should be noted that authenticated access to the vulnerable Exchange Server is necessary to successfully exploit either of the two vulnerabilities.
We are working on an accelerated timeline to release a fix. Until then, we’re providing the mitigations and detections guidance below to help customers protect themselves from these attacks.
Microsoft Exchange Online has detections and mitigation in place to protect customers. Microsoft is also monitoring these already deployed detections for malicious activity and will take necessary response actions to protect customers.
We will continue to provide updates here to help keep customers informed.
Mitigations
Microsoft Exchange Online Customers do not need to take any action. On premises Microsoft Exchange customers should review and apply the following URL Rewrite Instructions and block exposed Remote PowerShell ports.
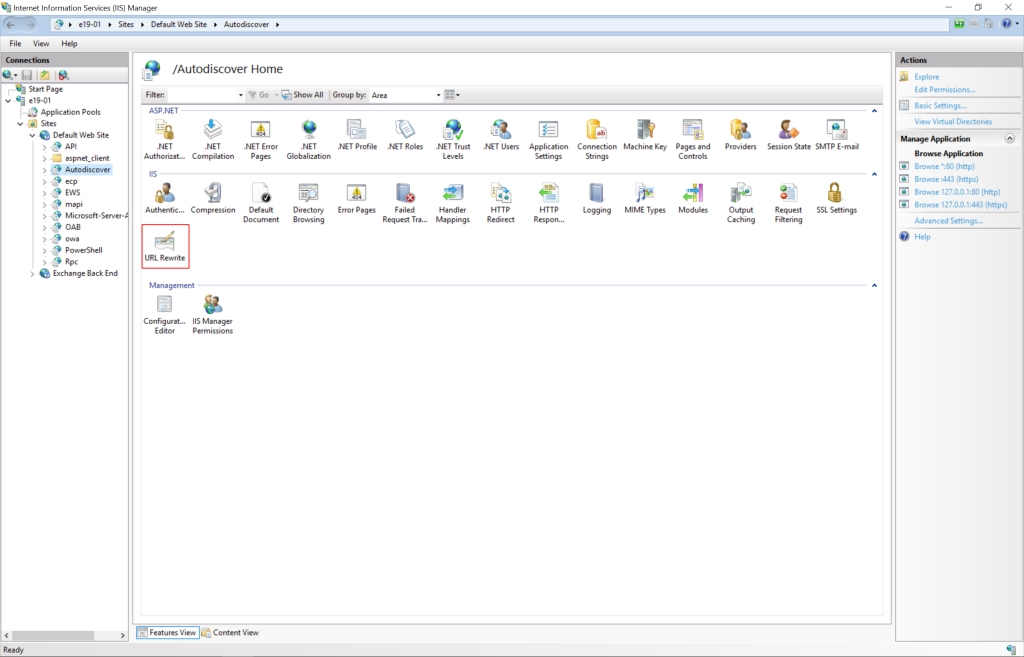
The current mitigation is to add a blocking rule in “IIS Manager -> Default Web Site -> Autodiscover -> URL Rewrite -> Actions” to block the known attack patterns.
Microsoft has confirmed that the following URL Rewrite Instructions, which are currently being discussed publicly, are successful in breaking current attack chains.
- Open the IIS Manager.
- Expand the Default Web Site.
- Select Autodiscover.
- In the Feature View, click URL Rewrite.

- In the Actions pane on the right-hand side, click Add Rules.

- Select Request Blocking and click OK.

- Add String “.*autodiscover\.json.*\@.*Powershell.*” (excluding quotes) and click OK.

- Expand the rule and select the rule with the Pattern “.*autodiscover\.json.*\@.*Powershell.*” and click Edit under Conditions.

- Change the condition input from {URL} to {REQUEST_URI}

Impact: There is no known impact to Exchange functionality if the URL Rewrite module is installed as recommended.
Authenticated attackers who can access PowerShell Remoting on vulnerable Exchange systems will be able to trigger RCE using CVE-2022-41082. Blocking the ports used for Remote PowerShell can limit these attacks.
- HTTP: 5985
- HTTPS: 5986
Detections
Microsoft Sentinel
While we do not currently have a specific detection query for this issue, based on what we are seeing in the wild, these techniques will help defenders. Our post on Web Shell Threat Hunting with Microsoft Sentinel also provides valid guidance for looking for web shells in general.
The Exchange SSRF Autodiscover ProxyShell detection, which was created in response to ProxyShell, can be used for queries as there are similarities in function with this threat. Also, we have a new Exchange Server Suspicious File Downloads query which specifically looks for suspicious downloads in IIS logs. In addition to those, we have a few more that could be helpful in looking for post-exploitation activity:
- Exchange OAB Virtual Directory Attribute Containing Potential Webshell
- Web Shell Activity
- Malicious web application requests linked with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint alerts
- exchange-iis-worker-dropping-webshell
- Web shell Detection
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint detects post-exploitation activity. The following alerts can be related to this threat:
- Possible web shell installation
- Possible IIS web shell
- Suspicious Exchange Process Execution
- Possible exploitation of Exchange Server vulnerabilities
- Suspicious processes indicative of a web shell
- Possible IIS compromise
Defender for Endpoint customers with Microsoft Defender Antivirus enabled can also detect the web shell malware used in in-the-wild exploitation of this vulnerability as of this writing with the following alerts:
- ‘Chopper’ malware was detected on an IIS Web server
- ‘Chopper’ high-severity malware was detected
Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender Antivirus detects the post exploitation malware used in current in-the-wild exploitation of this vulnerability as the following:
- Backdoor:ASP/Webshell.Y (Backdoor:ASP/Webshell.Y threat description – Microsoft Security Intelligence)
- Backdoor:Win32/RewriteHttp.A (Backdoor:Win32/RewriteHttp.A threat description – Microsoft Security Intelligence)