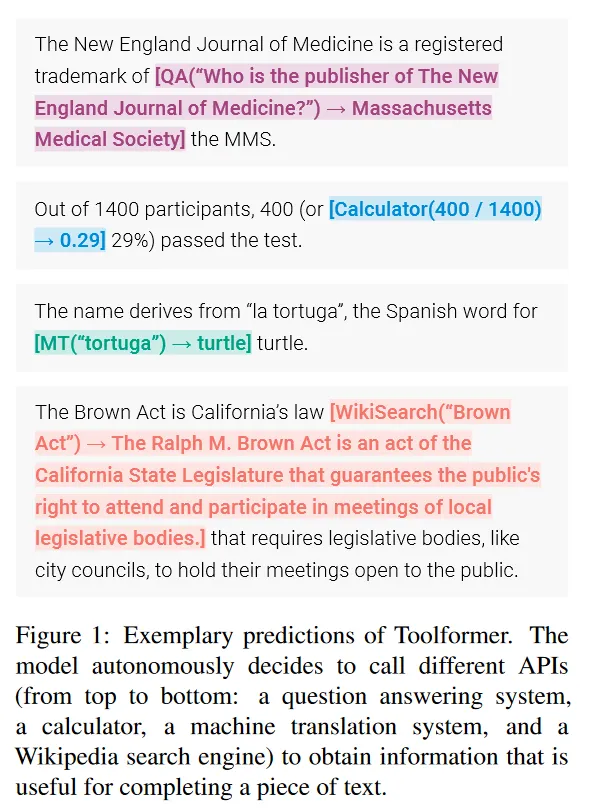
大型语言模型在各种任务(prompt)上实现了令人深刻的零样本(zero-shoht prompt)和少样本(few-shot prompt)结果,但是仍存在一些局限性,包括无法获取最新信息,幻觉倾向,精确计算,不知道时间的推移等。
Bing Chat利用Bing搜索关键词并将结果通过embedding注入prompt中调用底层大模型,解决了一些实时性和数值计算方面的问题。但是其能力有限,无法执行逻辑操作(本质还是在静态的历史数据库中进行搜索)。
克服这些限制的一个简单方法是让它们能够使用搜索引擎(动态获取外部世界最新的事实性知识)、计算器或日历等外部工具。然而,现有的方法要么依赖于大量的人工注释,要么仅将工具的使用限制在特定任务的设置中,阻碍了在LMs中更广泛地使用工具。
在论文中,作者提出了Toolformer,以自监督的方式微调语言模型,在不失模型的通用性下,让模型学会自动调用API。通过调用一系列工具,包括计算器、问答系统、搜索引擎、翻译系统和日历,Toolformer在各种下游任务中实现了实质性改进的零样本性能,通常可与更大的模型竞争,而不牺牲其核心语言建模能力。
参考链接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.04761
0x1:构造增强数据集
作者将每个API调用表示为元组 c = (ac,ic) ,其中:
- ac是API的名称
- ic是相应的输入
API输出为 r。
不包括和包括输出的API调用的线性化序列分别表示为:
- e (c) = <API> ac(ic) </API>
- e (c,r) = <API> ac(ic)-> r </API>
其中“<API>”、“</API>”和“→” 是特殊的token,用于指示LLM指令边界和输出边界的位置。
插入文本序列的API调用的一些示例如图所示:
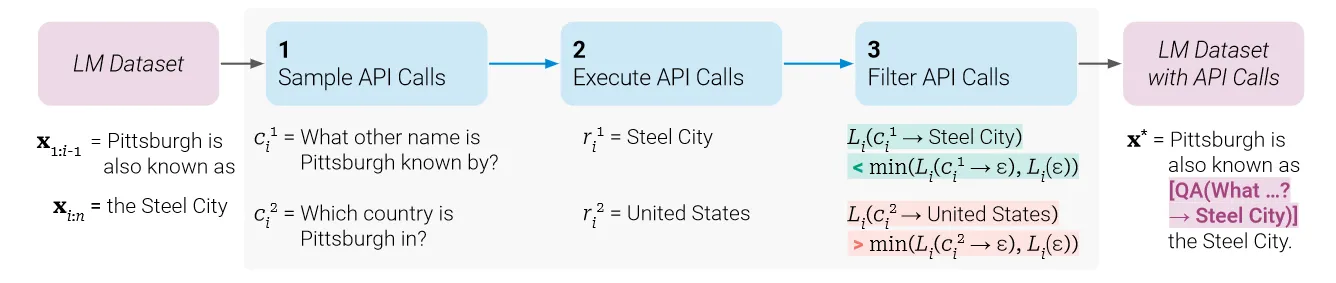
给定纯文本的数据集 ,首先将该数据集转换为通过API调用增强的数据集 C∗ 。包含三个步骤:
,首先将该数据集转换为通过API调用增强的数据集 C∗ 。包含三个步骤:
- 采样API调用
- 执行API调用
- 过滤API调用
1、采样API调用
对于每个API,首先编写一个prompt P(x) ,prompt里包含一些人工构造的演示样例,输入为 x=x1,…,xn 。
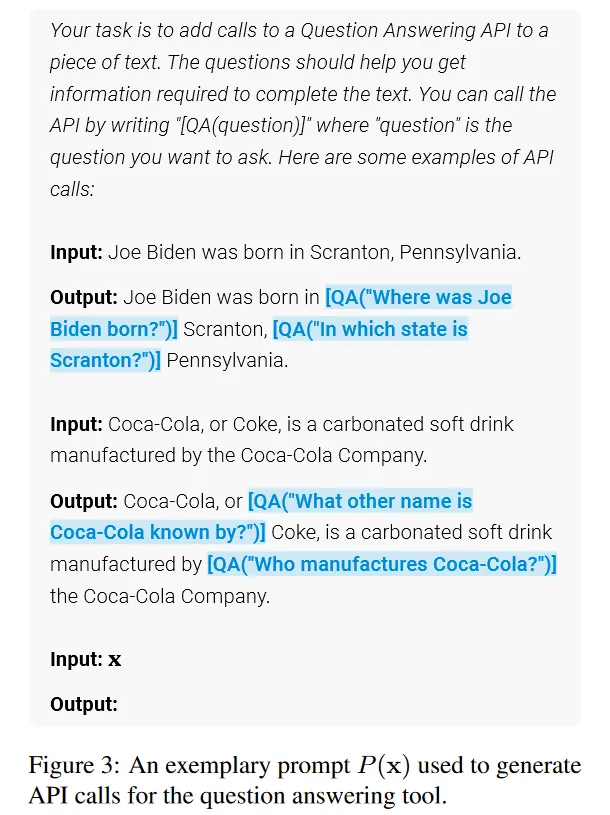
首先需要判断在哪些位置需要调用QA API,然后得到生成API的输入(问题)
采样位置:对于每个 i ∈ {1,…,n} ,根据 x1:i−1 计算第 i 个token预测为 <API> 的概率
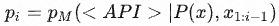
- 给定采样阈值 τs ,保留所有大于阈值的位置 I = { i | pi > τs}
- 如果有超过 k 个这样的位置,只保留topK。这个k决定了要计算多少比例token的API query结果正确性的概率熵,k越大,训练时的计算量就越大
在每个位置生成API调用(的输入问题):对于每个位置 i ∈ I,将 [P(x),x1,…,xi−1,<API>] 作为前缀输入到M中生成若干次(只保留以</API>token结尾的输出),从而获得m个API调用 ci1,…,cim
2、执行API调用
执行M生成的所有API调用,以获得相应的结果。每个API调用 ci 的响应都需要是一个单独的文本序列 ri
3、过滤API调用
设位置 i 处的API调用 ci 的响应输出为 ri 。以 z 为前缀,模型 M 在token x1,…,xn 上的加权交叉熵损失为:
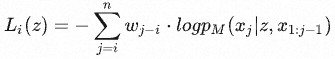
( wi | i ∈ N)是一个权重序列,越靠近API调用,权重越大,以确保API调用发生在API提供的信息对模型有帮助的地方附近。
- 当前缀为API调用及其结果时,即 z = e(ci,ri) ,损失记为 Li+ = Li (e(ci,ri))
- 当前缀为空,即根本不进行API调用时,损失记为 Li(ε) ( ε 表示一个空序列)
- 当前缀为只包含API调用但不提供响应时,损失记为 Li(e(ci,ε)) ;
因此,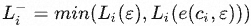 代表根本不接收API调用或只接收其输入的交叉熵。
代表根本不接收API调用或只接收其输入的交叉熵。
给定过滤阈值 τf ,只保留满足条件的API调用:
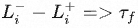
即,与不进行任何API调用或不从中获得结果相比,过滤出添加API调用及其结果将损失至少减少 τf 的调用。
0x2:微调和推理
1、微调
过滤后,通过合并对不同工具(计算器、问答系统、搜索引擎、翻译系统和日历)的API调用,得到增强的数据集 C∗,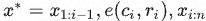 。
。
在此数据集使用标准的语言建模目标微调 M 。
2、推理
当用 M 生成文本时,执行常规解码,直到 M 生成“ → ” token,指示它接下来期望对API调用的响应。此时,中断解码过程,调用API以获得响应,并在插入响应和 </API> token后继续解码过程。
这一步需要LLM能够和外部系统按照一定的协议和交互进行指令和数据交互。
0x3:核心思路通俗理解
构造增强数据集这个步骤是这个算法设计最精彩的地方,笔者提请读者朋友思考一个问题:
基于一段原始的正常的语料文本,你该如何让程序自动化地识别出哪些地方(词)需要扩展为通过API query获取更高质量的结果吗?
现在让我们先从一个最基本的常识开始入手,
世界上的知识从大略上可以分为两种类型:
- 常识性知识,基于一些底层的知识框架可以推理得出,在不同的时空和语境下结论基本不变。这部分内容适合LLM生成
- 事实性知识,和具体的对象、时间、空间、语境等多方面因素都有关,内容不确定且处于不断变化中。这部分内容适合通过数据库搜索、计算器、程序模拟器等外部工具生成。
基于以上认知,我们就可以通过概率损失,将任何一段语料文本的内容(主要是词)分为【常识性内容】和【事实性内容】。
大致的逻辑流程如下:
- 逐token遍历整段语料,针对每一个token都生成一个API query元组。通俗地理解就是说:逐字尝试看看用API query后能得到什么结果。
- 在训练开始前,原始语料的每一个token都被增加一个API query元组。通俗地理解就是说:假设原始语料每一个token都属于常识性知识,但是每一个token都有概率是事实性知识,到目前为止我们还不知道谁是谁不是,需要通过训练和损失函数优化,来筛选出两拨人。
- 通过损失目标函数,引导生成的API query元组尽量满足以下2个特性:
- API query生成的内容,尽量和该API query元组附近的token接近。通俗地理解就是,API query生成的内容,尽量和原始语料中该token以及该token附近的词接近,即更接近正确答案。可以想象,如果原本该token对应的是事实性知识,那么API query的结果和原始语料的结果应该相对比较接近(语义和词义熵),那么最终的损失熵相对就会很低
- API query应该尽量去产生结果内容,避免不做就会错的优化倾向
- 通过极大似然概率训练后,得到一份增强数据集M,相比于原始的文本语料,增强数据集语料M中的某一些token后增加API query元组,表明该token属于一个事实性知识,需要调用外部插件进行额外处理。
- 将增强数据集M输入原始的LLM进行fine-tune,让LLM对齐学会对特定的事实性知识token之后增加一个API query元祖,本质上就是让LLM学会在输出语料的特定token后新增了一个特定的”协议定界符“,这个”协议定界符“可以标明该处需要调用特定的外部插件进行额外的数据扩展处理
- 微调对齐后的LLM,在之后的文本生成任务中,自动就会在生成的语料中包含特定的”协议定界符“,这些”协议定界符“是非常容易被标准化程序处理的,到了这一步就是常规的协议处理和接口调用的逻辑了,难度不大。
总体上说,它以自监督的方式学习如何通过简单的API调用使用不同的工具。这是通过对大量采样的API调用进行微调来实现的,这些API调用是根据它们是否减少了对未来token的困惑度来过滤的。
参考链接:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9f9aa24090f0
0x1:Baseline
- GPT-J:一个没有任何微调的常规GPT-J模型,参数为6.7B。
- GPT-J+CC:GPT-J在没有任何API调用的CCNet子集C上进行了微调。
- Toolformer:GPT-J对 C∗ 进行了微调, C∗ 是CCNet子集通过API调用进行了增强后的数据集。
- Toolformer(disabled):与Toolformer的模型相同,但在解码过程中会禁用API调用。
对于大多数任务,作者还与OPT(66B)和GPT-3 (不加微调的davinci,175B)进行了比较。
0x2:对比实验
LAMA基准的SQuAD、GoogleRE和T-REx子集,任务是完成一个简短的陈述,其中缺少一个事实(例如,日期或地点):

此任务下,Toolformer被禁用维基百科API
数学推理:

问答:
 此任务下被禁用问答API
此任务下被禁用问答API
多语言:
每个问题的上下文段落都是用英语提供的,问题是多种语言。
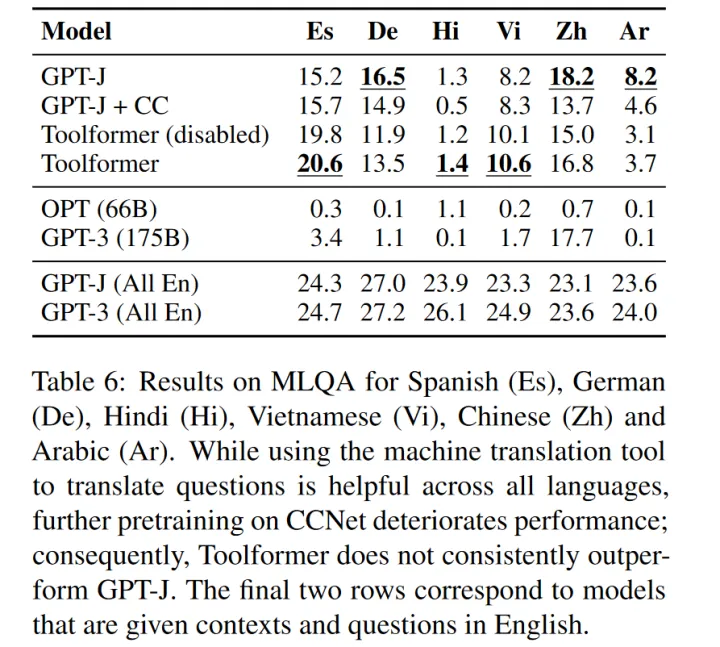
时间数据集:
0x3:模型尺寸的影响
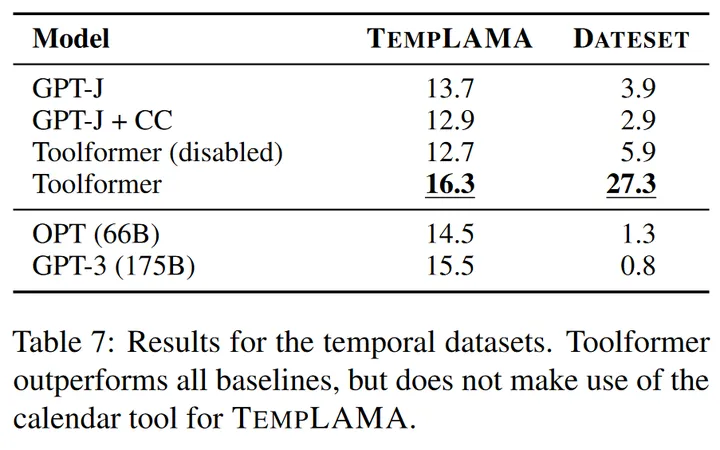
作者不仅将该方法应用于GPT-J(6.7B),还应用于GPT-2家族的四个较小模型,分别具有124M、355M、775M和1.6B的参数。
结果显示,只有在775M左右的参数下模型才能利用所提供的工具,对于这里最大的模型GPT-J,使用和不使用API调用的预测之间仍然存在很大的差距。
0x4:算法局限性
- 法链式使用工具(即,将一个工具的输出用作另一个工具)。这是由于每个工具的API调用都是独立生成的,因此,在微调数据集中没有使用链式工具的例子。
- 不允许LM以交互方式使用工具,这对于一些应用API,比如搜索引擎,可能至关重要。
参考链接:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/618901006
Models are available on huggingface! toolformer_v0
安装依赖:
pip install --upgrade google-api-python-client
pip install wolframalpha
pip install transformers
pip install openai
pip install langchain
0x1:Data generation(生成增强数据集)
python3 data_generator.py --num_devices=x, --device_id=y //Will let you run it without collision on x devices, so if you only have one, python3 data_generator.py --num_devices=1, --device_id=0
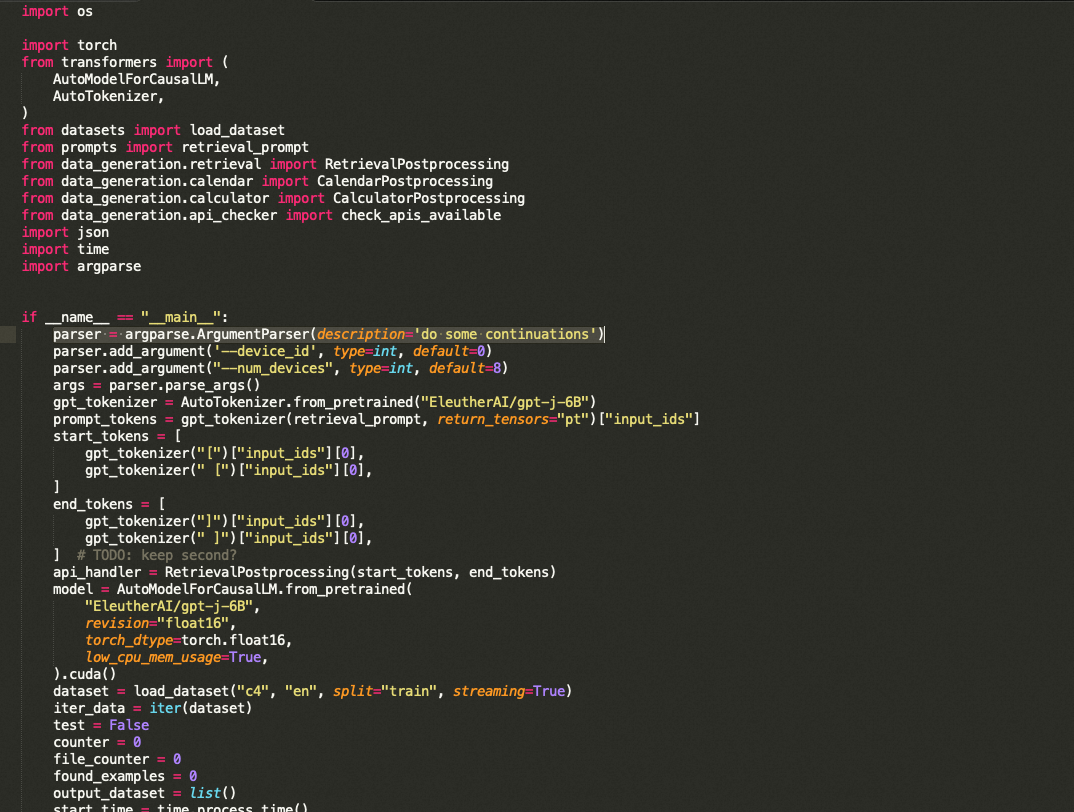

import os import torch from transformers import ( AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, ) from datasets import load_dataset from prompts import retrieval_prompt from data_generation.retrieval import RetrievalPostprocessing from data_generation.calendar import CalendarPostprocessing from data_generation.calculator import CalculatorPostprocessing from data_generation.api_checker import check_apis_available import json import time import argparse if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='do some continuations') parser.add_argument('--device_id', type=int, default=0) parser.add_argument("--num_devices", type=int, default=8) args = parser.parse_args() gpt_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B") prompt_tokens = gpt_tokenizer(retrieval_prompt, return_tensors="pt")["input_ids"] start_tokens = [ gpt_tokenizer("[")["input_ids"][0], gpt_tokenizer(" [")["input_ids"][0], ] end_tokens = [ gpt_tokenizer("]")["input_ids"][0], gpt_tokenizer(" ]")["input_ids"][0], ] # TODO: keep second? api_handler = RetrievalPostprocessing(start_tokens, end_tokens) model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained( "EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B", revision="float16", torch_dtype=torch.float16, low_cpu_mem_usage=True, ).cuda() dataset = load_dataset("c4", "en", split="train", streaming=True) iter_data = iter(dataset) test = False counter = 0 file_counter = 0 found_examples = 0 output_dataset = list() start_time = time.process_time() num_examples = int(25000.0/float(args.num_devices)) start_count = -1 if os.path.isfile(f"retrieval_data_{args.device_id}.json"): with open(f"retrieval_data_{args.device_id}.json") as f: output_dataset = json.load(f) start_count = output_dataset[-1]['file_index'] for item in output_dataset: num_examples -= len(item['retrieval_outputs']) while found_examples < num_examples: data = next(iter_data) if file_counter < start_count: file_counter += 1 continue if file_counter % args.num_devices != args.device_id: file_counter += 1 continue available = check_apis_available(data, gpt_tokenizer) test = available.retrieval if test: data_outputs = api_handler.parse_article(data, model, gpt_tokenizer) output_dataset.append( { "file_index": file_counter, "text": data["text"], "retrieval_outputs": data_outputs } ) prev_found = found_examples found_examples += len(output_dataset[-1]["retrieval_outputs"]) eta_s = (num_examples - found_examples) * (time.process_time()-start_time) / max(1, found_examples) eta_m = eta_s // 60 eta_h = eta_m // 60 eta_m = eta_m - (eta_h*60) eta_s = eta_s - ((eta_m*60) + (eta_h*60*60)) print(f"Found: {found_examples}/{num_examples}, ETA: {eta_h}H:{eta_m}M:{eta_s}s") if found_examples//100 > prev_found//100: with open(f"retrieval_data_{args.device_id}.json", 'w') as f: json.dump(output_dataset, f, indent=2) counter += 1 file_counter += 1 with open(f"retrieval_data_{args.device_id}.json", 'w') as f: json.dump(output_dataset, f, indent=2)
View Code
数据增强前的训练语料如下:

数据增强后的训练语料如下:


可以看到,训练语料中特定事实性token后面跟上了API query定界符。
0x2:使用增强数据集进行LLM微调训练
We used huggingface's run_clm.py which we put in this repository as train_gptj_toolformer.py.
We used a batch size of 32 (1/device), command used is belowCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 train_gptj_toolformer.py --model_name_or_path=EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --per_device_train_batch_size=4 \
--num_train_epochs 20 --save_strategy=epoch --output_dir=finetune_toolformer_v0 --report_to "wandb" \ --dataset_name dmayhem93/toolformer-v0-postprocessed --tokenizer_name customToolformer \ --block_size 2048 --gradient_accumulation_steps 1 --do_train --do_eval --evaluation_strategy=epoch \ --logging_strategy=epoch --fp16 --overwrite_output_dir --adam_beta1=0.9 --adam_beta2=0.999 \ --weight_decay=2e-02 --learning_rate=1e-05 --warmup_steps=100 --per_device_eval_batch_size=1 \ --cache_dir="hf_cache" --gradient_checkpointing=True
参考链接:
https://huggingface.co/datasets/dmayhem93/toolformer-v0-postprocessed/viewer/dmayhem93--toolformer-v0-postprocessed/train?row=5 https://huggingface.co/datasets/dmayhem93/toolformer_raw_v0/viewer/dmayhem93--toolformer_raw_v0/train https://huggingface.co/datasets/dmayhem93/toolformer_raw_v0/resolve/8432a6615939d947fce807716ed89ace20befbdd/calc_data_0.json https://openi.pcl.ac.cn/yangyang/toolformer/src/branch/master#user-content-data-generation
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh