2024-7-17 21:16:29 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:7 收藏
It is a widely acknowledged fact that quantum computing poses a grave threat to traditional cryptography. As we prepare for the post-quantum era, transitioning to quantum-safe cryptography is a critical action item for all organizations.
However, upgrading the entire infrastructure to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is a highly complex, resource-intensive process that may take years, depending on the number and types of systems and applications. One effective way to secure the infrastructure during this long transition is to use hybrid TLS certificates. These certificates provide a practical and flexible solution for the migration, maintaining strong security while gradually integrating post-quantum cryptography.
Here’s a quick look at what hybrid certificates are and how they can help with migration to PQC.

What Are Hybrid Certificates?
Hybrid certificates are digital certificates that use both classical (RSA or ECC) and PQC (Post-Quantum Cryptography) algorithms. Also known as Catalyst, hybrid certificates are signed with two digital signatures and link two independent public keys—one classical and one post-quantum—to a single identity. This dual support allows for secure authentication and key exchange using both classical and post-quantum methods, thereby helping secure communications against current and future threats posed by quantum computers.
To understand hybrid certificates better, let’s take the analogy of making a payment at a small convenience store. We can pay using physical cash, digital wallet, or a credit/debit card. Let’s assume the store hasn’t switched to digital payments yet or the card reader is not working, we then pay using physical cash. Having all the payment options handy ensures smooth payments. Similarly, hybrid certificates combine both classical and post-quantum algorithms, providing robust security during the transition process.
The primary goal of hybrid certificates is to enable gradual migration to PQC by providing a bridge between the current traditional systems and future quantum-safe systems. This allows organizations to use a single hybrid certificate instead of two separate certificates (a traditional digital certificate and a quantum-safe digital certificate) for authentication until all the systems are fully upgraded to PQC standards.
What Are PQC Algorithms?
PQC algorithms are cryptographic algorithms that can withstand the attacks launched by quantum computers. Unlike traditional encryption and digital signature algorithms such as RSA, ECDH, EDSA, and EdDSA, which could be easily broken by large-scale quantum computers, using algorithms like Shor’s, PQC algorithms rely on mathematical problems believed to be resistant to quantum attacks. PQC algorithms aim to provide long-term security for digital communications, ensuring that data remains protected even when quantum computing applications become mainstream.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. has been driving the effort to develop and standardize PQC algorithms. In July 2022, NIST announced the first group of algorithms chosen for standardization. These include CRYSTALS-KYBER for key exchange mechanism and CRYSTALS-Dilithium, FALCON, and SPHINCS+ for digital signatures. In addition, NIST is also considering four other algorithms for the final round of standardization this year. These algorithms will form the basis for quantum-resistant standards.
Crypto-Agility and Preparing for Post-Quantum Cryptography
Hybrid certificates will utilize these PQC algorithms to provide the same functionalities as traditional TLS certificates but with enhanced security against quantum-enabled attacks.
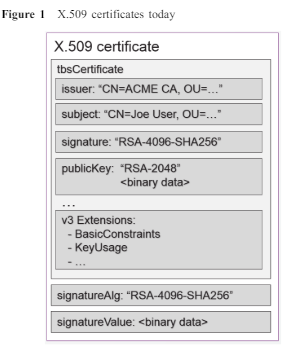
What Does a Hybrid Certificate Look Like?
Hybrid certificates are, in essence, X.509 certificates with additional fields for PQC. In the hybrid certificate format, all post-quantum (PQ) data, such as public keys and signatures, are included in non-critical X.509 certificate extensions. This allows protocols to utilize these certificates even if they don’t support PQC algorithms.
The PQC information includes:
- Alternative public key
- Alternative signature algorithm
- Alternative digital signature


– Impact of post-quantum hybrid certificates on PKI, common libraries, and protocols
Benefits of Hybrid Certificates
- Seamless and Secure Transition to PQC
Hybrid certificates help adopt PQC algorithms without abandoning existing encryption and digital signature algorithms such as RSA, ECDH, EDSA, and EdDSA. This means that during the TLS handshake process when the client and the server negotiate encryption algorithms, legacy systems that only support traditional cryptographic algorithms can continue to operate as usual, while PQC-upgraded systems can choose to use PQC algorithms for encryption. This eliminates the need for a complete and immediate overhaul of the entire infrastructure, which can be both costly, complex, and overwhelming.
- Enhanced Security
Hybrid certificates offer enhanced security by combining classical and PQC algorithms. Even if a future quantum computer compromises a classical algorithm, the quantum-safe algorithm within the hybrid certificate ensures that the overall security of the communication remains intact. This dual-layer protection provides an added level of security during the transition period.
- Flexibility in Deployment
Hybrid certificates provide flexibility in deployment, allowing organizations to choose the right time and approach for transitioning to quantum-safe cryptography. Organizations can test and validate PQC algorithms in a controlled manner, ensuring that they meet security and performance requirements before full-scale implementation.
Challenges and Considerations
- Performance Impact
Hybrid certificates can introduce additional computational overhead due to the use of multiple cryptographic algorithms. Organizations must carefully evaluate the performance impact and optimize their systems to balance security and efficiency.
- Interoperability
Ensuring interoperability between systems that support hybrid certificates and those that do not can be challenging. Organizations must work with CAs and vendors to ensure that their systems are compatible with hybrid certificates.
- Complexity in Management
Managing hybrid certificates adds complexity to the certificate lifecycle management process. Organizations need robust processes and CLM solutions to handle the continuous issuance, renewal, and revocation of hybrid certificates.
Hybrid certificates are an essential tool in the transition to post-quantum cryptography. By leveraging their benefits, organizations can navigate the complexities of post-quantum migration and ensure the continued protection of their sensitive data and communications.
How AppViewX Can Help with Hybrid Certificates
AVX ONE CLM is a ready-to-consume, scalable, certificate lifecycle management (CLM) solution that automates all certificate processes end-to-end. You can discover, inventory, monitor, and automate the complete lifecycle for all public and private certificates, through a central management console. AppViewX brings together visibility, automation, and control across on-premises, multi-cloud, hybrid cloud, IoT, and containerized environments to simplify certificate lifecycle management, improve efficiency, build crypto-agility, and ensure continuous compliance.
Talk to our experts to know how you can manage all your certificates including hybrid certificates with AVX ONE CLM.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Blogs Archive - AppViewX authored by Krupa Patil. Read the original post at: https://www.appviewx.com/blogs/preparing-for-the-quantum-leap-with-hybrid-certificates/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh