01.
前言
OLLVM现在是经常遇到了,在学习之前我们先了解一些LLVM的知识。
LLVM
LLVM是一套编译器基础设施项目,分为前端、中间层标识(IR)、后端。
前端就包括Clang、Rustc等,前端负责将对应语言的源代码转为中间层代码(IR),后端负责将IR转为特定平台的机器码或汇编代码。
pass分类介绍
Pass,翻译是通过,通过一遍IR也就是遍历IR。在遍历IR的时候进行一些操作,比如优化、插桩、混淆。Pass的通常为.so文件。
分类:
◆ModulePass 基于模块
◆FunctionPass 基于函数
◆CallGraphPass 基于调用图
◆LoopPass 基于循环
functionPass
重点介绍一下functionPass,因为控制流平坦化的pass就是基于函数的
◆以函数为单位进行处理
◆FunctionPass的子类必须实现runOnFunction函数
◆在FunctionPass运行时,会对程序中的每个函数执行runOnFunction函数
环境搭建
参考:https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-279624.htm#msg_header_h2_1
OLLVM
可以这样理解,LLVM的pass是用来优化分析的,将这些pass的功能改为混淆代码,就是OLLVM项目。
IR
由于后面的pass编写都是针对IR指令的,所以我们有必要对它有更进一步的了解。
IR主要有两种表现形式:
1.人类可阅读的文本形式,对应后缀为 .ll
转换命令:
可阅读文本
clang -S -emit-llvm fileName.c -o fileName.ll
二进制
clang -c -emit-llvm fileName.c -o fileName.bc
这两种文件只是表现形式不同,均可以被优化编译成可执行文件。
Opt
opt为optimizer的缩写,优化器的意思,使用opt对IR进行优化操作。
opt -load LLVMObfuscator.so -hlw -S fileName.ll -o fileName_opt.ll
◆-load 加载指定的Pass进行优化(.so文件)
◆-hlw LLVM Pass中自定义的参数,用来指定使用Pass的哪些功能,这个例子就是启动高等级混淆。
◆-S同前面clang参数的作用相同,生成可阅读文本。
流程
test.c --> test.ll --> test_opt.ll (可选)-> test
clang fileName_opt.ll -o fileName
02.
编写一个简单的PASS入门
◆Build存放生成的Pass
◆Test文件夹存放测试程序
◆Transforms/include存放LLVM Pass项目的头文件
◆Transforms/src 存放Pass源码
◆Transforms/CMakeLists.txt 整个CMake项目的配置文件。
test.sh
cd ./Build
cmake ../Transforms //对transforms的项目进行编译,得到编译后的`.so`文件
make //得到pass.so
cd ../Test
clang -S -emit-llvm TestProgram.cpp -o TestProgram.ll //clang将源代码转换为中间代码
opt -load ../Build/LLVMObfuscator.so -hlw -S TestProgram.ll -o TestProgram_hlw.ll ////opt加载so文件,用hlw pass进行优化
clang TestProgram_hlw.ll -o TestProgram_hlw //将优化后的中间代码编译为可执行文件
./TestProgram_hlw //运行可执行文件
Test/Testprogram.cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
int func1(int a,int b);
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",func1(1,2));
return 0;
}int func1(int a,int b)
{
int result;
if(a>0){
result=a+b;
}
else{
result=a-b;
}
return result;
}
Transforms/Helloworld.cpp
前面提到的在FunctionPass运行时,会对程序中的每个函数执行runOnFunction函数
//在此编写LLVM Pass的代码 //导入llvm所需的头文件
#include "llvm/Pass.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Function.h"
#include "llvm/Support/raw_ostream.h" //和输入输出有关
using namespace llvm;
//定义我们自己的命名空间
namespace{
//首先需要继承FunctionPass
class HelloWorld : public FunctionPass{ //自定义的HelloWorld类继承FunctionPass
public:
static char ID;
HelloWorld() : FunctionPass(ID) {} //HelloWorld的构造函数
bool runOnFunction(Function &F);
};
}
bool HelloWorld::runOnFunction(Function &F){
//todo 对函数的分析或修改代码
outs() << "Hello," << F.getName() << "\n"; //获取llvm的输出流
}
char HelloWorld::ID = 0;
//注册
static RegisterPass<HelloWorld> X("hlw","对Pass的描述"); //注册该Pass
CMakeLists.txt
# 参考官方文档:https://llvm.org/docs/CMake.html#developing-llvm-passes-out-of-source
project(OLLVM++) #项目名称 OLLVM++
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.13.4) #和llvm有关的环境变量
find_package(LLVM REQUIRED CONFIG) list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH "${LLVM_CMAKE_DIR}")
include(AddLLVM)
include_directories("./include") # 包含 ./include 文件夹中的头文件
separate_arguments(LLVM_DEFINITIONS_LIST NATIVE_COMMAND ${LLVM_DEFINITIONS})
add_definitions(${LLVM_DEFINITIONS_LIST})
include_directories(${LLVM_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_llvm_library( LLVMObfuscator MODULE #注册LLVMObfuscator模块
src/HelloWorld.cpp #添加项目的源代码文件
)
得到的.ll文件,和汇编语言很很相似
03.
OLLVM控制流平坦化
简单介绍平坦化
顾名思义,就是让流程图平坦、扁平
源码
https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/blob/llvm-4.0/lib/Transforms/Obfuscation/Flattening.cpp
正常的程序执行流程图
基本块1
基本块2
if(condition){
基本块3
}else{
基本块4
}
基本块5
基本块6
控制流平坦化之后的
基本块1
switchVar = 2;
while(true){
switch(switchVar){
case 2:
基本块2
switchVar = condition ? 3 : 4;
case 3:
基本块3
switchVar = 5
case 4:
基本块4
switchVar = 5
case 5:
基本块5
switchVar = 6
case 6:
基本块6
goto end;
}
}
end:
pass编写
下面开始控制流平坦化pass的编写,demo还是上面的Testprogram.cpp
编译成IR
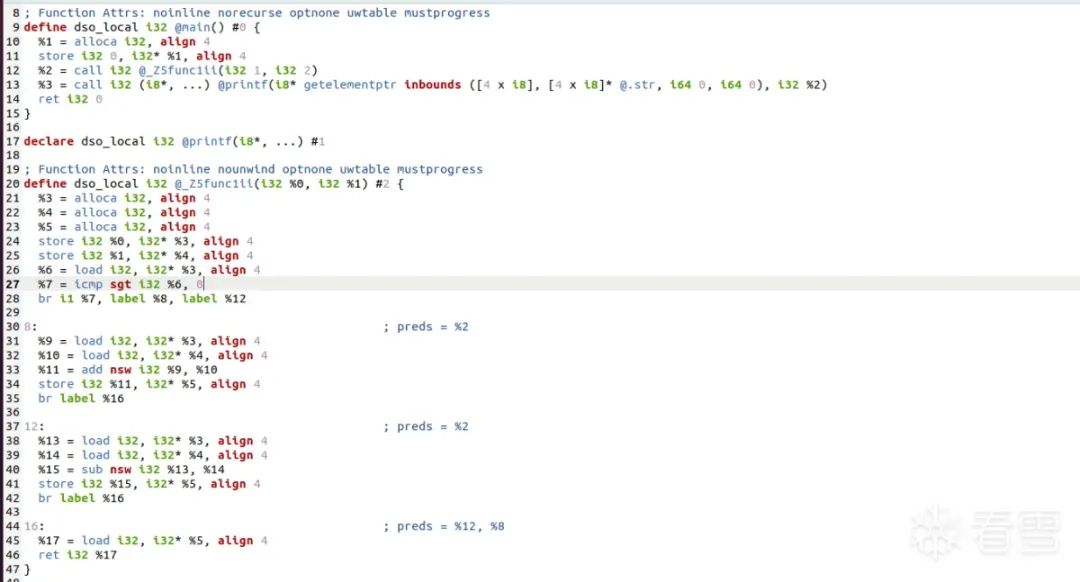
clang -S -emit-llvm TestProgram.cpp -o TestProgram.ll
对应的流程图
保存所有基本块
首先将本function中除了第一个BasicBlock的所有块保存到vector容器中,接着对bb的数量进行判断,当bb数量小于等于1时,flatten函数会直接退出并返回false。
vector<BasicBlock*> origBB; //save all
for(Function::iterator i=f->begin();i!=f->end();++i){
//address of bb
BasicBlock *tmp=&*i;
origBB.push_back(tmp);
BasicBlock *bb=&*i;
//if have invoke eg:call function
if(isa<InvokeInst>(bb->getTerminator())){
return false;
}
}
//outs() << "Hello," << origBB.size() << "\n";
//printf("\nsizeof origbb\n");
if(origBB.size()<=1){
return false;
}
接着通过F-begin获取本function的第一个bb,并将其从vector中擦除
// Remove first BB
origBB.erase(origBB.begin());
分离第一个基本块
获取第一个BB进行特殊处理,首先会判断结尾是不是分支指令(必须是条件分支),如果是则把跳转的两个IR指令(类似汇编语言的cmp和jz jnz)单独分离作为一个基本块。
//Get a pointer on the first BB
Function::iterator tmp=f->begin();
BasicBlock* entryBB=&*tmp; //if first bb have if
BranchInst*br=NULL;
if(isa<BranchInst>(entryBB->getTerminator())){
//change type
br=cast<BranchInst>(entryBB->getTerminator());
}
//if
if((br!=NULL&&br->isConditional())||
entryBB->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors()>1){
//cmp a,b ; jz lab ;xxx 这里则指向了xxx
BasicBlock::iterator i=entryBB->end();
//point at jz
--i;
if(entryBB->size()>1){
//point at cmp
--i;
}
//split bb from i and new bb named first
BasicBlock *tmpBB=entryBB->splitBasicBlock(i,"first");
// insert firstBB to vector
origBB.insert(origBB.begin(),tmpBB);
}
分割第一个基本块之后
对应的流程图
//erase jump of entry
entryBB->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();
创建三个基本块switch case
然后再第一个bb的末尾创建switchVar并赋予他一个随机的值,接着创建三个新的basicblock块,分别为loopEntry、loopEnd、swDefault,并设置好跳转关系。
//set swtich case
srand(time(0));
int randNumCase=rand();
AllocaInst *swVarPtr = new AllocaInst(int32Type, 0, "swVar.ptr", entryBB);
new StoreInst(ConstantInt::get(int32Type,randNumCase),swVarPtr,entryBB); // creat loopEntry loopEnd swDefault
// name loopEntry , belong to BasicBlock f , location entryBB (end)
BasicBlock *loopEntry= BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEntry", f, entryBB);
BasicBlock *loopEnd= BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEnd", f, entryBB);
BasicBlock *swDefault=BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(),"swtichDefault",f,loopEnd);
entryBB->moveBefore(loopEntry);
//create swVar at loopEntry
LoadInst *swVar = new LoadInst(int32Type, swVarPtr, "swVar", false, loopEntry);
//entryBB-->loopEntry swDefault-->loopEnd
BranchInst::Create(loopEntry,entryBB);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd,swDefault);
BranchInst::Create(loopEntry,loopEnd);
//create switch at loopEntry
SwitchInst *switchI=SwitchInst::Create(swVar,swDefault,0,loopEntry);
对应的流程图
将块加入swtch case语句
下面开始将vector中的每一个bb都添加到switch-case语句中,每一个bb对应一个case
for(vector<BasicBlock*>::iterator b=origBB.begin();b!=origBB.end();++b)
{
BasicBlock *i=*b;
ConstantInt *numCase=NULL; i->moveBefore(loopEnd);
//case numCase : b i
numCase=cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(int32Type,randNumCase));
switchI->addCase(numCase,i);
randNumCase=rand();
}
添加全部的basicblock块之后,还需要修复跳转关系,使得每个bb执行完之后,会重新设置switchVar,从而顺利跳转到下一个case。
分为三类来处理:
◆第一类为没有后继的,一般是以retn、call、exit结尾的基本块,不需要处理。
◆第二类,有一个后继,也就是非条件跳转,需要在末尾更新switchVar
◆第三类,有两个后继,也就是以条件跳转结尾的基本块,这类基本块需要插入select指令,类似于C语言的三元运算符
for(vector<BasicBlock*>::iterator b=origBB.begin();b!=origBB.end();++b)
{
BasicBlock *i=*b;
ConstantInt *numCase=NULL; i->moveBefore(loopEnd);
//case numCase : b i
numCase=cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(int32Type,randNumCase));
switchI->addCase(numCase,i);
randNumCase=rand();
}
//three scenarios
for(vector<BasicBlock*>::iterator b=origBB.begin();b!=origBB.end();++b)
{
BasicBlock*i=*b;
ConstantInt*numCase=NULL;
//no successor
if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors()==0)
{
continue;
}
//non-conditional jump
if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors()==1)
{
BasicBlock*succ=i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0);
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();
numCase=switchI->findCaseDest(succ);
//set value at end
new StoreInst(numCase,swVarPtr,i);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd,i);
continue;
}
//conditional jump
if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors()==2)
{
ConstantInt *numCaseTrue=switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0));
ConstantInt *numCaseFalse=switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1));
BranchInst *br=cast<BranchInst>(i->getTerminator());
//%sel = select i1 %condition, %numCaseTrue,%numCaseFalse
SelectInst*sel=SelectInst::Create(
br->getCondition(),
numCaseTrue,
numCaseFalse,
"",
i->getTerminator());
i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();
//update
new StoreInst(sel,swVarPtr,i);
BranchInst::Create(loopEnd,i);
}
}
然后我们就能得到
对应的流程图就是
太糊了我画了一个
拖入ida看看效果
Next
下一篇的内容大概是控制流平坦化的对抗和魔改。
参考 ❤
https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/blob/llvm-4.0/lib/Transforms/Obfuscation/Flattening.cpp
https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-279624.htm
https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-282305.htm
https://www.cnblogs.com/BobHuang/p/17640378.html
https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-255130.htm
https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-266082.htm
看雪ID:马先越
https://bbs.kanxue.com/user-home-984774.htm
# 往期推荐
2、Fuzzing原理探究:afl,afl++背后的变异算法
球分享
球点赞
球在看
点击阅读原文查看更多
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh