2023-4-1 12:10:37 Author: www.freebuf.com(查看原文) 阅读量:8 收藏
整个环境我已搭建完毕 https://github.com/Drun1baby/JavaSecurityLearning/tree/main/JavaSecurity/Shiro/shiro682
在看后续漏洞之前我觉得有必要在这个地方提一提 Shiro682 这个洞
关于 Shiro 682
漏洞详情
在 Spring 中,/drunkbaby/xx与/drunkbaby/xx/都会被处理成/drunkbaby/xx。
而在 Shiro 中,/drunkbaby/xx与/drunkbaby/xx/被视为不同的路径,所以在 Spring 集成 Shiro 时,只需要在访问路径后添加/就存在绕过权限校验的可能。
漏洞影响版本
Shiro < 1.5.0
环境搭建
环境同最开始 Shiro 流程分析的环境,修改一下 Shiro 版本即可。
漏洞复现与分析
Shiro682 的攻击方式
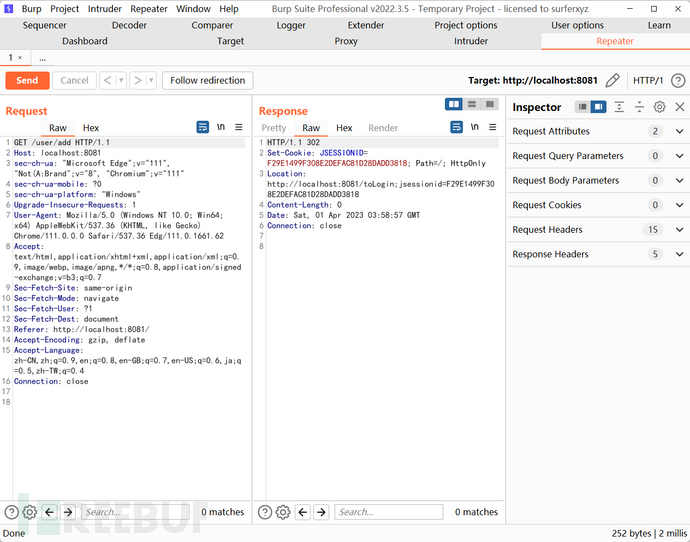
直接访问authc路径,302

修改 url,也就是在最后面加上/,成功 bypass

既然是个 Spring 和 Shiro 的解析差异,那么应该去 Shiro 的处理 uri 的地方和 Spring 处理 uri 的地方下两个断点进行调试。
Shiro 的 uri 处理还是在org.apache.shiro.web.filter.mgt.PathMatchingFilterChainResolver#getChain(),spring 对于 uri 中结尾带/的处理是在这里org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.PatternsRequestCondition#getMatchingPatterns();这里先做 Shiro 的鉴权,再做 spring 的 uri 识别。
Shiro 的鉴权,不会把/user/add识别为/user/add/,如图

跟进pathMatches()方法,最终是返回 false

接着我们来看 Spring 的处理,spring 在分发请求时
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch,会根据我们请求的 URI 选择一个最合适的 handler,其实就是从DispatcherServlet#handlerMappings找到能匹配路径的 Handler
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.PatternsRequestCondition#getMatchingPatterns()
整条调用栈如下
getMatchingPatterns:236, PatternsRequestCondition (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition)
getMatchingCondition:221, PatternsRequestCondition (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition)
getMatchingCondition:240, RequestMappingInfo (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
getMatchingMapping:94, RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
getMatchingMapping:58, RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
addMatchingMappings:427, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
lookupHandlerMethod:393, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
getHandlerInternal:367, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
getHandlerInternal:449, RequestMappingHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)
getHandlerInternal:67, RequestMappingHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)
getHandler:393, AbstractHandlerMapping (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler)
getHandler:1234, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
doDispatch:1016, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)

这里其实就可以看到matches()的判断为 true

跟进matches(),最终这里判断的代码其实是org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping#match()方法

漏洞修复
Commit地址如链接,这是高版本用于修复 Shiro682 的补丁,本质上只是进行了尾部的/的处理,迁就了 Spring

而关于 Shiro682 的处理,我们可以看到对于 Spring 不同版本实际上也有处理,但更为关键的是 Shiro 的处理。
关于 CVE-2020-1957 的漏洞
自己发现的一种 bypass,在高版本 SpringBoot 中可用
说是/user;/add的 bypass,虽然也有一种说法,说这一种攻击才是正统的 CVE payload(后面发现这是我自己乱搞出来的,笑死
从PathMatchingFilterChainResolver.getChain()下断点,跟进到this.getPathWithinApplication()方法,这里uri = request.getRequestURI();出来的 uri 还是我们原始请求的那一个,往下走,跟进normalize(decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri)),这个方法之前我们提到过,会处理/../,/./这一系列的 uri

通过indexOf()截取到了;之前的内容,所以 uri 最后返回回来的值的为/user,那么后续自然而然,/user与/user/add肯定不匹配,返回 false

下面我们去看 Spring 是怎么处理请求的,其实当时看的参考文章和我的不太一样,这里算是踩坑了,不过还是自己分析吧,也是很快的 。
倒也不完全是,我发现这里很多文章写的 payload 都是/xxx/..;/user/add这一种的越权,实际测试下来发现这一种不行,有的文章里面说是因为 SpringBoot 版本太高了,既然如此,能够有这一种的方便 bypass,还是自己分析一下吧。后续会简单提一下之前的 payload 是怎么打的。
这里我先把断点下在了org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch()方法处,因为这个方法是用来做 SpringBoot 的处理的,相当于是一个前端控制器。

往下走,第 1043 行,DispatcherServlet类收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。处理器映射器根据请求 url 找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象 Handler 及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。

这里匹配到的第一个 ——RequestMappingHandlerMapping就是,我们跟进getHandler()方法看一下,一路跟进至org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal方法,在这个方法里做了具体业务,当然这里我们继续跟进initLookupPath()方法。

initLookupPath()方法主要是做了 Uri 处理的初始化,这个 Uri 变量最终还是要经过一些处理,继续跟进removeSemicolonContent()方法。removeSemicolonContent()方法的意思是判断是否需要删除分号内容,如果需要则跟进removeSemicolonContentInternal()方法,如果不需要的话就销毁此 session,将 Uri 返回,这一 Uri 就是正确的 Uri 了。

这里我们需要去除分号,所以跟进removeSemicolonContentInternal(requestUri)方法

后续就是老一套的 MVC 了,这里不再赘述。
顺带再提一提/xxx/..;/user/add这个 payload
这个 payload 是有要求的,要求 SpringBoot 的版本 < 2.3,是很多师傅文章里面的 payload
流程都是一样,DispatcherServlet类收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。这里匹配到的是org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper#getLookupPathForRequest
public String getLookupPathForRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.alwaysUseFullPath) {
return this.getPathWithinApplication(request);
} else {
String rest = this.getPathWithinServletMapping(request);
return !"".equals(rest) ? rest : this.getPathWithinApplication(request);
}
}
一整个调用栈如下
getRequestUri:326, UrlPathHelper (org.springframework.web.util)
getPathWithinApplication:244, UrlPathHelper (org.springframework.web.util)
getPathWithinServletMapping:195, UrlPathHelper (org.springframework.web.util)
getLookupPathForRequest:171, UrlPathHelper (org.springframework.web.util)
直接跟进decodeAndCleanUriString()方法,代码如下,其实这一段在 Y4tacker 师傅 CVE-2016-6802 分析的时候也出现过
private String decodeAndCleanUriString(HttpServletRequest request, String uri) {
uri = this.removeSemicolonContent(uri);
uri = this.decodeRequestString(request, uri);
uri = this.getSanitizedPath(uri);
return uri;
}
跟进removeSemicolonContent()方法,主要问题是在这里
public String removeSemicolonContent(String requestUri) {
return this.removeSemicolonContent ? this.removeSemicolonContentInternal(requestUri) : this.removeJsessionid(requestUri);
}
private String removeSemicolonContentInternal(String requestUri) {
for(int semicolonIndex = requestUri.indexOf(59); semicolonIndex != -1; semicolonIndex = requestUri.indexOf(59, semicolonIndex)) {
int slashIndex = requestUri.indexOf(47, semicolonIndex);
String start = requestUri.substring(0, semicolonIndex);
requestUri = slashIndex != -1 ? start + requestUri.substring(slashIndex) : start;
}
return requestUri;
}
这里分别依次调用三个方法,分别用来过滤;、urldecode、过滤//,这就导致最后返回的其实就是/admin/index
漏洞修复
在 1.5.2 版本中对其进行了修复,获取 requestURI 的方式从request.getRequestUri直接获取的方式更改为获取 request 的 ContextPath,ServletPath,PathInfo,然后再重新拼接而成。

输入的/xxx/..;/user/add,将会被拼接为//xxx/user/add再进行 URI 路径匹配,则无法绕过拦截器。或者就返回 404,导致无法成功越权。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh