2024-5-22 17:57:31 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:1 收藏
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a diverse range of services, from storage options to app development, tailored to fulfill the requirements of its users. However, these opportunities are accompanied by various security challenges. This is where Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles become essential, adding an additional layer of protection for your data and services.
At the heart of this system lies roles, which act as predefined sets of permissions that grant users specific levels of access. Mastering role assignment is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient cloud environment.
What are GCP IAM Roles?
GCP IAM roles are a fundamental component designed to help manage access control and permissions within GCP environments. These roles are essentially collections of permissions that determine what actions an identity (a user, group, or service account) can perform on GCP resources. IAM roles provide a flexible and secure way to manage who has access to GCP resources and what actions they can perform, thereby ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and perform operations within a GCP project.
Three Types of GCP IAM Roles
IAM roles in GCP are categorized into three main types: predefined roles, custom roles, and basic roles. Predefined roles are created by Google and are designed to provide granular access for specific Google Cloud services, covering common use cases and ensuring best practices in security and compliance. Custom roles, on the other hand, allow organizations to create tailored sets of permissions to meet specific needs that aren’t covered by predefined roles. This is particularly useful for defining precise access control policies that align with an organization’s unique operational requirements. Basic roles, which include Owner, Editor, and Viewer roles, offer broad access control across GCP services and are generally recommended for use in limited scenarios due to their wide-ranging permissions.
Effectively managing IAM roles is crucial for securing GCP environments against unauthorized access and potential security breaches. By understanding the structure and purpose of these roles, organizations can implement robust access control policies that protect resources while facilitating smooth operations across their cloud environments.
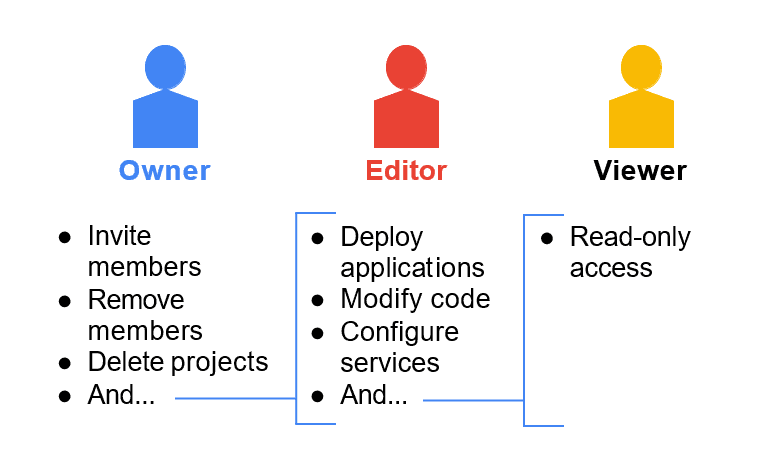
Basic Roles
Basic roles, formerly known as “primitive roles,” are the most broad and straightforward options available. These roles encompass a vast array of permissions spanning multiple Google Cloud services, granting users extensive access within a project. The three primary basic roles are:
- Owner: Bestows complete control over a project, including the ability to manage roles, permissions, and billing settings.
- Editor: Permits modification and creation of resources within a project, excluding certain sensitive operations.
- Viewer: Grants read-only access to resources, enabling users to view but not alter existing data or configurations.
While basic roles offer unparalleled simplicity, their far-reaching permissions can pose significant security risks if misused. As a general guideline, it is advisable to reserve basic role assignments for testing or sandboxed environments and avoid their use in production scenarios involving sensitive data.
Predefined Roles
Predefined roles, meticulously crafted and maintained by Google, offer a balanced approach to access control. These roles provide granular access to specific Google Cloud services, ensuring users receive only the permissions necessary to perform their assigned tasks. By adhering to the principle of least privilege, predefined roles enhance security and reduce the risk of unintended data exposure or resource misuse.
Google’s product teams have carefully reviewed the available permissions for each service and curated predefined roles that encapsulate the essential permissions required for common job functions. For instance, the BigQuery service offers predefined roles such as BigQuery Admin, BigQuery Data Owner, and BigQuery Job User, enabling precise access control for various data management tasks.
One of the key advantages of predefined roles is their seamless integration with Google Cloud’s evolving feature set. As new services or capabilities are introduced, Google automatically updates the corresponding predefined roles with the necessary permissions, ensuring users remain empowered with the latest access privileges without manual intervention.
Custom Roles
In scenarios where predefined roles fall short of meeting an organization’s specific requirements, custom roles emerge as a powerful solution. Custom roles enable administrators to meticulously curate a unique set of permissions, granting users access to only the resources and actions they genuinely require.
The creation of custom roles is a two-fold process. First, organizations must identify the specific permissions needed for a particular task or job function. Subsequently, they can bundle these permissions into a custom role, ensuring a precise and tailored access control mechanism.
While custom roles offer unparalleled flexibility, they also introduce additional complexity and maintenance overhead. Organizations must diligently monitor and update custom roles as new permissions or services are introduced, ensuring their continued relevance and effectiveness.
GCP IAM Roles: 6 Steps for a Seamless Setup
Setting up IAM (Identity and Access Management) roles within Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a fundamental task for securing and efficiently managing access to your cloud resources. This process allows administrators to assign specific permissions to users, groups, and service accounts, dictating who can do what within the scope of GCP projects and services. The following steps outline a professional approach to setting up GCP IAM roles, ensuring a secure and organized access management system.
- Log into your Google Cloud Console. This is the web interface where you can manage all aspects of your GCP resources.
- Navigate to the IAM & Admin section on the dashboard. This area is dedicated to identity and access management, where you can oversee roles, permissions, and the organizational structure of your resources.
- Learn the hierarchy of GCP resources. GCP organizes resources into projects, folders, and organizations. This hierarchy influences how IAM roles are inherited and applied. It’s crucial to understand this structure as it will dictate how you assign roles at different levels (project, folder, or organization) to meet your access control requirements.
- Identify the roles that suit your needs. GCP offers a wide range of predefined roles, each encapsulating a set of permissions designed for specific tasks within the platform. These roles range from broad (Owner, Editor, Viewer) to service-specific (e.g., Compute Admin, Storage Object Admin). Assess the responsibilities of your team members and select the roles that best match their needs. If necessary, you can also create custom roles with a tailored set of permissions.
- Assign the appropriate roles. In the IAM & Admin section of the Google Cloud Console, navigate to the IAM page. Here you can add members (users, groups, and service accounts) and assign them roles. When adding a member, you’ll enter their email address and select the role from a dropdown menu. It’s important to apply the principle of least privilege—only grant the permissions necessary for users to perform their tasks. Optionally, for more advanced scenarios, consider setting up conditional IAM policies. These policies allow you to specify conditions under which the assigned roles are effective. For example, you might restrict certain actions to specific IP ranges or times of day. This adds an extra layer of security and control over how and when your cloud resources can be accessed.
- Regularly review and audit your IAM settings. GCP provides tools for monitoring access logs and analyzing permissions. Use these tools to ensure that only authorized users have access and that they are using their permissions responsibly. Regular audits help maintain a secure and efficient access management system by identifying unused roles or overly permissive settings that could be tightened.
In conclusion, setting up IAM roles in GCP involves understanding your organizational structure, selecting appropriate roles, assigning them judiciously, optionally implementing conditional policies for enhanced security, and conducting regular audits. By following these steps meticulously, organizations can ensure robust security and efficient management of their cloud resources within Google Cloud Platform.
Conclusion: Tailoring Roles for Optimal Security and Efficiency
Mastering the art of role assignment within Google Cloud Platform’s Identity and Access Management framework is a critical endeavor for organizations seeking to strike the perfect balance between security and operational efficiency. By understanding the nuances of basic, predefined, and custom roles, organizations can meticulously tailor access privileges to align with their unique requirements and risk profiles.
Embracing principles such as least privilege, separation of duties, and periodic access reviews, coupled with seamless integration with identity providers and robust logging and monitoring capabilities, organizations can cultivate a secure and well-governed cloud environment. With careful role management and adherence to best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of Google Cloud Platform while safeguarding their valuable data and resources from unauthorized access or misuse.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) framework that allows organizations to define who has access to their resources and what actions they can perform. Within this context, the use of Apono, a third-party tool, can significantly enhance the management of GCP IAM roles, offering a layer of automation and oversight that simplifies the complexities involved in permissions management.
Apono integrates seamlessly with GCP IAM, providing administrators with a more intuitive and granular control over roles and permissions. By utilizing Apono, organizations can automate the assignment and revocation of IAM roles based on user activities, job functions, or defined policies. This not only reduces the administrative burden but also minimizes the risk of human error, ensuring that only the right individuals have access to sensitive resources at the right time. Moreover, Apono’s capabilities extend to monitoring and auditing, giving teams clear insights into permissions usage and anomalies, which is critical for compliance and security governance.
Incorporating Apono with GCP IAM roles elevates an organization’s ability to manage cloud resources efficiently. It aligns with best practices for least privilege access, a principle that limits users’ access rights to only what is strictly required to perform their tasks in addition to just-in-time access, which makes sure users only have the access they need for the time they need it. These approaches are essential in mitigating potential security risks, such as data breaches or unauthorized access. As cloud environments become increasingly complex, leveraging tools such as Apono to enhance GCP IAM roles management is a strategic move for organizations aiming to bolster their cloud security posture while maintaining operational agility.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Apono authored by Rom Carmel. Read the original post at: https://www.apono.io/blog/gcp-iam-roles-all-types-and-recommended-setup/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh