2024-7-5 16:46:57 Author: hackernoon.com(查看原文) 阅读量:3 收藏
For several reasons, it’s not always convenient to deal with an asset directly but to trade with a “synthetic version” of it. That’s how stablecoins came to life: they represent underlying assets, often with the same value, but they’re not that asset itself. Futures and perpetual futures contracts in the finance world are very similar, but looking for speculative earnings or hedging risks instead of mere stability.
Futures are contracts to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. Perpetual futures are a type of futures contract without an expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. When trading non-perpetual futures contracts, traders are agreeing to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specified price and date in the future. However, they do not take ownership of the asset at the time of entering into the contract. Instead, futures contracts allow traders to speculate on the price movements of the asset without needing to possess it.
This kind of financial tool is often centralized, complex, and expensive, though. Just recently, the cryptocurrency world has opened the doors to more investors, creating more readily available futures contracts on different platforms. However, the way they are now, they are totally centralized and have many limitations.
One of them, important to note, is the risk of being liquidated if the price moves enough against your position. Liquidation is an event when your position is automatically closed by the exchange to prevent further losses that would exceed your investment, typically resulting in the loss of your initial investment. Also, centralized future contracts are not usable outside the exchange where they are traded, so no other financial instruments can be independently built on top of them.
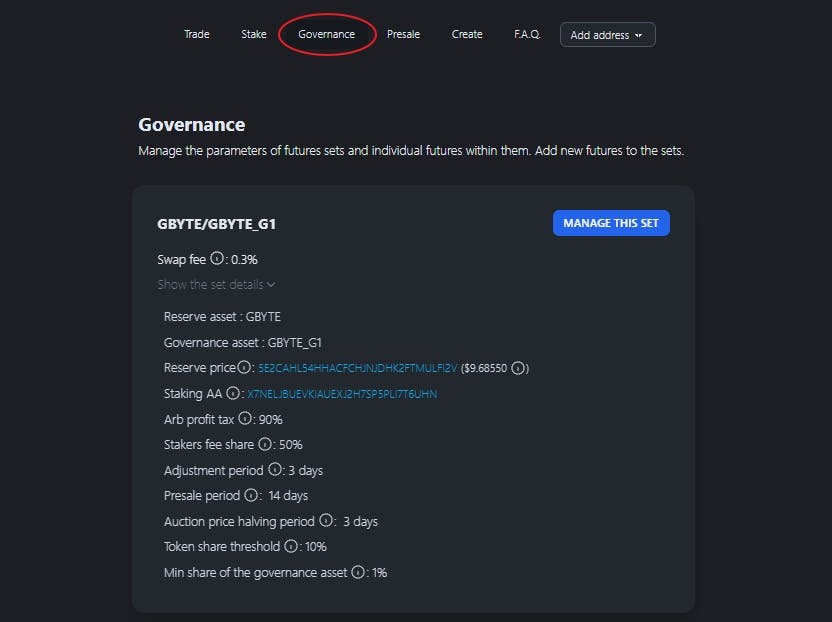
The Obyte-based
Unique Features
As you can imagine by now, Pythagorean Perpetual Futures are a type of perpetual futures, but instead of relying on centralized entities like exchanges, they work with Pythagorean bonding curves and
Pythagorean bonding curves are mathematical formulas used to determine token issuance and pricing. They dynamically adjust parameters to maintain the price alignment of the futures tokens with the tracked asset, ensuring stability and accuracy in price tracking., AAs are somewhat similar to smart contracts, but they work as
This way, these futures closely follow the price of the asset they track by dynamically adjusting the parameters of the bonding curve. Besides, unlike other perpetual futures, Pythagorean futures eliminate the risk of liquidation, providing traders with more security.
Another standout feature of them is their DeFi composability: they’re designed as fungible tokens, allowing seamless integration with other
How to Use Pythagorean Perpetul Futures?
As they function on top of the
Next, you can visit the official webpage of the
Once you've made your choice, acquire the desired futures token. To do it, you can use assets like GBYTE, or ETH, WBTC, USDC, and others if you previously imported them from other chains through the
With your future tokens in hand, it's time to apply your trading strategies! You can sell and buy futures tokens at any time. Additionally, you can consider acquiring the governance token of a futures set to collect trading fees and actively participate in parameter decisions. Users who choose to stake (lock) their governance tokens for participation in governance will receive a greater portion of the fees generated. Extending the duration of the locking period results in an even higher proportion of fees earned.
With their innovative use of Pythagorean bonding curves and autonomous operation, these tokens provide security, autonomy, and investment opportunities for traders of all levels. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader,
Featured Vector Image by storyset /
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh

