一
前言
环境:LLVM 9.0、CMake:3.16.3
二
LLVM介绍及编译
OLLVM 使用的就是 LLVM IR 来处理源代码,它能够获取到程序的结构和控制流信息,通过对这些信息的处理增强代码混淆的效果。
LLVM IR有两种文件格式.ll和.bc,.ll 文件和 .bc 文件都是 LLVM 中间表示的不同表示形式,.ll 文件是文本形式的可读表示,方便分析和调试;.bc 文件是二进制形式的紧凑表示,用于编译过程中的处理和优化,所以主要看.ll格式文件内容。
再介绍一些IR相关的概念1.Pass是用于处理IR的关键组成部分,LLVM中自带的Pass主要是lib/Transforms中的.cpp文件2.IR结构,Module->Function->Basic Block->Instruction,这些是IR的不同层次结构从左到右是一对多的包含关系。
define dso_local i32 @main(i32 %argc, i8** %argv) #0 函数 {
...
first: ; preds = %loopEnd
%.reload = load volatile i32, i32* %.reg2mem 指令
%cmp = icmp eq i32 %.reload, 2
%1 = select i1 %cmp, i32 769163483, i32 -1060808858
store i32 %1, i32* %switchVar
br label %loopEnd
first就是一个名为first的基本块以br结尾
if.then: S ; preds = %loopEnd2
%2 = load i8*, i8** %str, align 8
%3 = load i8*, i8** @globalString, align 8
%call = call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* getelementptr inbounds ([13 x i8], [13 x i8]* @.str.5, i64 0, i64 0), i8* %2, i8* %3)
store i32 -1907967449, i32* %switchVar
br label %loopEnd2if.else: ; preds = %loopEnd
%4 = load i32, i32* %argc.addr, align 4
%cmp1 = icmp eq i32 %4, 3
%5 = select i1 %cmp1, i32 1950105811, i32 1575411630
store i32 %5, i32* %switchVar
br label %loopEnd
...
}
LLVM编译
https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/releases
编译没啥注意事项建文件打命令即可,-DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS这个参数把clang编译了,后面要用到,这里还有一个常用的工具lldb这个调试Pass需要这个。
cd到解压的文件夹里
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -G Ninja -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=release -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS="clang" ../llvm
二
在源码外开发一个函数名变量名加密Pass
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"{LLVM解压文件路径}/build_debug/include",
"{LLVM解压文件路径}/llvm/include"
],
"defines": [],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/gcc",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "gnu++14",
"intelliSenseMode": "linux-clang-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
https://llvm.org/docs/CMake.html#developing-llvm-passes-out-of-source
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16)
project(HelloPass)#这个可以随便取# 设置 LLVM 路径
set(LLVM_DIR "{llvm源码路径}/build/lib/cmake/llvm")
find_package(LLVM REQUIRED CONFIG)project(ProjectName)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH "${LLVM_CMAKE_DIR}")
include(AddLLVM) //支持add_llvm_librarySET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-Wall -fno-rtti")
separate_arguments(LLVM_DEFINITIONS_LIST NATIVE_COMMAND ${LLVM_DEFINITIONS})
add_definitions(${LLVM_DEFINITIONS_LIST})
include_directories(${LLVM_INCLUDE_DIRS})add_subdirectory(下级目录名)
主体代码:
namespace {
struct EncodeFunctionName2 : public ModulePass {
static char ID;
EncodeFunctionName2() : ModulePass(ID) {}
bool runOnFunction(Function &F) {
Module *M = F.getParent();
LLVMContext &context = M->getContext();
errs() << "EncodeFunctionName: " << F.getName() << " -> ";if (F.getName().compare("main") != 0&&F.getName().compare("main") != 0) {
llvm::MD5 Hasher;
llvm::MD5::MD5Result Hash;
Hasher.update("kanxue_");
Hasher.update(F.getName());
Hasher.final(Hash);SmallString<32> HexString;
llvm::MD5::stringifyResult(Hash, HexString);F.setName(HexString);
}
errs() << F.getName() << "\r\n";
return true;//当修改了IR代码的话返回True
}
bool runOnModule(Module &M) override {
llvm::MD5 Hasher;
llvm::MD5::MD5Result Hash;for (auto &F : M) {
runOnFunction(F);
}
for (GlobalVariable &GV : M.globals()) {
StringRef oldName = GV.getName();
Hasher.update("kanxue_");
Hasher.update(oldName);
Hasher.final(Hash);
SmallString<32> HexString;
llvm::MD5::stringifyResult(Hash, HexString);
errs() << "EncodeVariableName: " << oldName << " -> ";
// llvm::MD5::stringifyResult(Hash, HexString);
// std::string newName = encryptName(oldName.str());
GV.setName(HexString);
// modified = true;
errs() << GV.getName() << "\r\n";
}
return true;
}};
}
char EncodeFunctionName2::ID = 0;
//注册Pass
static RegisterPass<EncodeFunctionName2> X("encode", "Encode Function and Variable Name Pass",
false /* Only looks at CFG */,
false /* Analysis Pass */);
使用opt工具生成.ll文件,opt在设置了环境变量后就能直接用,新版llvm加 -enable-new-pm=0。
opt -load "./EncodeFunctionName2/LLVMEncodeFunctionName2.so" --encode -S ../../hello.ll -o ../hello.ll
opt -load "./EncodeFunctionName2/LLVMEncodeFunctionName2.so" --help |grep encode
三
控制流平坦化分析及魔改
先顺着原版的OLLVM代码说一下控制流平坦化的实现原理:
bool Flattening::runOnFunction(Function &F) {
Function *tmp = &F;
// Do we obfuscate
// if (toObfuscate(flag, tmp, "fla")) {
if (flatten(tmp)) {
++Flattened;
}
// }return false;
}
vector<BasicBlock *> origBB;
BasicBlock *loopEntry;
BasicBlock *loopEnd;
LoadInst *load;
SwitchInst *switchI;
AllocaInst *switchVar;// SCRAMBLER
char scrambling_key[16];
llvm::cryptoutils->get_bytes(scrambling_key, 16);
// END OF SCRAMBLER// Lower switch
FunctionPass *lower = createLowerSwitchPass();
lower->runOnFunction(*f);
// Save all original BB
for (Function::iterator i = f->begin(); i != f->end(); ++i) {
BasicBlock *tmp = &*i;
origBB.push_back(tmp);BasicBlock *bb = &*i;
if (isa<InvokeInst>(bb->getTerminator())) {
return false;
}
}// Nothing to flatten
if (origBB.size() <= 1) {
return false;
}// Remove first BB
origBB.erase(origBB.begin());// Get a pointer on the first BB
Function::iterator tmp = f->begin(); //++tmp;
BasicBlock *insert = &*tmp;// If main begin with an if
BranchInst *br = NULL;
if (isa<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator())) {
br = cast<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator());
}if ((br != NULL && br->isConditional()) ||
insert->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() > 1) {
BasicBlock::iterator i = insert->end();
--i;
// 指令多大于一可能还有cmp指令所以要和跳转指令一起分割
if (insert->size() > 1) {
--i;
}BasicBlock *tmpBB = insert->splitBasicBlock(i, "first");
origBB.insert(origBB.begin(), tmpBB);
}// Remove jump 移除掉splitBasicBlock函数分割后第一个块跳转到frist块的指令。
insert->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();
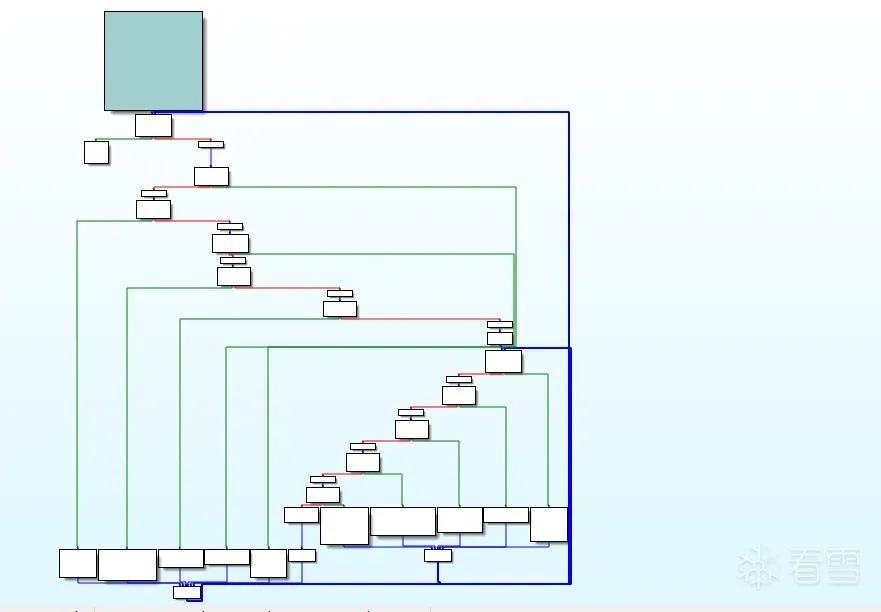
类似这样,entry作为入口代码块平坦化后会设置switchVar为first对应的switchVar,再通过first来进入第二个代码块,这样就不能直接看出正常逻辑entry之后该执行的真实代码块是哪个了。
// Create switch variable and set as it 创建switchVar变量并设置一个随机生成的值
switchVar =
new AllocaInst(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()), 0, "switchVar", insert);
new StoreInst(
ConstantInt::get(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(0, scrambling_key)),
switchVar, insert);// Create main loop 第三个参数是插入在哪个块之前
loopEntry = BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEntry", f, insert);
loopEnd = BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEnd", f, insert);load = new LoadInst(switchVar, "switchVar", loopEntry);
// Move first BB on top
insert->moveBefore(loopEntry);
BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, insert);// loopEnd jump to loopEntry
BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, loopEnd);BasicBlock *swDefault =
BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "switchDefault", f, loopEnd);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, swDefault);// Create switch instruction itself and set condition
switchI = SwitchInst::Create(&*f->begin(), swDefault, 0, loopEntry);
switchI->setCondition(load);// Remove branch jump from 1st BB and make a jump to the while
f->begin()->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, &*f->begin());
// Put all BB in the switch
for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();
++b) {
BasicBlock *i = *b;
ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;// Move the BB inside the switch (only visual, no code logic)
i->moveBefore(loopEnd);// Add case to switch
//llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32这个函数的第一个参数是加密字段,第二个是key,switchI->getNumCases的值是从0开始递增那这里生成的跳转条件就和llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(0, scrambling_key)是一样的
numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(
switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(switchI->getNumCases(), scrambling_key)));
switchI->addCase(numCase,i);
}
// Recalculate switchVar 这里开始遍历所有块去除块中最后的br
for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();
++b) {
BasicBlock *i = *b;
ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;// Ret BB
if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 0) {
continue;
}if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 1) {//1个的类似if{} 判断是一个block条件为真后的代码是一个代码块
// Get successor and delete terminator
BasicBlock *succ = i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0);
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();// Get next case
numCase = switchI->findCaseDest(succ);// If next case == default case (switchDefault)
if (numCase == NULL) {
numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}// Update switchVar and jump to the end of loop
new StoreInst(numCase, load->getPointerOperand(), i);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);
continue;
}// If it's a conditional jump
if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 2) { //有两个的类似if(){}else{}
// Get next cases
ConstantInt *numCaseTrue =
switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0));
ConstantInt *numCaseFalse =
switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1));// Check if next case == default case (switchDefault)
if (numCaseTrue == NULL) {
numCaseTrue = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}if (numCaseFalse == NULL) {
numCaseFalse = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}// Create a SelectInst
BranchInst *br = cast<BranchInst>(i->getTerminator());
SelectInst *sel =
SelectInst::Create(br->getCondition(), numCaseTrue, numCaseFalse, "",
i->getTerminator());// Erase terminator
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();// Update switchVar and jump to the end of loop
new StoreInst(sel, load->getPointerOperand(), i);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);
continue;
}
}
fixStack(f);
return true;
接下来开始实现之前说的两个改进,首先是不通过loopEntry分发loopEntry只作为入口,直接进入loopEnd,把分发流程做到loopEnd中,这里要做的是把switch生成到loopEnd中,然后把loopEnd跳转loopEntry的跳转指令删除掉,这样就可以实现loopEnd直接分发代码块。
LoadInst *load2 = new LoadInst(switchVar, "switchVar", loopEnd);
BasicBlock *swDefault =
BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "switchDefault", f, loopEnd);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, swDefault);
SwitchInst *switch2=SwitchInst::Create(load2, loopEnd2, 0, loopEnd);
//修改查找Case的switch为loopEnd里的switch
numCase = switch2->findCaseDest(succ)生成的LR
loopEnd: ; preds = %for.end, %for.body, %if.else5, %if.else, %first, %loopEnd2, %switchDefault
%switchVar2 = load i32, i32* %switchVar
switch i32 %switchVar2, label %loopEnd2 [
i32 -256601636, label %first
i32 -1060808858, label %if.else
i32 1575411630, label %if.else5
i32 1213754259, label %for.body
i32 420055895, label %for.end
i32 -1907967449, label %if.end9
]
SwitchInst *switch2=SwitchInst::Create(load2, loopEnd2, 0, loopEnd);
SwitchInst *switch3=SwitchInst::Create(load3, loopEnd, 0, loopEnd2);
int addCase_flag=1;
size_t count1=0;
for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();
++b,count1++) {
BasicBlock *i = *b;
ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;// Move the BB inside the switch (only visual, no code logic)
i->moveBefore(loopEnd);
//change
if(addCase_flag==1){
// Add case to switch
numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(
switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(count1, scrambling_key)));
switch2->addCase(numCase, i);
addCase_flag=0;
}
else{
// Add case to switch
numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(
switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(count1, scrambling_key)));
switch3->addCase(numCase, i);
addCase_flag=1;
}
//change
// switch2->addCase(numCase, i);
}
size_t conut2=0;
int a=1;
for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();
++b,conut2++) {
BasicBlock *i = *b;
ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;// Ret BB
if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 0) {
continue;
}// If it's a non-conditional jump
if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 1) {
// Get successor and delete terminator
BasicBlock *succ = i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0);
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();// Get next case
if(switch2->findCaseDest(succ)!=nullptr)
{numCase = switch2->findCaseDest(succ);}
else
{numCase = switch3->findCaseDest(succ);}// If next case == default case (switchDefault)
if (numCase == NULL) {
numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}// Update switchVar and jump to the end of loop
new StoreInst(numCase, load->getPointerOperand(), i);if(a==1){
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);
a=0;
}
else{
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd2, i);
a=1;
}
// BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);
continue;
}// If it's a conditional jump
if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 2) {
// Get next cases
ConstantInt *numCaseTrue =nullptr;
ConstantInt *numCaseFalse =nullptr;
if(switch2->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0))!=nullptr)
{numCaseTrue = switch2->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0));
}
else
{
numCaseTrue =
switch3->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0));
}if(switch2->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1))!=nullptr)
{
numCaseFalse =
switch2->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1));
}
else
{
numCaseFalse =
switch3->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1));
}// Check if next case == default case (switchDefault)
if (numCaseTrue == NULL) {
numCaseTrue = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}if (numCaseFalse == NULL) {
numCaseFalse = cast<ConstantInt>(
ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),
llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(
switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));
}// Create a SelectInst
BranchInst *br = cast<BranchInst>(i->getTerminator());
SelectInst *sel =
SelectInst::Create(br->getCondition(), numCaseTrue, numCaseFalse, "",
i->getTerminator());// Erase terminator
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();// Update switchVar and jump to the end of loop
new StoreInst(sel, load->getPointerOperand(), i);
if(a==1){
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);
a=0;
}
else{
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd2, i);
a=1;
}
continue;
}
}
不过对于OLLVM来说控制流平坦化只是其中的一环,配合OLLVM中的其他模块或一些的新型混淆Pass才能发挥最大的作用。
五
参考文章
http://www.qfrost.com/posts/llvm/llvmflattening%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/#%E5%A4%8D%E6%9D%82%E5%88%86%E5%8F%91%E8%BF%87%E7%A8%8B
https://groups.google.com/g/llvm-dev/c/-ihkMNlDvEQ
看雪ID:mb_edqxbbqv
https://bbs.kanxue.com/user-home-978849.htm
# 往期推荐
2、恶意木马历险记
球分享
球点赞
球在看
点击阅读原文查看更多
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh