作者:oliverdding,腾讯 CSIG 测试开发工程师
你想要的 ClickHouse 优化,都在这里。
ClickHouse 是 OLAP(Online analytical processing)数据库,以速度见长[1]。ClickHouse 为什么能这么快?有两点原因[2]:
架构优越 列式存储 索引 数据压缩 向量化执行 资源利用 关注底层细节
但是,数据库设计再优越也拯救不了错误的使用方式,本文以 MergeTree 引擎家族为例讲解如何对查询优化。
ClickHouse 查询执行过程
⚠️ 本节基于 ClickHouse 22.3 版本分析
clickhouser-server启动后会在 while 循环中等待请求,接收到查询后会调用executeQueryImpl()行数构建 AST、优化并生成执行计划 pipeline,最后在executeImpl()中多线程执行 DAG 获取结果,这篇文章只关心 SQL 执行,省略掉网络交互部分,查询执行流程如下图所示:
SQL 的解析优化和编译原理息息相关,本节将包含大量编译原理和代码细节,属扩展知识。
词法解析和语法解析
ClickHouse 拿到需要执行的 SQL,首先需要将 String 格式的字符串解析为它能理解的数据结构,也就是 AST 和执行计划。构造 AST 部分代码如下所示:
// src/Interpreters/executeQuery.cppstatic std::tuple<ASTPtr, BlockIO> executeQueryImpl()
{
// 构造Parser
ParserQuery parser(end, settings.allow_settings_after_format_in_insert);
// 将SQL转为抽象语法树
ast = parseQuery(parser, begin, end, "", max_query_size, settings.max_parser_depth);
// 设置query的上下文,比如SETTINGS
...
if (async_insert)
{
...
} else {
// 生成interpreter实例
interpreter = InterpreterFactory::get(ast, context, SelectQueryOptions(stage).setInternal(internal));
// interpreter优化AST并返回执行计划
res = interpreter->execute();
}
// 返回抽象语法树和执行计划
return std::make_tuple(ast, std::move(res));
}
值得一提的是,解析 SQL 生成语法树这是编译原理中词法分析和语法分析部分覆盖的事情。词法分析只是简单拆解数据流为一个个 token,而语法分析分为自顶向下和自底向上两种方式,常见的语法分析方式也分为手写语法分析(往往是自顶向下的有限状态机,递归下降分析)和语法分析工具(往往是自底向上,如 Flex、Yacc/Bison 等)。
手写语法分析比起语法分析工具有几个优势(当然要写得好的情况):
性能更好。可以优化热点路径等 诊断和错误恢复更清晰明了。手写状态机可以完全掌控系统状态,错误处理更容易 简单。不需要掌握新语法
ClickHouse 解析 SQL 的函数如下所示:
// src/Parsers/parseQuery.cppASTPtr tryParseQuery()
{
// 将SQL拆分为token流
Tokens tokens(query_begin, all_queries_end, max_query_size);
IParser::Pos token_iterator(tokens, max_parser_depth);
// 将token流解析为语法树
ASTPtr res;
const bool parse_res = parser.parse(token_iterator, res, expected);
return res;
}
可以看到先将 SQL 字符串拆解为 token 流(词法分析),再调用perser.parse()函数进行语法分析,它的实现如下:
// src/Parsers/ParserQuery.cppbool ParserQuery::parseImpl(Pos & pos, ASTPtr & node, Expected & expected)
{
ParserQueryWithOutput query_with_output_p(end, allow_settings_after_format_in_insert);
ParserInsertQuery insert_p(end, allow_settings_after_format_in_insert);
ParserUseQuery use_p;
ParserSetQuery set_p;
ParserSystemQuery system_p;
ParserCreateUserQuery create_user_p;
ParserCreateRoleQuery create_role_p;
ParserCreateQuotaQuery create_quota_p;
ParserCreateRowPolicyQuery create_row_policy_p;
ParserCreateSettingsProfileQuery create_settings_profile_p;
ParserCreateFunctionQuery create_function_p;
ParserDropFunctionQuery drop_function_p;
ParserDropAccessEntityQuery drop_access_entity_p;
ParserGrantQuery grant_p;
ParserSetRoleQuery set_role_p;
ParserExternalDDLQuery external_ddl_p;
ParserTransactionControl transaction_control_p;
ParserBackupQuery backup_p;
bool res = query_with_output_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| insert_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| use_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| set_role_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| set_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| system_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_user_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_role_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_quota_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_row_policy_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_settings_profile_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| create_function_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| drop_function_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| drop_access_entity_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| grant_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| external_ddl_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| transaction_control_p.parse(pos, node, expected)
|| backup_p.parse(pos, node, expected);
return res;
}
可以发现 ClickHouse 将 Query 分为了 18 种类型(截止 2022-11-12 日),每种 Query 都有自己的 Parser,通过关键词匹配构造 AST 上的节点,最终生成语法树。递归下降部分超纲了,这里就不铺开讲。
优化器
经过语法分析后生成的 AST 并不是执行最优解,ClickHouse 包含大量基于规则的优化(rule based optimization),每个 Query 会遍历一遍优化规则,将满足的情况进行不改变查询语义地重写。
每一种 Query 类型都有对应的 Interpreter,后文都以 Select 查询举例,代码如下:
// src/Interpreters/InterpreterFactory.cppstd::unique_ptr<IInterpreter> InterpreterFactory::get()
{
...
if (query->as<ASTSelectQuery>())
{
return std::make_unique<InterpreterSelectQuery>(query, context, options);
}
...
}
在InterpreterSelectQuery类的构造函数中将 AST 优化、重写,代码详见src/Interpreters/InterpreterSelectQuery.cpp,这里只画流程图:
是否初始化 settings 优化 with 优化 joins 谓词下推将 where 下推到 prewhere 是否要再次优化检查 storage 权限生成 analysis_result 和 result_header
构造执行计划
src/Interpreters/InterpreterSelectQuery.cpp文件InterpreterSelectQuery::executeImpl()方法将优化分析得到的中间数据辅助生成最终的执行计划,代码如下:
// src/Interpreters/InterpreterSelectQuery.cppvoid InterpreterSelectQuery::executeImpl()
{
...
// 个人理解针对EXPLAIN PLAN,只构建执行计划不执行
if (options.only_analyze)
{
...
}
else
{
// 从磁盘读取所需列,注意这一行,后文跳转进去分析
executeFetchColumns(from_stage, query_plan);
}
if (options.to_stage > QueryProcessingStage::FetchColumns)
{
// 在分布式执行Query时只在远程节点执行
if (expressions.first_stage)
{
// 当storage不支持prewhere时添加FilterStep
if (!query_info.projection && expressions.filter_info)
{
...
}
if (expressions.before_array_join)
{
...
}
if (expressions.array_join)
{
...
}
if (expressions.before_join)
{
...
}
// 可选步骤:将join key转为一致的supertype
if (expressions.converting_join_columns)
{
...
}
// 添加Join
if (expressions.hasJoin())
{
...
}
// 添加where
if (!query_info.projection && expressions.hasWhere())
executeWhere(query_plan, expressions.before_where, expressions.remove_where_filter);
// 添加aggregation
if (expressions.need_aggregate)
{
executeAggregation(
query_plan, expressions.before_aggregation, aggregate_overflow_row, aggregate_final, query_info.input_order_info);
/// We need to reset input order info, so that executeOrder can't use it
query_info.input_order_info.reset();
if (query_info.projection)
query_info.projection->input_order_info.reset();
}
// 准备执行:
// 1. before windows函数
// 2. windows函数
// 3. after windows函数
// 4. 准备DISTINCT
if (expressions.need_aggregate)
{
// 存在聚合函数,在windows函数/ORDER BY之前不执行
}
else
{
// 不存在聚合函数
// 存在windows函数,应该在初始节点运行
// 并且,ORDER BY和DISTINCT依赖于windows函数,这里也不能运行
if (query_analyzer->hasWindow())
{
executeExpression(query_plan, expressions.before_window, "Before window functions");
}
else
{
// 没有windows函数,执行before ORDER BY、准备DISTINCT
assert(!expressions.before_window);
executeExpression(query_plan, expressions.before_order_by, "Before ORDER BY");
executeDistinct(query_plan, true, expressions.selected_columns, true);
}
}
// 如果查询没有GROUP、HAVING,有ORDER或LIMIT,会在远程排序、LIMIT
preliminary_sort();
}
// 在分布式执行Query时只在初始节点执行或optimize_distributed_group_by_sharding_key开启时
if (expressions.second_stage || from_aggregation_stage)
{
if (from_aggregation_stage)
{
// 远程节点聚合过,这里啥也不干
}
else if (expressions.need_aggregate)
{
// 从不同节点拉取数据合并
if (!expressions.first_stage)
executeMergeAggregated(query_plan, aggregate_overflow_row, aggregate_final);
if (!aggregate_final)
{
// 执行group by with totals/rollup/cube
...
}
// 添加Having
else if (expressions.hasHaving())
executeHaving(query_plan, expressions.before_having, expressions.remove_having_filter);
}
// 报个错
else if (query.group_by_with_totals || query.group_by_with_rollup || query.group_by_with_cube)
throw Exception("WITH TOTALS, ROLLUP or CUBE are not supported without aggregation", ErrorCodes::NOT_IMPLEMENTED);
// 准备执行:
// 1. before windows函数
// 2. windows函数
// 3. after windows函数
// 4. 准备DISTINCT
if (from_aggregation_stage)
{
if (query_analyzer->hasWindow())
throw Exception(
"Window functions does not support processing from WithMergeableStateAfterAggregation",
ErrorCodes::NOT_IMPLEMENTED);
}
else if (expressions.need_aggregate)
{
executeExpression(query_plan, expressions.before_window,
"Before window functions");
executeWindow(query_plan);
executeExpression(query_plan, expressions.before_order_by, "Before ORDER BY");
executeDistinct(query_plan, true, expressions.selected_columns, true);
}
else
{
if (query_analyzer->hasWindow())
{
executeWindow(query_plan);
executeExpression(query_plan, expressions.before_order_by, "Before ORDER BY");
executeDistinct(query_plan, true, expressions.selected_columns, true);
}
else
{
// Neither aggregation nor windows, all expressions before
// ORDER BY executed on shards.
}
}
// 添加order by
if (expressions.has_order_by)
{
// 在分布式查询中,没有聚合函数却有order by,将会在远端节点order by
...
}
// 多source order by优化
...
// 多条流时再次执行distinct
if (!from_aggregation_stage && query.distinct)
executeDistinct(query_plan, false, expressions.selected_columns, false);
// 处理limit
...
// 处理projection
...
// 处理offset
...
}
// 需要子查询结果构建set
if (!subqueries_for_sets.empty())
executeSubqueriesInSetsAndJoins(query_plan, subqueries_for_sets);
}
}
其中InterpreterSelectQuery::executeFetchColumns()函数是读取所需列的阶段。从代码中可以看到它也做了很多的优化:
count()优化只有 LIMIT 情况的优化 quota限制
可以看到:
limit 大部分情况下是计算完成后再执行,而 quota 是在读取数据时执行的 加速的关键是减少读入的数据量,也就是说善用索引 用 count()、count(1)和count(*),ClickHouse 都有优化,但不要count(any_field)
索引设计
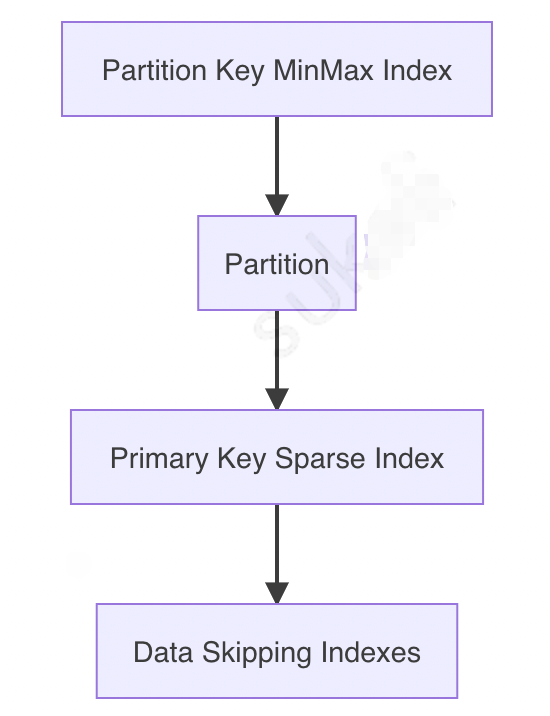
索引是 ClickHouse 快速查询最重要的一环,分为主键索引(sparse indexes)和跳表索引(data skipping indexes)。在执行查询时,索引命中顺序如下图所示:
Partition Key MinMax IndexPartitionPrimary Key Sparse IndexData Skipping Indexes
详见代码:
// src/Processors/QueryPlan/ReadFromMergeTree.cppMergeTreeDataSelectAnalysisResultPtr ReadFromMergeTree::selectRangesToRead()
{
...
try
{
// 使用partition by选取需要parts
MergeTreeDataSelectExecutor::filterPartsByPartition(...);
// 处理抽样
...
// 使用主键索引和跳表索引
result.parts_with_ranges = MergeTreeDataSelectExecutor::filterPartsByPrimaryKeyAndSkipIndexes(...);
}
catch(...)
{
...
}
...
}
值得注意的是,主键的 sparse index 使用二分查找直接缩小范围到所需要的 parts,而跳表索引就需要在选出来的 parts 里,每 n 个(用户自定义)granules 就需要比较 n 次。
最佳实践:
partition by 需要一个可以转为时间的列,比如 Datatime、Date 或者时间戳,而如果 primary key 中也有时间字段,可以使用同一个字段避免查询时需要同时指定两个时间字段。比如:指定为数据处理时间。
Partition
首先要辨析 part 和 partition 的区别,ClickHouse 应用层面定义了 partition,用户指定 partition by 关键词设置不同的 partition,但是 partition 只是逻辑分区。真正存储到磁盘时按 part 来存储,每一个 part 一个文件夹,里面存储不同字段的.mrk和.bin文件,以及一个minmax_{PARTITION_KEY_COLUMN}.idx文件,不同 part 的 minmax 作为一个索引存储于内存。
当查询的 WHERE 带有 partition key 时,首先会比较每一个 part 的 minmax 索引过滤不相关 parts。之后再根据 PARTITION BY 定义的规则过滤不相关 partition。
可是 partition 不是越小越好。
partitioning 并不会加速查询(有主键存在),过小的 partition 反而会导致大量的 parts 无法合并(MergeTree 引擎家族会在后台不断合并 parts),因为属于不同 partition 的 parts 无法合并。[5]
最佳实践[6]:
一个(Replicated)MergeTree 的 partition 大概 1 ~ 300GB Summing/ReplacingMergeTree 的 partition 大概 400MB ~ 40GB 查询时涉及尽量少 partition 插入时最好只有 1 ~ 2 个分区 一张表维持 100 个分区以内
Primary key index
主键是 ClickHouse 最重要的索引,没有之一。好的主键应该能有效排除大量无关的数据 granules,减少磁盘读取的字节数。
先讲几个主键的背景知识:
主键用于数据排序 ClickHouse 讲数据按主键排序,再按 index_granularity设置的大小(默认 8192)将数据分为一个个 granules[7]每个 granules 的第一行作为主键索引中的一个元素[8] 查询时在主键上使用二分查找跳过无关 granules[9] 主键只能通过前缀命中索引[10] 每一个 part 内的 .bin文件存储了 n 个 granules,用.mrk文件记录每一个 granules 在.bin文件的地址偏移[11]ClickHouse 会在后台不断合并同一个 partition 的不同 parts,直到大小/分布达到“预期”
主键的选择应该尽可能考虑周全,因为主键是无法修改的,只能建新表后数据迁移。
最佳实践[12](针对(Replicated)MergeTree 引擎):
选择永远会用于过滤条件的列 越重要的、基数越低的放左边 主键中不要出现两个高基数字段,一般最后一列可以为总体增长的时间字段 将行的特征字段加入,将相似的行放一起,提高压缩率 若主键包含主从关系,主放左边,从放右边
Data skipping indexes
最后一步是跳表索引,这个没有太多可以讲的地方,和其他数据库相同,跳表索引用于尽量减少读取的行数。具体参看官方文档。
配置优化
配置优化分为两部分,全局配置优化和 MergeTree 表配置优化。
全局配置优化
参看Altinity选择性配置优化项。
这里写三个推荐的配置:
添加 force_index_by_date和force_primary_key避免全盘读取调整内存配置,参考Altinity 系统表添加 TTL 和 ttl_only_drop_parts表配置
表配置优化
除了全局配置,MergeTree 引擎家族每张表也有自己的配置项。[13]
推荐设置如下配置:
ttl_only_drop_parts=1。只有 parts 中所有数据都过期了才会 DROP,可以有效减少TTL_MERGE发生的频率,降低磁盘负载。merge_with_ttl_timeout=86400。配合上一项配置,将 TTL 检查调整为 1 天一次(默认 4 小时一次)。use_minimalistic_part_header_in_zookeeper=1。可以有效降低 Zookeeper 负载,避免 Zookeeeper 成为性能瓶颈(插入)。
字段优化
除了索引、分区和配置外,还有表字段可以优化。接下来将讲述 Schema 类型、CODEC 和缓存三个方面。
注意,尽量避免使用 Null,在 ClickHouse 中 Null 会用一个单独 Null masks 文件存储哪些行为 Null[14],因此读取某个普通字段只需要.bin和.mrk两个文件,而读取 Nullable 字段时需要.bin、.mrk和 masks 文件。社区查询验证,最高会有 2 倍性能损失。[15]
Schema 类型
使用 ClickHouse 存储时,一般用户都会创建大宽表,包含大量数值、字符串类型的字段。这里提及两种 Schema 类型[16],没有哪个更优越,由读者执行评估业务适合哪一种。
平铺字段
这是我们主表正在使用的类型,将可能用到的字段预留平铺,除了一系列基础字段外,增加大量metric1, metric2...metricN和tag1, tag2...tagN等等字段。
优点:
简单 只读取所需要的列,非常高效 每个指标、标记都可以有特殊类型 适合密集记录(所有预留字段几乎全用上)
缺点:
添加字段需要改变 schema 预留字段不能过多,最多 100 ~ 200 个 如果使用很稀疏,会创建大量 sparse file 字段 需要标识“数据缺失”的情况(Null 或者默认值) 读取的列越多,需要读取文件越多,IO 次数越多
arrays/nested/map 字段
这是我们 ctree 功能正在使用的类型。将业务字段塞入嵌套数据类型中,比如 array、nested struct 和 map。后文以 array 举例:metric_array、tag_array。
优点:
动态扩展 ClickHouse 有大量高效的相关处理函数,甚至可以针对 Array、Map 设置索引 适合稀疏记录(每行存储少量值,尽管总基数很高)
缺点:
只需要其中一个 metric/tag 时,需要将整个 array 全部读入内存 不通用,与其他系统交互时比较麻烦。比如 spark 使用 jdbc 时,嵌套类型无法支持比如 array(array(string)) 不通意义的值存储在相同字段,压缩率变低 需要不同类型的预留字段时需要创建不同类型
总结
关于 Schema 设计这里,读者可以考虑 28 原则,理论上 80%查询只会用到 20%的业务字段,因此可以将使用频率高的业务字段平铺,将使用频率低的字段放入嵌套结构中。
CODEC
CODEC 分为压缩算法 CODEC、存储格式 CODEC 和加密 CODEC,一般可以组合一起使用。在 ClickHouse 中,未显示指定 CODEC 的字段都会被分配一个 DEFAULT 默认 CODEC LZ4(除非用户修改 clickhouse 配置 compression 部分[17])。
压缩算法 CODEC 的选择是一个平衡板问题,更高的压缩度可以有更少的 IO 但是更高的 CPU,更低的压缩度有更多的 IO 但是更少的 CPU。这需要读者根据部署机器配置自行选择合适的压缩算法和压缩等级。
这里提供两个判断策略:
存在索引的字段可以设置更高的压缩等级 用于 where 条件的字段应该设置更低压缩等级
存储格式 CODEC 主要是Delta、DoubleDelta、Gorilla、FPC和T64几种。
Delta存储行之间的变化值,适合变化较小且比较固定的列,比如时间戳。需要配合 ZSTD 使用DoubleDelta存储Delta的Delta。适合变化很慢的序列Gorilla适合不怎么变动的 integer、float 类型[18]FPC适合于 float 类型,由于我们未使用 float 字段这里略过T64存储编码范围内最大、最小值,以转为 64bit 存储,适合较小的 integer 类型
扩展阅读:
缓存
mark_cache_size可以调整.mrk文件的缓存大小,默认为 5GB。适当调大可以减少查询时 IO 次数,有效降低磁盘压力。[19]
字段越多, .mrk文件越大index_granularity与.mrk文件大小成负相关
可以通过如下 SQL 查询当前所有表的 parts 信息:
SELECT
database,
table,
count() AS parts,
uniqExact(partition_id) AS partition_cnt,
sum(rows),
formatReadableSize(sum(data_compressed_bytes) AS comp_bytes) AS comp,
formatReadableSize(sum(data_uncompressed_bytes) AS uncomp_bytes) AS uncomp,
uncomp_bytes / comp_bytes AS ratio,
formatReadableSize(sum(marks_bytes) AS mark_sum) AS marks,
mark_sum / uncomp_bytes AS mark_ratio
FROM cluster(default_cluster, system.parts)
WHERE active
GROUP BY
database,
table
ORDER BY comp_bytes DESC
可以通过如下查询获取当天 mrk 缓存命中情况:
WITH (ProfileEvents.Values[indexOf(ProfileEvents.Names, 'MarkCacheHits')]) AS MARK_CACHE_HITS
SELECT
toHour(event_time) AS time,
countIf(MARK_CACHE_HITS != 0) AS hit_query_count,
count() AS total_query_count,
hit_query_count / total_query_count AS hit_percent,
avg(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS average_hit_files,
min(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS minimal_hit_files,
max(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS maximal_hit_files,
quantile(0.5)(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS "50",
quantile(0.9)(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS "90",
quantile(0.99)(MARK_CACHE_HITS) AS "99"
FROM clusterAllReplicas('default_cluster', system.query_log)
WHERE event_date = toDate(now())
AND (type = 2 OR type = 4)
AND query_kind = 'Select'
GROUP BY time
ORDER BY time ASC
以及如下查询获取当前 mrk 缓存内存占用情况:
SELECT formatReadableSize(value)
FROM asynchronous_metrics
WHERE metric = 'MarkCacheBytes'
以及 mrk 缓存具体缓存多少文件:
SELECT value
FROM asynchronous_metrics
WHERE metric = 'MarkCacheFiles'
除此之外,ClickHouse 还可以调整uncompressed_cache缓存一定量原始数据于内存中。[20]但是这个缓存只对大量短查询有效,对于 OLAP 来说,查询千奇百怪,不太建议调整这个配置。
业务优化
到了最难的部分,由于接下来的部分和不同业务息息相关,为了讲解我们业务上的优化,我先介绍下我们业务情况:
QAPM 主打应用性能监控,主要分为指标、个例两张表。个例表包含更多基础字段,一般用户展示;指标表主要用于聚合计算。
首先确定主键,毋庸置疑的前两个一定是
app_id。放首位,因为可能存在同一个产品不同功能联动的情况,比如会话分析 category。放第二位,因为功能之间独立,大量查询只涉及单功能
指标没有特征键值,因此只添加处理时间作为第三个主键。
对于指标表,设置的主键为:app_id, category, entrance_time
个例存在特征 feature,由于:
大量查询都包含 feature_md5 feature 是行的特征,相同的特征表明两行相似,
将特征的 md5 增加到主键中,用于加速查询、提高压缩率。但是这里有两个方向:
若 feature_md5 是高基数、大量长尾的字段 设置的主键为: app_id, category, intDiv(entrance_time, 3600000), feature_md5若 feature_md5 基数可以降低到千、万量级 设置的主键为: app_id, category, feature_md5, entrance_time
分区键设置为`PARTITION BY intDiv(entrance_time, 2592000000)
鉴于SAMPLE BY需要将 xxHash 字段放在主键中,主键都包含高基数字段,就不设置抽样键,而是在需要的时候软抽样[21]:
SELECT count() FROM table WHERE ... AND cityHash64(some_high_card_key) % 10 = 0; -- Deterministic
SELECT count() FROM table WHERE ... AND rand() % 10 = 0; -- Non-deterministic
插入优化
数据插入看起来和查询性能没什么联系,但是有间接影响。不合理的插入会导致更多的写盘、更多的数据 merge 甚至有可能插入失败,影响读盘性能。
聚合写入
ClickHouse 作为 OLAP 并不适合小批量、大并发写入,相反而适合大批量、小并发写入,官方建议插入数据每批次至少 1000 行,或者每秒钟最多 1 次插入。[22]
这一小节我想强调原子(Atomic Insert)写入的概念:一次插入创建一个数据 part。
前文提及,ClickHouse 一个 part 是一个文件夹,后台有个 merge 线程池不断 merge 不同的 part。原子插入可以减少 merge 次数,让 ClickHouse 负载更低,性能更好。
原子写入的充分条件[23]:
数据直接插入 MergeTree表(不能有 Buffer 表)数据只插入一个 partition(注意前文提到的 partition 和 part 的区别) 对于 INSERT FORMAT 插入行数少于 max_insert_block_size(默认 1048545)关闭并行格式化 input_format_parallel_parsing=0对于 INSERT SELECT 插入行数少于 max_block_size小 block 被合并到合适的 block 大小 min_insert_block_size_rowsandmin_insert_block_size_bytesMergeTree表不包含物化视图
这里贴一下我们生产的配置(users.xml)。
经过统计,个例表每行大约 2KB,指标表每行大约 100B(未压缩)。
设置min_insert_block_size_rows为 10000000,指标会先满足这个条件,大概一个 block 原始大小 1GB。设置min_insert_block_size_bytes为 4096000000,个例会先满足这个条件,大概一个 block 原始大小 1G,约 1024000 行。
这三个配置项是客户端配置,需要在插入的 session 中设置,而不是在那几个.xml中配置。
max_insert_block_size: 16777216
input_format_parallel_parsing: 0
min_insert_block_size_rows: 10000000
min_insert_block_size_bytes: 1024000000
注意,min_insert_block_size_rows和min_insert_block_size_bytes是“或”的关系:
// src/Interpreters/SquashingTransform.cppbool SquashingTransform::isEnoughSize(size_t rows, size_t bytes) const
{
return (!min_block_size_rows && !min_block_size_bytes)
|| (min_block_size_rows && rows >= min_block_size_rows)
|| (min_block_size_bytes && bytes >= min_block_size_bytes);
}
读写分离
⚠️:本方案并没有经过生产验证,酌情考虑
ClickHouse 有 Shard 和 Replica 可以配置,作用如下图所示:
所谓读写分离也就是将 Shard 分为两半,一半只用于查询,只要让分布式表查询都导入到 Shard1 即可(在users.xml中配置load_balancing为first_or_random);一半用于写入,插入的程序手动控制插入 Shard2 的节点,由 ClickHouse 的 ReplicatedMergeTree 不同 Shard 数据依靠 zookeeper 自动同步的策略将数据同步到 Shard1。[24]
这种策略有天然的缺陷:
写的那半 Shard 持续有一定量(不会很高)的资源消耗用于写入 读的那半 Shard 会有资源消耗用于同步写入(由于不用处理,会比直接写入的情况资源消耗更低),但是读请求会导致资源消耗突增 并发增加时性能不如混合情况,因为读写分离相当于将读资源砍半
🤔:或许可以配置两边 Shard 资源不一致来解决问题,比如写入的 Shard 资源拉低,专用于处理数据插入;读的 Shard 资源更高,专门用于处理突增并发流量。
BufferEngine
Buffer 并不推荐常规业务使用,只有在迫切需要查询实时性+插入无法大批量预聚合时使用:
无法 atomic insert 即使使用 BufferEngine,数据插入也至少 1000 行每次,或者每秒钟最多 1 次插入[25]
KafkaEngine+MV
该部分待补充,想看的同学可以在评论区踢踢 😄
预聚合
预聚合有三种方法,ETL、物化视图和投影,他们的区别如下[26]:
| ETL | MV | Projections | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Realtime | no | yes | yes |
| How complex queries can be used to build the preaggregaton | any | complex | very simple |
| Impacts the insert speed | no | yes | yes |
| Are inconsistancies possible | Depends on ETL. If it process the errors properly - no. | yes (no transactions / atomicity) | no |
| Lifetime of aggregation | any | any | Same as the raw data |
| Requirements | need external tools/scripting | is a part of database schema | is a part of table schema |
| How complex to use in queries | Depends on aggregation, usually simple, quering a separate table | Depends on aggregation, sometimes quite complex, quering a separate table | Very simple, quering the main table |
| Can work correctly with ReplacingMergeTree as a source | Yes | No | No |
| Can work correctly with CollapsingMergeTree as a source | Yes | For simple aggregations | For simple aggregations |
| Can be chained | Yes (Usually with DAGs / special scripts) | Yes (but may be not straightforward, and often is a bad idea) | No |
| Resources needed to calculate the increment | May be signigicant | Usually tiny | Usually tiny |
在我们业务中,个例是不应该预聚合的,因为数据需要被拉取展示而不用计算。指标需要聚合,数据量较大,每次实时计算对 ClickHouse 负载太大。
其实还有一种聚合方式,过期数据聚合。可以参考,同样限制要求 group by 的键值为主键前缀。
在我们业务使用时,什么时候用哪一个呢?
需要针对某个功能加速时,可以考虑物化视图/投影 全表预聚合加速查询,需要使用 ETL
资源控制
最后,为了避免集群被某个查询、插入弄垮,需要合理安排内存使用,需要给访问账户分权限,在我们业务分为:
default:最高级账号,不使用root:数据插入,配置聚合写入部分的几个配置项monitor:内部开发使用,权限较高viewer:web 使用,添加大量限制
viewer账户配置如下所示:
<yandex>
<profiles>
<query>
<max_memory_usage>10000000000</max_memory_usage>
<max_memory_usage_for_all_queries>100000000000</max_memory_usage_for_all_queries>
<max_rows_to_read>1000000000</max_rows_to_read>
<max_bytes_to_read>100000000000</max_bytes_to_read>
<max_rows_to_group_by>1000000</max_rows_to_group_by>
<group_by_overflow_mode>any</group_by_overflow_mode>
<max_rows_to_sort>1000000</max_rows_to_sort>
<max_bytes_to_sort>1000000000</max_bytes_to_sort>
<max_result_rows>100000</max_result_rows>
<max_result_bytes>100000000</max_result_bytes>
<result_overflow_mode>break</result_overflow_mode>
<max_execution_time>60</max_execution_time>
<min_execution_speed>1000000</min_execution_speed>
<timeout_before_checking_execution_speed>15</timeout_before_checking_execution_speed>
<max_columns_to_read>25</max_columns_to_read>
<max_temporary_columns>100</max_temporary_columns>
<max_temporary_non_const_columns>50</max_temporary_non_const_columns>
<max_subquery_depth>2</max_subquery_depth>
<max_pipeline_depth>25</max_pipeline_depth>
<max_ast_depth>50</max_ast_depth>
<max_ast_elements>100</max_ast_elements>
<readonly>1</readonly>
</query>
</profiles>
</yandex>
同时建议设置 quota,减少大量读盘计算、LIMIT 少量数据返回的情况发生。
我们是 CSIG 性能工程二组 QAPM 团队,QAPM 时一款应用性能监控工具,覆盖 android、ios、小程序、mac 和 win 多端,已有腾讯会议、优衣库等大用户接入,值得信赖,欢迎同事试用我们 QAPM 产品~跳转链接
在 ClickHouse 优化过程遇到无数的问题,卡在 ClickHouse 自身监控无法覆盖的角落时,全靠性能工程三组员工的 Drop(雨滴)工具的鼎力相助,高效直观监控 CVM 各项指标,降低优化门槛,助力业务增效~跳转链接
参考
脚注
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh