Published at 2024-02-15 | Last Update 2024-02-15
整理一些 Linux 服务器性能相关的 CPU 硬件基础及内核子系统知识。
水平有限,文中不免有错误或过时之处,请酌情参考。
- Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(一):CPU 硬件基础(2024)
- Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(二):几个内核子系统的设计(2024)
- Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(三):cpuidle 子系统的实现(2024)
- Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(四):监控、配置、调优(2024)
- Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(五):问题讨论(2024)
1.1 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu{N}/ 目录
系统中的每个 CPU,都对应一个 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpuidle/ 目录,
其中 N 是 CPU ID,
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── cache
│ ├── index0
│ ├── ...
│ ├── index3
│ └── uevent
├── cpufreq -> ../cpufreq/policy0
├── cpuidle
│ ├── state0
│ │ ├── above
│ │ ├── below
│ │ ├── default_status
│ │ ├── desc
│ │ ├── disable
│ │ ├── latency
│ │ ├── name
│ │ ├── power
│ │ ├── rejected
│ │ ├── residency
│ │ ├── time
│ │ └── usage
│ └── state1
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
├── crash_notes
├── crash_notes_size
├── driver -> ../../../../bus/cpu/drivers/processor
├── firmware_node -> ../../../LNXSYSTM:00/LNXCPU:00
├── hotplug
│ ├── fail
│ ├── state
│ └── target
├── node0 -> ../../node/node0
├── power
│ ├── async
│ ├── autosuspend_delay_ms
│ ├── control
│ ├── pm_qos_resume_latency_us
│ ├── runtime_active_kids
│ ├── runtime_active_time
│ ├── runtime_enabled
│ ├── runtime_status
│ ├── runtime_suspended_time
│ └── runtime_usage
├── subsystem -> ../../../../bus/cpu
├── topology
│ ├── cluster_cpus
│ ├── cluster_cpus_list
│ ├── cluster_id
│ ├── core_cpus
│ ├── core_cpus_list
│ ├── core_id
│ ├── core_siblings
│ ├── core_siblings_list
│ ├── die_cpus
│ ├── die_cpus_list
│ ├── die_id
│ ├── package_cpus
│ ├── package_cpus_list
│ ├── physical_package_id
│ ├── thread_siblings
│ └── thread_siblings_list
└── uevent
里面包括了很多硬件相关的子系统信息,跟我们本次主题相关的几个:
- cpufreq
- cpuidle
- power:PM QoS 相关信息,可以在这里面查到
- topology:第一篇介绍的 PKG-CORE-CPU 拓扑,信息可以在这里面查到
下面分别看下这几个子目录。
1.1.1 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpufreq/ (p-state)
处理器执行任务时的运行频率、超频等等相关的参数,管理的是 p-state:
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/
├── affected_cpus
├── cpuinfo_max_freq
├── cpuinfo_min_freq
├── cpuinfo_transition_latency
├── related_cpus
├── scaling_available_governors
├── scaling_cur_freq
├── scaling_driver
├── scaling_governor
├── scaling_max_freq
├── scaling_min_freq
└── scaling_setspeed
1.1.2 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpuidle/ (c-states)
每个 struct cpuidle_state 对象都有一个对应的 struct cpuidle_state_usage
对象(上一篇中有更新这个 usage 的相关代码),其中包含了这个 idle state 的统计信息,
也是就是我们下面看到的这些:
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/
├── state0
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
├── state1
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── s2idle
│ │ ├── time
│ │ └── usage
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
│...
state0、state1 等目录对应 idle state 对象,也跟这个 CPU 的 c-state 对应,数字越大,c-state 越深。
文件说明,
desc/name:都是这个 idle state 的描述。name 比较简洁,desc 更长。除了这俩,其他字段都是整型。above:idle duration < target_residency的次数。也就是请求到了这个状态,但是 idle duration 太短,最终放弃进入这个状态。below:idle duration虽然大于target_residency,但是大的比较多,最终找到了一个更深的 idle state 的次数。disable:唯一的可写字段:1表示禁用,governor 就不会在这个 CPU 上选这状态了。注意这个是 per-cpu 配置,此外还有一个全局配置。default_status:default status of this state, “enabled” or “disabled”.latency:这个 idle state 的exit latency,单位us。power:这个字段通常是0,表示不支持。因为功耗的统计很复杂,这个字段的定义也不是很明确。建议不要参考这个值。residency:这个 idle state 的target residency,单位us。time:内核统计的该 CPU 花在这个状态的总时间,单位 ms。这个是内核统计的,可能不够准,因此如有处理器硬件统计的类似指标,建议参考后者。usage:成功进入这个 idle state 的次数。rejected:被拒绝的要求进入这个 idle state 的 request 的数量。
1.1.3 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/power/
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── power
│ ├── async
│ ├── autosuspend_delay_ms
│ ├── control
│ ├── pm_qos_resume_latency_us
│ ├── runtime_active_kids
│ ├── runtime_active_time
│ ├── runtime_enabled
│ ├── runtime_status
│ ├── runtime_suspended_time
│ └── runtime_usage
1.1.4 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/topology/
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── topology
│ ├── cluster_cpus
│ ├── cluster_cpus_list
│ ├── cluster_id
│ ├── core_cpus
│ ├── core_cpus_list
│ ├── core_id
│ ├── core_siblings
│ ├── core_siblings_list
│ ├── die_cpus
│ ├── die_cpus_list
│ ├── die_id
│ ├── package_cpus
│ ├── package_cpus_list
│ ├── physical_package_id
│ ├── thread_siblings
│ └── thread_siblings_list
└── uevent
1.2 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/:governor/driver
这个目录是全局的,可以获取可用的 governor/driver 信息,也可以在运行时更改 governor。
$ ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/
available_governors current_driver current_governor current_governor_ro
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/available_governors
menu
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver
acpi_idle
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_governor
menu
除了 sysfs,还可以通过内核命令行参数做一些配置,可以加在 /etc/grub2.cfg 等位置。
2.1 idle loop 配置
5.15 内核启动参数文档:
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt
idle= [X86]
Format: idle=poll, idle=halt, idle=nomwait
1. idle=poll forces a polling idle loop that can slightly improve the performance of waking up a
idle CPU, but will use a lot of power and make the system run hot. Not recommended.
2. idle=halt: Halt is forced to be used for CPU idle. In such case C2/C3 won't be used again.
3. idle=nomwait: Disable mwait for CPU C-states
2.1.1 idle=poll
CPU 空闲时,将执行一个“轻量级”的指令序列(”lightweight” sequence of instructions in a tight loop) 来防止 CPU 进入任何节能模式。
这种配置除了功耗问题,还超线程场景下可能有副作用,性能反而降低,后面单独讨论。
2.1.2 idle=halt
强制 cpuidle 子系统使用 HLT 指令
(一般会 suspend 程序的执行并使硬件进入最浅的 idle state)来实现节能。
这种配置下,最大 c-state 深度是 C1。
2.1.3 idle=nomwait
禁用通过 MWAIT 指令来要求硬件进入 idle state。
内核文档 CPU Idle Time Management
说,在 Intel 机器上,这会禁用 intel_idle,用 acpi_idle(idle states / p-states 从 ACPI 获取)。
2.2 厂商相关的 p-state 参数
2.2.1 intel_pstate
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt#L1988
intel_pstate= [X86]
disable
Do not enable intel_pstate as the default
scaling driver for the supported processors
passive
Use intel_pstate as a scaling driver, but configure it
to work with generic cpufreq governors (instead of
enabling its internal governor). This mode cannot be
used along with the hardware-managed P-states (HWP)
feature.
force
Enable intel_pstate on systems that prohibit it by default
in favor of acpi-cpufreq. Forcing the intel_pstate driver
instead of acpi-cpufreq may disable platform features, such
as thermal controls and power capping, that rely on ACPI
P-States information being indicated to OSPM and therefore
should be used with caution. This option does not work with
processors that aren't supported by the intel_pstate driver
or on platforms that use pcc-cpufreq instead of acpi-cpufreq.
no_hwp
Do not enable hardware P state control (HWP)
if available.
hwp_only
Only load intel_pstate on systems which support
hardware P state control (HWP) if available.
support_acpi_ppc
Enforce ACPI _PPC performance limits. If the Fixed ACPI
Description Table, specifies preferred power management
profile as "Enterprise Server" or "Performance Server",
then this feature is turned on by default.
per_cpu_perf_limits
Allow per-logical-CPU P-State performance control limits using
cpufreq sysfs interface
2.2.2 AMD_pstat
AMD_idle.max_cstate=1 AMD_pstat=disable 等等,上面的内核文档还没收录,或者在别的地方。
2.3 *.max_cstate
intel_idle.max_cstate=<n>AMD_idle.max_cstate=<n>processor.max_cstate=<n>
这里面的 n 就是我们在 sysfs 目录中看到
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/state{n}。
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt
intel_idle.max_cstate= [KNL,HW,ACPI,X86]
0 disables intel_idle and fall back on acpi_idle.
1 to 9 specify maximum depth of C-state.
processor.max_cstate= [HW,ACPI]
Limit processor to maximum C-state
max_cstate=9 overrides any DMI blacklist limit.
AMD 的没收录到这个文档中。
2.4 cpuidle.off
cpuidle.off=1 完全禁用 CPU 空闲时间管理。
加上这个配置后,
- 空闲 CPU 上的 idle loop 仍然会运行,但不会再进入 cpuidle 子系统;
- idle loop 通过
CPU architecture support code使硬件进入 idle state。
不建议在生产使用。
2.5 cpuidle.governor
指定要使用的 CPUIdle 管理器。例如 cpuidle.governor=menu 强制使用 menu 管理器。
2.6 nohz
可设置 on/off,是否启用每秒 HZ 次的定时器中断。
3.1 频率
可以从 /proc/cpuinfo 获取,
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | awk '/cpu MHz/ { printf("cpu=%d freq=%s\n", i++, $NF)}'
cpu=0 freq=3393.622
cpu=1 freq=3393.622
cpu=2 freq=3393.622
cpu=3 freq=3393.622
某些开源组件可能已经采集了,如果没有的话自己采一下,然后送到 prometheus。
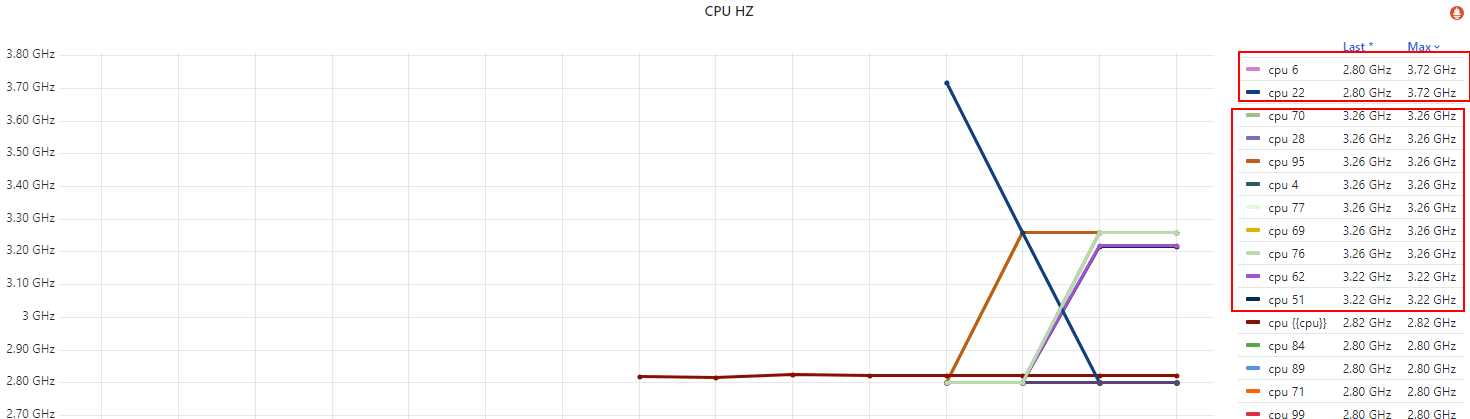
这里拿一台 base freq 2.8GHz、max freq 3.7GHz,配置了 idle=poll 测试机,
下面是各 CPU 的频率,
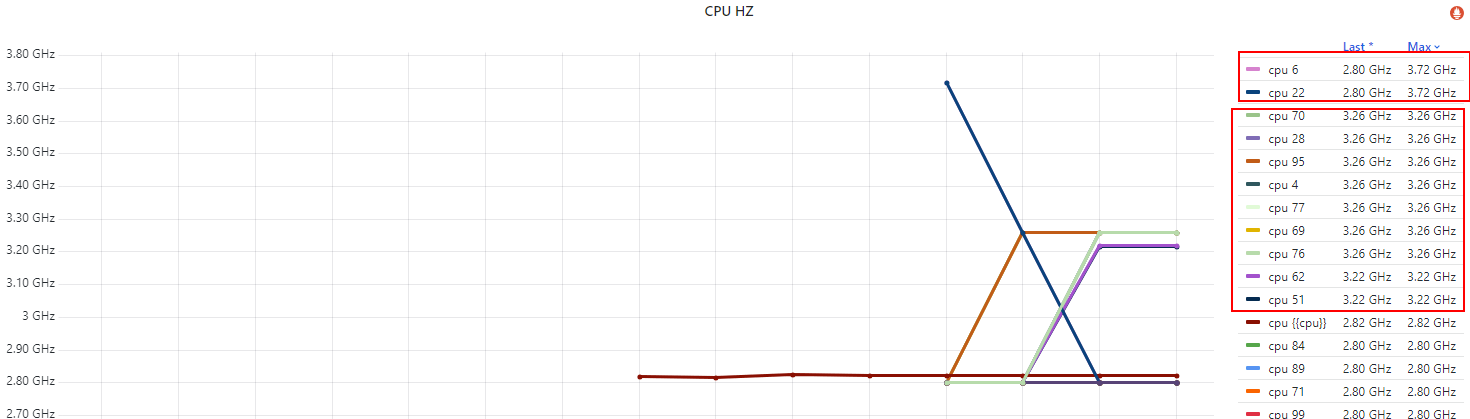
Fig. Per-CPU running frequency
几点说明,
idle=poll禁用了节能模式(c1/c2/c3..),没有负载也会空转(执行轻量级指令),避免频率掉下去;- 不是所有 CPU 都能同时达到 3.7GHz 的
max/turbo freq,原因我们在第二篇解释过了; - 实际上,只有很少的 CPU 能同时达到 max freq。
3.2 功耗、电流
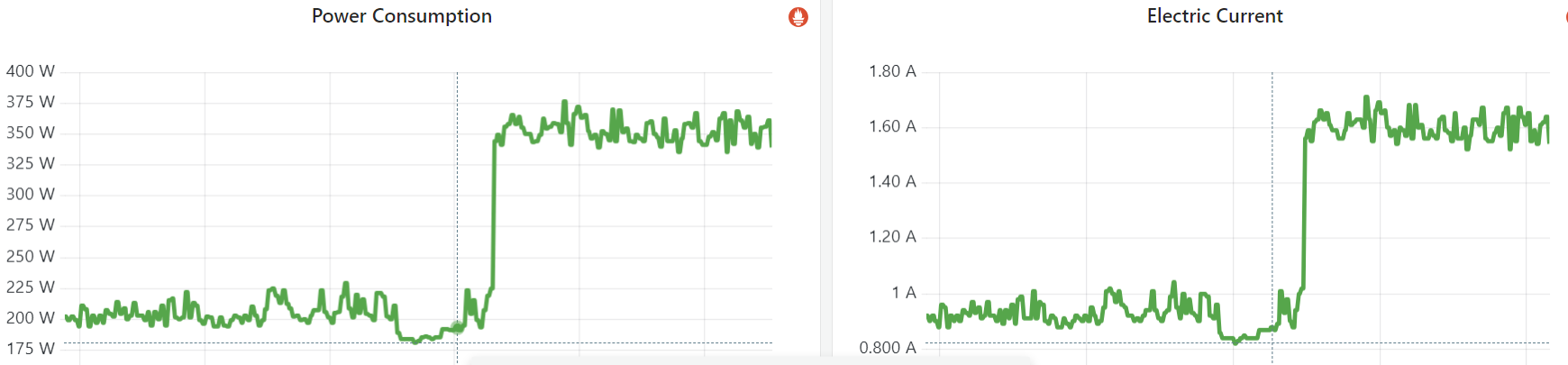
Fig. Power consumption and electic current of an empty node (no workload before and after)
after setting idle=poll for test
3.3 温度等
服务器厂商一般能提供。
3.4 sysfs 详细信息
按需。
除了通过 sysfs 和内核启动项,还可以通过一些更上层的工具配置功耗和性能模式。
4.1 tuned/tuned-adm
$ tuned-adm list
Available profiles:
- balanced - General non-specialized tuned profile
- desktop - Optimize for the desktop use-case
- latency-performance - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
- network-latency - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption, focused on low latency network performance
- network-throughput - Optimize for streaming network throughput, generally only necessary on older CPUs or 40G+ networks
- powersave - Optimize for low power consumption
- throughput-performance - Broadly applicable tuning that provides excellent performance across a variety of common server workloads
- virtual-guest - Optimize for running inside a virtual guest
- virtual-host - Optimize for running KVM guests
Current active profile: latency-performance
$ tuned-adm active
Current active profile: latency-performance
$ tuned-adm profile_info latency-performance
Profile name:
latency-performance
Profile summary:
Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
$ tuned-adm profile_mode
Profile selection mode: manual
4.2 turbostat:查看 turbo freq
来自 man page:
turbostat - Report processor frequency and idle statistics
turbostat reports processor topology, frequency, idle power-state statistics, temperature and power on X86 processors.
- –interval
- –num_iterations
例子:
$ turbostat --quiet --hide sysfs,IRQ,SMI,CoreTmp,PkgTmp,GFX%rc6,GFXMHz,PkgWatt,CorWatt,GFXWatt
Core CPU Avg_MHz Busy% Bzy_MHz TSC_MHz CPU%c1 CPU%c3 CPU%c6 CPU%c7
- - 488 12.52 3900 3498 12.50 0.00 0.00 74.98
0 0 5 0.13 3900 3498 99.87 0.00 0.00 0.00
0 4 3897 99.99 3900 3498 0.01
1 1 0 0.00 3856 3498 0.01 0.00 0.00 99.98
1 5 0 0.00 3861 3498 0.01
2 2 1 0.02 3889 3498 0.03 0.00 0.00 99.95
2 6 0 0.00 3863 3498 0.05
3 3 0 0.01 3869 3498 0.02 0.00 0.00 99.97
3 7 0 0.00 3878 3498 0.03
- 出于性能考虑,turbostat 以 topology order 运行,这样同属一个 CORE 的两个 hyper-thread 在输出中是相邻的。
Busy%:C0状态所占的时间百分比。
Note that cpu4 in this example is 99.99% busy, while the other CPUs are all under 1% busy. Notice that cpu4’s HT sibling is cpu0, which is under 1% busy, but can get into CPU%c1 only, because its cpu4’s activity on shared hardware keeps it from entering a deeper C-state.
5.1 c-state 太深导致网络收发包不及时
- Controlling Processor C-State Usage in Linux, A Dell technical white paper describing the use of C-states with Linux operating systems, 2013
- Linux 网络栈接收数据(RX):配置调优
- C-state tuning guide opensuse.org
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh