
2024-1-10 04:39:49 Author: blog.qualys.com(查看原文) 阅读量:19 收藏
The first edition of the Microsoft Patch Tuesday for 2024 is now live! In this month’s update, Microsoft has released fewer than usual security updates. We invite you to join us to review and discuss the details of these security updates and patches.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday for January 2024
Microsoft Patch Tuesday’s January 2024 edition addressed 53 vulnerabilities, including two critical and 47 important severity vulnerabilities. Microsoft has addressed four Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) vulnerabilities in the updates patched earlier this month. In this month’s updates, Microsoft has not addressed any vulnerability known to be exploited in the wild.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, January edition includes updates for vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office and Components, SQL Server, .NET and Visual Studio, Windows Scripting, .NET Framework, Windows TCP/IP, Windows Win32K, Windows Kernel, Windows Hyper-V, and more.
Microsoft has fixed several types of flaws in multiple software, including Denial of Service (DoS), Elevation of Privilege (EoP), Information Disclosure, Remote Code Execution (RCE), Security Feature Bypass, and Spoofing.
The January 2024 Microsoft vulnerabilities are classified as follows:
| Vulnerability Category | Quantity | Severities |
| Spoofing Vulnerability | 3 | Important: 3 |
| Denial of Service Vulnerability | 6 | Important: 6 |
| Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 10 | Important: 10 |
| Information Disclosure Vulnerability | 11 | Important: 11 |
| Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 12 | Critical: 1 Important: 11 |
| Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 7 | Critical: 1 Important: 6 |
Critical Severity Vulnerabilities Patched in January Patch Tuesday Edition
CVE-2024-20674: Windows Kerberos Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Kerberos is a secure authentication protocol used as a default authentication policy for Windows. It is used to authenticate users and computers on a Windows network. Kerberos is also used as a basis for single sign-on and access control.
An attacker must first gain access to the restricted network before running an attack. An unauthenticated attacker could exploit the vulnerability by establishing a machine-in-the-middle (MITM) attack or other local network spoofing technique. An attacker must then send a malicious Kerberos message to the client victim machine to impersonate the Kerberos authentication server.
CVE-2024-20700: Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Windows Hyper-V allows hardware virtualization. IT professionals and software developers use virtualization to test software on multiple operating systems. Hyper-V enables working professionals to perform these tasks smoothly. With the help of Hyper-V, one can create virtual hard drives, virtual switches, and numerous different virtual devices, all of which can be added to virtual machines.
An attacker must first gain access to the restricted network before running an attack. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability requires an attacker to win a race condition.
Other Microsoft Vulnerability Highlights
- CVE-2024-20683 & CVE-2024-20686 are elevation of privilege vulnerabilities in Win32k. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2024-20698 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Kernel. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2024-21307 is a remote code execution vulnerability in a Remote Desktop Client. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability requires an attacker to win a race condition. An unauthenticated attacker must wait for a user to initiate a connection to exploit the vulnerability.
- CVE-2024-20652 is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Internet Explorer. An attacker must prepare the target environment to improve exploit reliability.
- CVE-2024-20653 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Microsoft Common Log File System. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2024-21310 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2024-21318 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server. An attacker must be authenticated with the Site Owner’s permission to exploit the vulnerability. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of SharePoint Server.
Microsoft Release Summary
This month’s release notes cover multiple Microsoft product families and products/versions affected, including, but not limited to, Windows Common Log File System Driver, Windows ODBC Driver, Windows Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) SnapIn, Visual Studio, Windows Group Policy, Microsoft Virtual Hard Drive, Windows Message Queuing, Windows BitLocker, .NET Core & Visual Studio, Windows Authentication Methods, Azure Storage Mover, Microsoft Office, Windows Subsystem for Linux, Windows Cryptographic Services, Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem, Windows AllJoyn API, Windows Nearby Sharing, Windows Themes, Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), Windows Collaborative Translation Framework, Windows Libarchive, Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, Microsoft Bluetooth Driver, Remote Desktop Client, Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers, Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver, Windows Server Key Distribution Service, Microsoft Office SharePoint, Microsoft Identity Services, Microsoft Devices, SQLite, and Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based).
EVALUATE Vendor-Suggested Mitigation with Policy Compliance (PC)
Qualys Policy Compliance’s Out-of-the-Box Mitigation or Compensatory Controls reduce the risk of a vulnerability being exploited because the remediation (fix/patch) cannot be done now; these security controls are not recommended by any industry standards such as CIS, DISA-STIG.
Qualys Policy Compliance team releases these exclusive controls based on vendor-suggested Mitigation/Workaround.
Mitigation refers to a setting, common configuration, or general best practice existing in a default state that could reduce the severity of the exploitation of a vulnerability.
A workaround is sometimes used temporarily for achieving a task or goal when the usual or planned method isn’t working. Information technology often uses a workaround to overcome hardware, programming, or communication problems. Once a problem is fixed, a workaround is usually abandoned.
The following Qualys Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs) and System Defined Controls (SDC) have been updated to support Microsoft recommended mitigation(s) for this Patch Tuesday:
CVE-2024-21320: Windows Themes Spoofing Vulnerability
This vulnerability has a CVSS:3.1 6.5 / 5.7
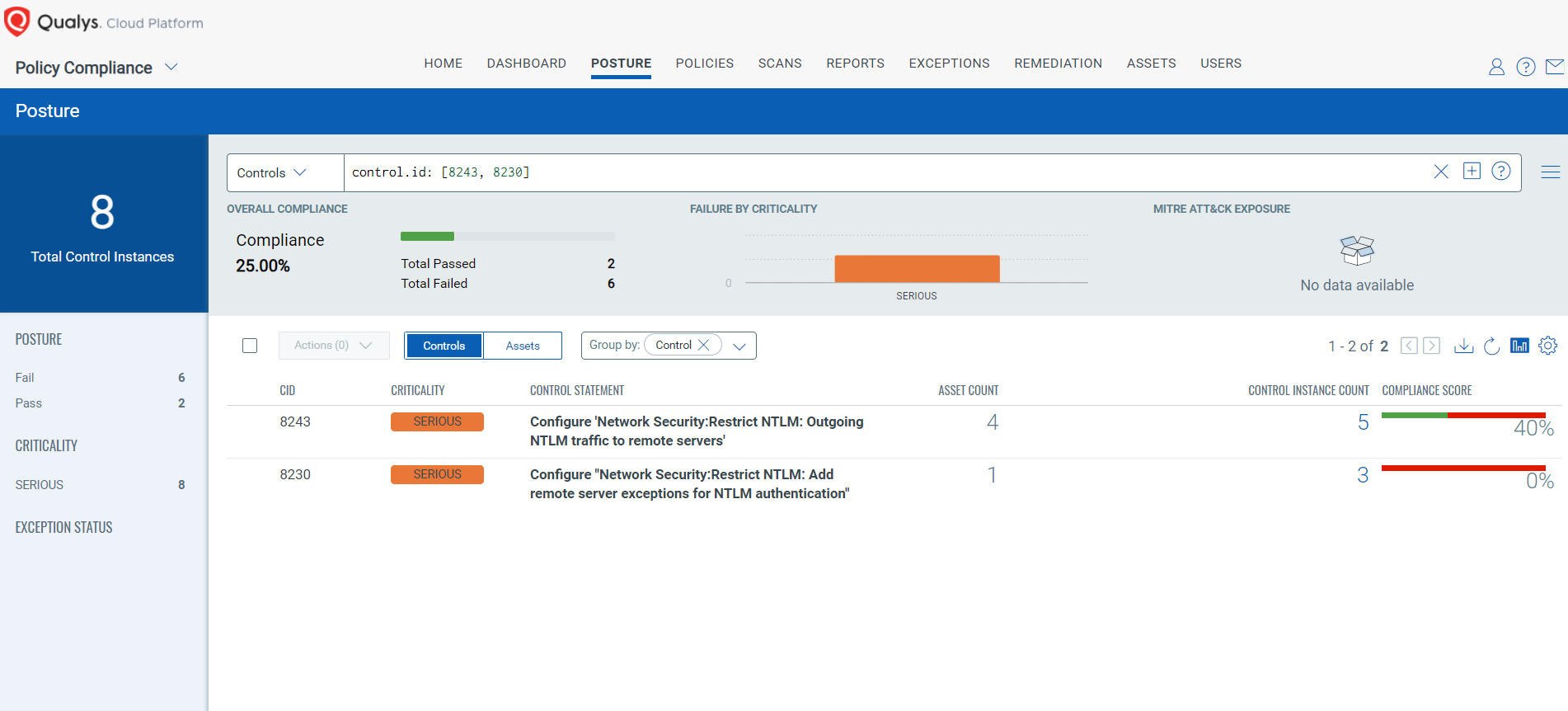
Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs):
- 8243 Configure ‘Network Security:Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers’
- 8230 Configure ‘Network Security:Restrict NTLM: Add remote server exceptions for NTLM authentication’
The following QQL will return a posture assessment for the CIDs for this Patch Tuesday:
control.id: [8243, 8230]
The next Patch Tuesday falls on February 13, and we’ll be back with details and patch analysis. Until next Patch Tuesday, stay safe and secure. Be sure to subscribe to the ‘This Month in Vulnerabilities and Patch’s webinar.’
Qualys Monthly Webinar Series

The Qualys Research team hosts a monthly webinar series to help our existing customers leverage the seamless integration between Qualys Vulnerability Management Detection Response (VMDR) and Qualys Patch Management. Combining these two solutions can reduce the median time to remediate critical vulnerabilities.
During the webcast, we will discuss this month’s high-impact vulnerabilities, including those that are a part of this month’s Patch Tuesday alert. We will walk you through the necessary steps to address the key vulnerabilities using Qualys VMDR and Qualys Patch Management.
Join the webinar
This Month in Vulnerabilities & Patches
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh