
2019-08-01 15:07:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:195 收藏
Author: mengchen@Knownsec 404 Team
Date: August 1, 2019
Chinese Version: https://paper.seebug.org/996/
1. Introduction
TYPO3 is a free and open-source Web content management system written in PHP. It is released under the GNU General Public License.
On July 16, 2019, the RIPS team revealed a vulnerability(CVE-2019-12747) detail for Typo3 CMS. It allows users to execute any PHP code in the back end.
Affected Versions: 8.0.0-8.7.26 and 9.0.0-9.5.7
2. Test Environment
Nginx/1.15.8
PHP 7.3.1 + xdebug 2.7.2
MySQL 5.7.27
Typo3 9.5.73. TCA
Before this , we need to know the TCA(Table Configuration Array) of Typo3. In the code of Typo3, it is represented as $GLOBALS['TCA'].
In Typo3, TCA is an extension of the definition of the database table. It defines which tables can be edited in the back end of Typo3. It has 3 main functions :
- Represents the relationship between tables
- Define the fields and layouts displayed in the back end
- Verifies fields
The two exploits of this vulnerability are in the CoreEngine and FormEngine structures, andTCA is the bridge between them. It tells the two core structures how to represent tables, fields and relationship.
Table entries (first level) :
$GLOBALS['TCA']['pages'] = [
...
];
$GLOBALS['TCA']['tt_content'] = [
...
];pages and tt_content are the tables in the database.
The next level is an array that defines how to process a table.
$GLOBALS['TCA']['pages'] = [
'ctrl' => [
....
],
'interface' => [
....
],
'columns' => [
....
],
'types' => [
....
],
'palettes' => [
....
],
];Above is all we need to know about for this analysis. More detailed information can be found in the Official Handbook.
4. Vulnerability analysis
The process of exploiting the entire vulnerability is not particularly complicated. It requires two steps. In the first step, the variable is overwritten to cause the deserialized input to be controllable. The second step is to construct a special deserialized string to write shell. The second step is the old routine. All we need to do is to find a class that can write files in the magic method. The fun part of this vulnerability is the variable covering, and the way to get into the vulnerability of the two components is also slightly different. Let's take a look at this vulnerability.
4.1 Patch analysis
From the official Notification of Typo3 we can see that the vulnerability affects two components - Backend & Core API (ext :backend, ext:core). We can find records on GitHub:
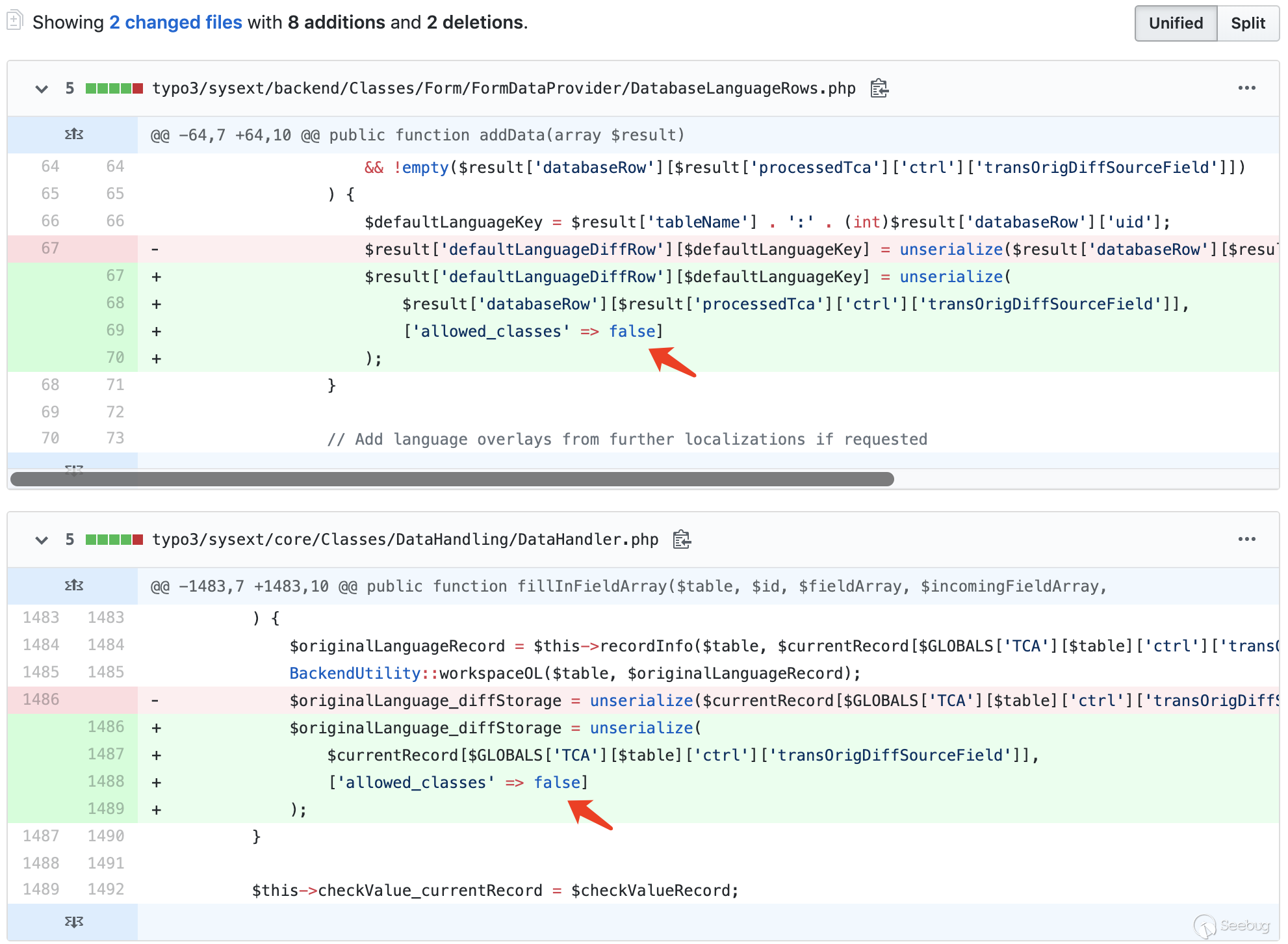
Obviously, the patch disables the deserialization operations in DatabaseLanguageRows.php of backend and DataHandler.php in core.
4.2 Backend ext vulnerability point exploit process analysis
Look at the vulnerability points in the Backend component based on the location of the patch.
Path: typo3/sysext/backend/Classes/Form/FormDataProvider/DatabaseLanguageRows.php:37
public function addData(array $result)
{
if (!empty($result['processedTca']['ctrl']['languageField'])
&& !empty($result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField'])
) {
$languageField = $result['processedTca']['ctrl']['languageField'];
$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord = $result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField'];
if (isset($result['databaseRow'][$languageField]) && $result['databaseRow'][$languageField] > 0
&& isset($result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord]) && $result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord] > 0
) {
// Default language record of localized record
$defaultLanguageRow = $this->getRecordWorkspaceOverlay(
$result['tableName'],
(int)$result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord]
);
if (empty($defaultLanguageRow)) {
throw new DatabaseDefaultLanguageException(
'Default language record with id ' . (int)$result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord]
. ' not found in table ' . $result['tableName'] . ' while editing record ' . $result['databaseRow']['uid'],
1438249426
);
}
$result['defaultLanguageRow'] = $defaultLanguageRow;
// Unserialize the "original diff source" if given
if (!empty($result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField'])
&& !empty($result['databaseRow'][$result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']])
) {
$defaultLanguageKey = $result['tableName'] . ':' . (int)$result['databaseRow']['uid'];
$result['defaultLanguageDiffRow'][$defaultLanguageKey] = unserialize($result['databaseRow'][$result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']]);
}
//......
}
//......
}
//......
}Many classes inherit the FormDataProviderInterface interface, so static analysis to find out who called the DatabaseLanguageRows addData method is not realistic. But according to the demo video in the article, we can know that there is a vulnerability point in the function of modifying the page in the website. Add a breakpoint to the addData method and send a normal request to modify the page.
When the program breaks at the addData method of DatabaseLanguageRows, we can get the call chain.
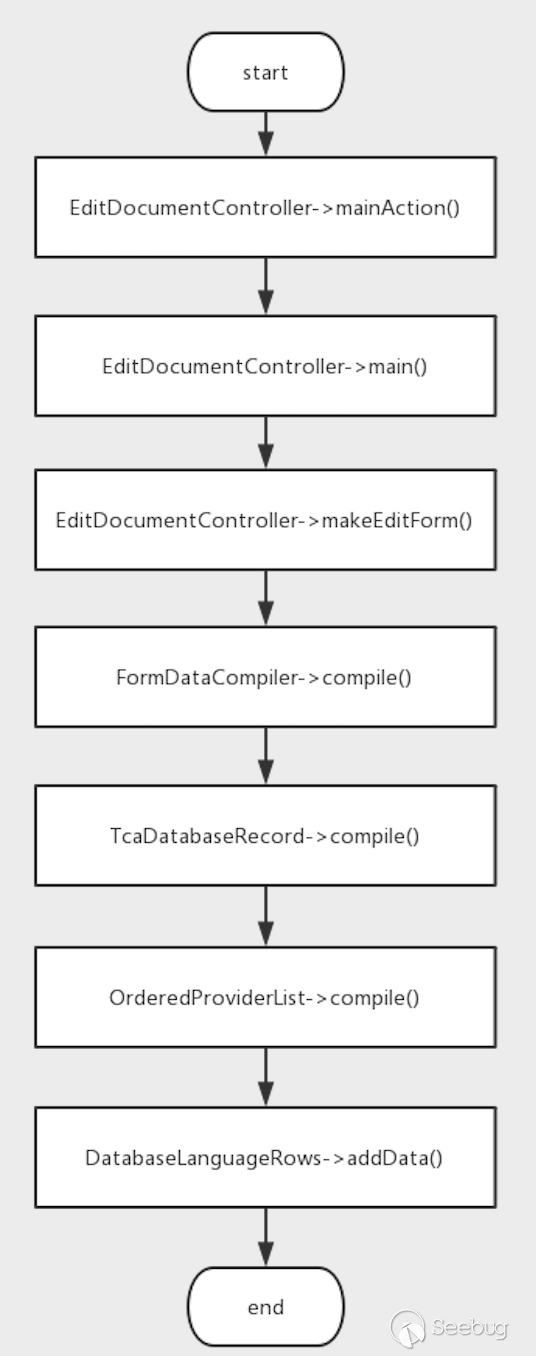
In DatabaseLanguageRows of this addData, only one $result array is passed in, and the target of the deserialization operation is a value in $result['databaseRow']. Depending on the name of the variable, it may be the value obtained from the database . Continue to analyze it.
Go to the compile method of OrderedProviderList.
Path: typo3/sysext/backend/Classes/Form/FormDataGroup/OrderedProviderList.php:43
public function compile(array $result): array
{
$orderingService = GeneralUtility::makeInstance(DependencyOrderingService::class);
$orderedDataProvider = $orderingService->orderByDependencies($this->providerList, 'before', 'depends');
foreach ($orderedDataProvider as $providerClassName => $providerConfig) {
if (isset($providerConfig['disabled']) && $providerConfig['disabled'] === true) {
// Skip this data provider if disabled by configuration
continue;
}
/** @var FormDataProviderInterface $provider */
$provider = GeneralUtility::makeInstance($providerClassName);
if (!$provider instanceof FormDataProviderInterface) {
throw new \UnexpectedValueException(
'Data provider ' . $providerClassName . ' must implement FormDataProviderInterface',
1485299408
);
}
$result = $provider->addData($result);
}
return $result;
}We can see that in the foreach loop, the program dynamically instantiates the class in $this->providerList, then calls its addData method, and uses $result as the argument to the method.
Before calling the DatabaseLanguageRows class, the addData method of the class shown in the figure is called.
After querying the manual and analyzing the code, we can know that in the DatabaseEditRow class, the data in the database table is read by calling the addData method and stored in the $result['databaseRow'] variable.
Path:typo3/sysext/backend/Classes/Form/FormDataProvider/DatabaseEditRow.php:32
public function addData(array $result)
{
if ($result['command'] !== 'edit' || !empty($result['databaseRow'])) {
return $result;
}
$databaseRow = $this->getRecordFromDatabase($result['tableName'], $result['vanillaUid']); // Get records in the database
if (!array_key_exists('pid', $databaseRow)) {
throw new \UnexpectedValueException(
'Parent record does not have a pid field',
1437663061
);
}
BackendUtility::fixVersioningPid($result['tableName'], $databaseRow);
$result['databaseRow'] = $databaseRow;
return $result;
}The addData method of the DatabaseRecordOverrideValues class is called later.
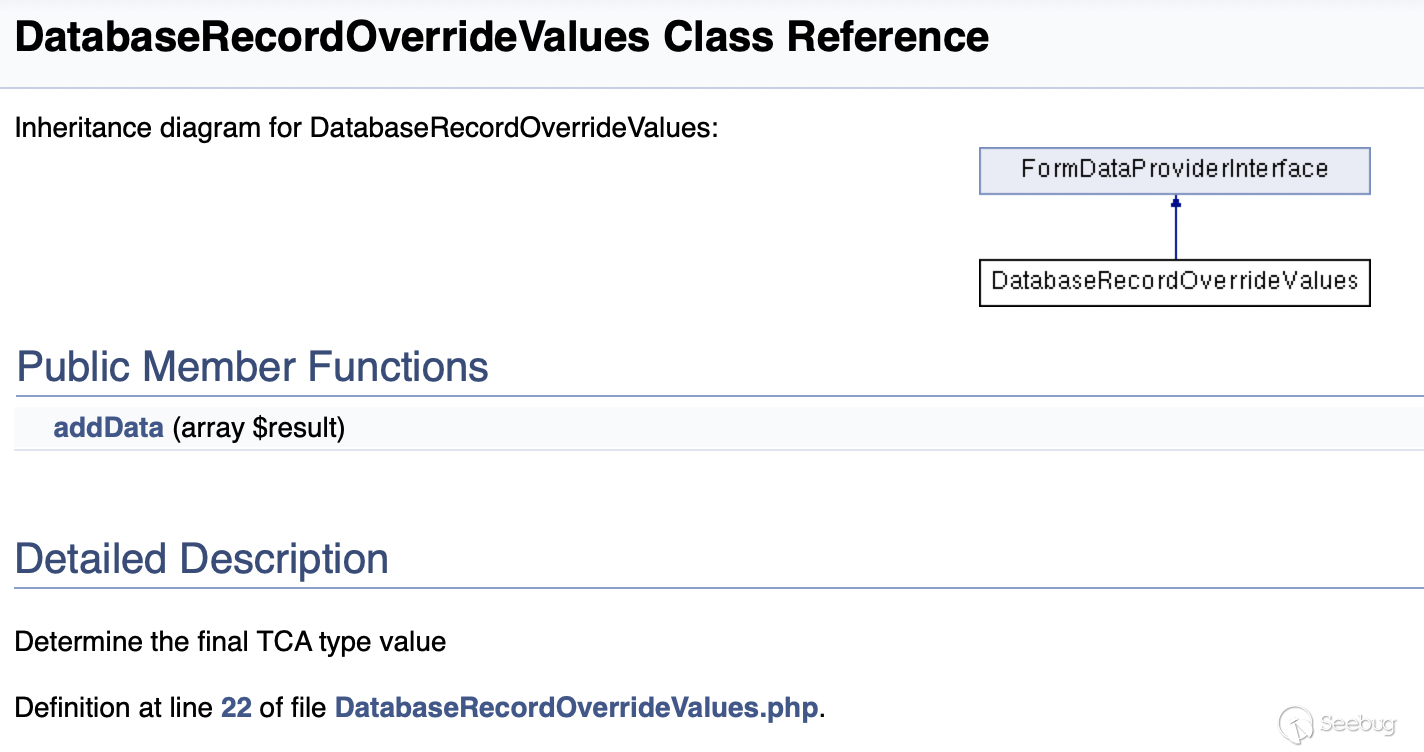
Path: typo3/sysext/backend/Classes/Form/FormDataProvider/DatabaseRecordOverrideValues.php:31
public function addData(array $result)
{
foreach ($result['overrideValues'] as $fieldName => $fieldValue) {
if (isset($result['processedTca']['columns'][$fieldName])) {
$result['databaseRow'][$fieldName] = $fieldValue;
$result['processedTca']['columns'][$fieldName]['config'] = [
'type' => 'hidden',
'renderType' => 'hidden',
];
}
}
return $result;
}Here, the key-value pairs in $result['overrideValues'] are stored in $result['databaseRow']. If $result['overrideValues'] is controllable, then through this class, we can control the value of $result['databaseRow'].
Go ahead and see where the value of $result comes from.
Path: typo3/sysext/backend/Classes/Form/FormDataCompiler.php:58
public function compile(array $initialData)
{
$result = $this->initializeResultArray();
//......
foreach ($initialData as $dataKey => $dataValue) {
// ......
$result[$dataKey] = $dataValue;
}
$resultKeysBeforeFormDataGroup = array_keys($result);
$result = $this->formDataGroup->compile($result);
// ......
}Obviously, the data in $initialData is stored in $result by calling the compile method of the FormDataCompiler class.
Go forward and we will come to the makeEditForm method in the EditDocumentController class.
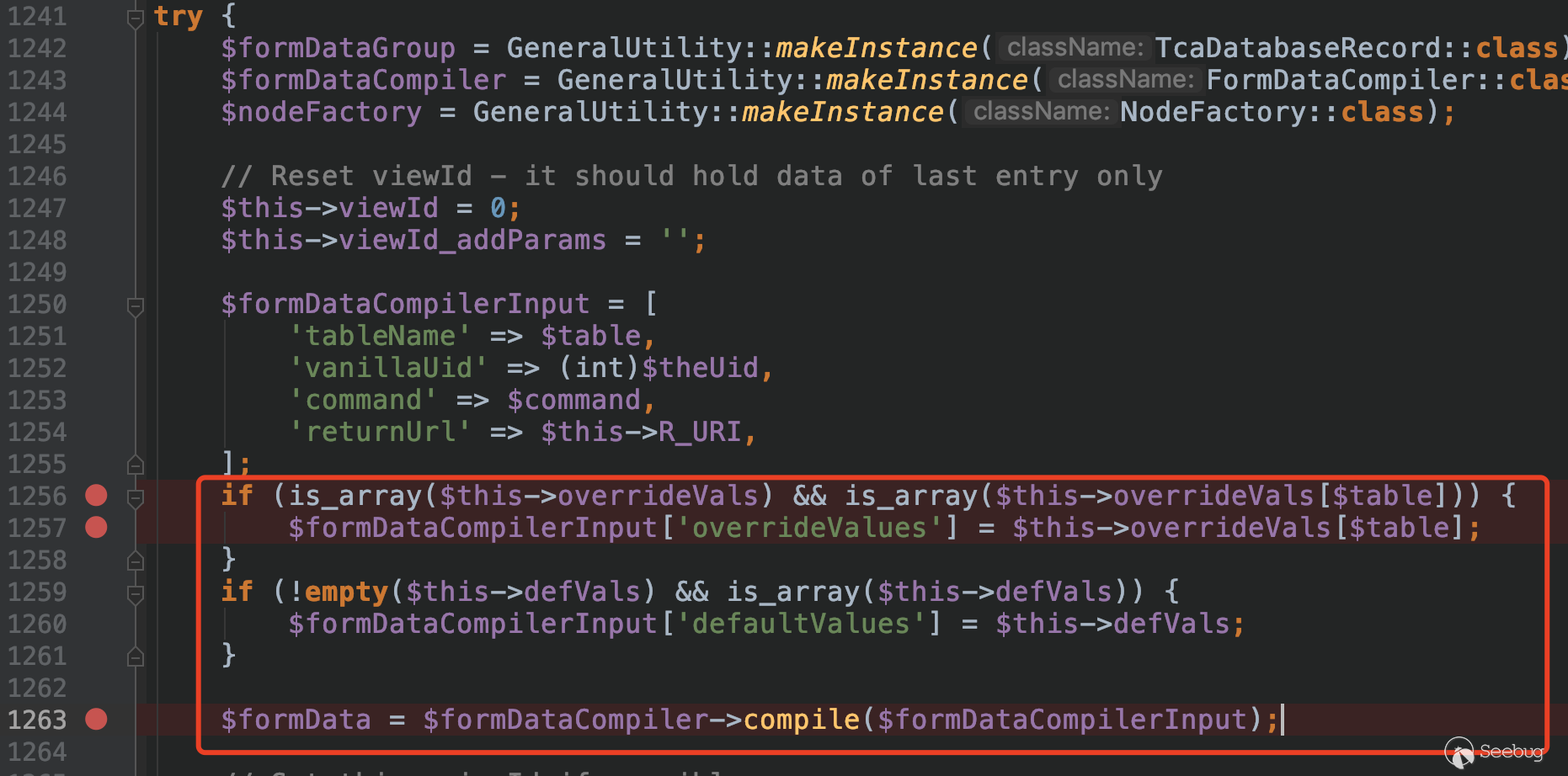
Here, $formDataCompilerInput['overrideValues'] gets the data from $this->overrideVals[$table].
While the value of $this->overrideVals is set in the method preInit, which gets the key-value pairs in the form passed in via the POST request.
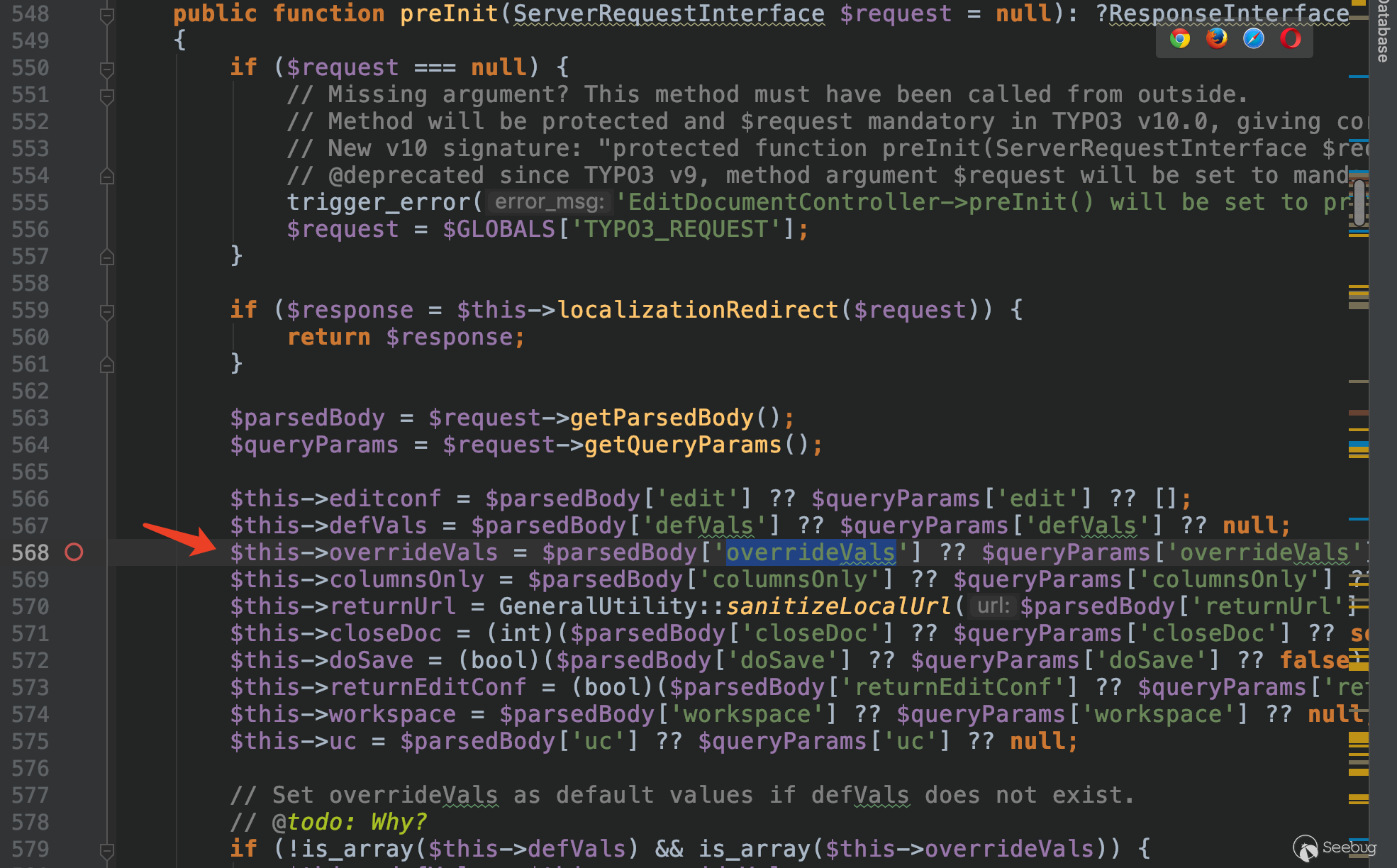 In this way, we can control the deserialized string during this request.
In this way, we can control the deserialized string during this request.
Submit any input in the form of an array. It will be parsed in the back end code, and then the back end will judge and process it according to TCA.
For example, we added a form item named a[b][c][d] in the submission form and set its value to be 233.
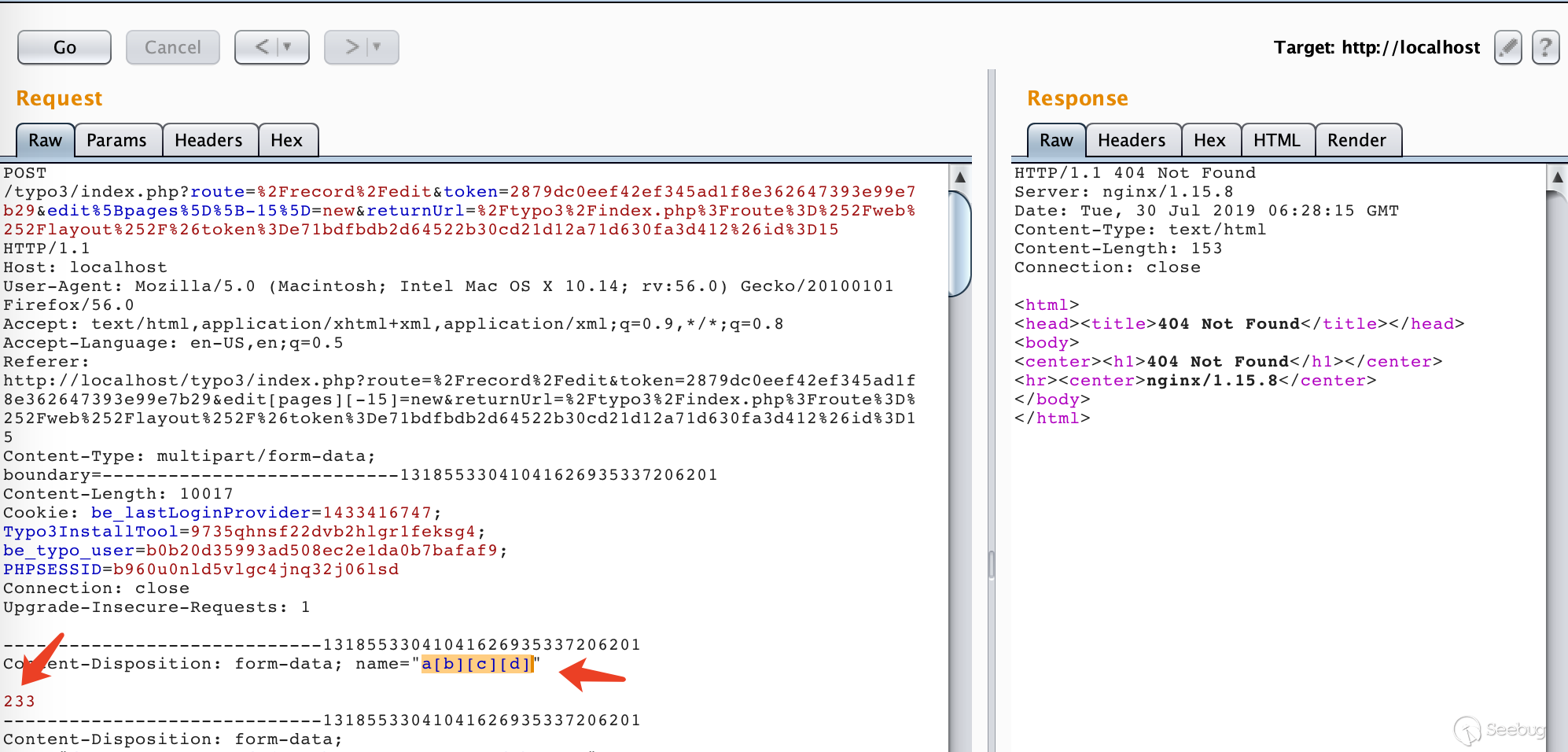
Add a breakpoint in the controller EditDocumentController.php of the edit form, then submit the request.
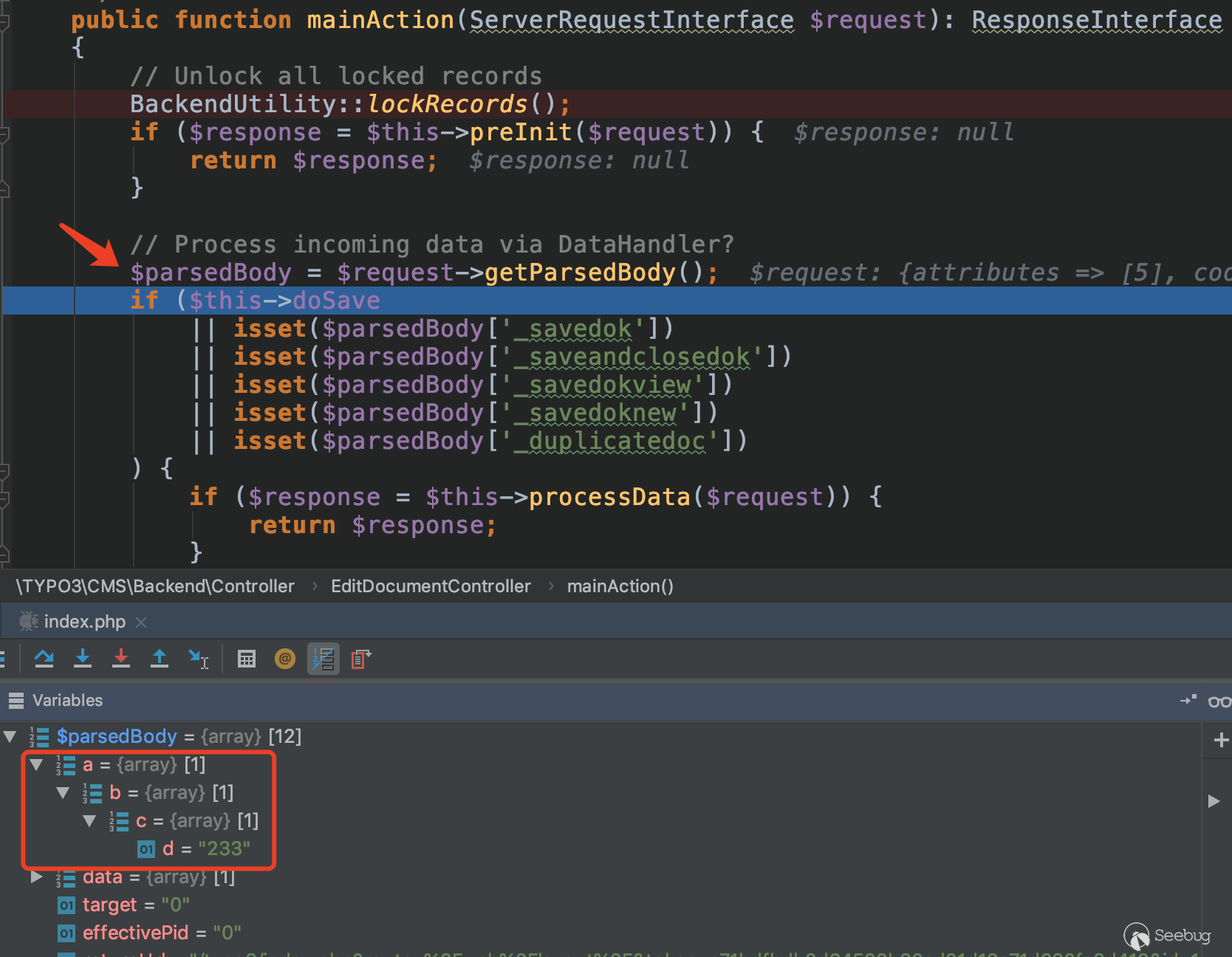
We can see that the passed key-value pairs become parsed arrays after being parsed by the getParsedBody method, and there are no restrictions.
We only need to pass in the overrideVals array in the form. For the specific key-value pairs in this array, you need to see which key value of $result['databaseRow'] is taken when deserializing.
if (isset($result['databaseRow'][$languageField]) && $result['databaseRow'][$languageField] > 0 && isset($result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord]) && $result['databaseRow'][$fieldWithUidOfDefaultRecord] > 0) {
//......
if (!empty($result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']) && !empty($result['databaseRow'][$result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']])) {
$defaultLanguageKey = $result['tableName'] . ':' . (int) $result['databaseRow']['uid'];
$result['defaultLanguageDiffRow'][$defaultLanguageKey] = unserialize($result['databaseRow'][$result['processedTca']['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']]);
}
//......
}In order to enter the deserialization , we also need to achieve the above condition if . We can debug it dynamically and then the below is called in the if statement.
$result['databaseRow']['sys_language_uid']
$result['databaseRow']['l10n_parent']Called later in deserialization is:
$result['databaseRow']['l10n_diffsource']Therefore, we only need to add three parameters to the request form.
overrideVals[pages][sys_language_uid] ==> 4
overrideVals[pages][l10n_parent] ==> 4
overrideVals[pages][l10n_diffsource] ==> serialized_shell_datas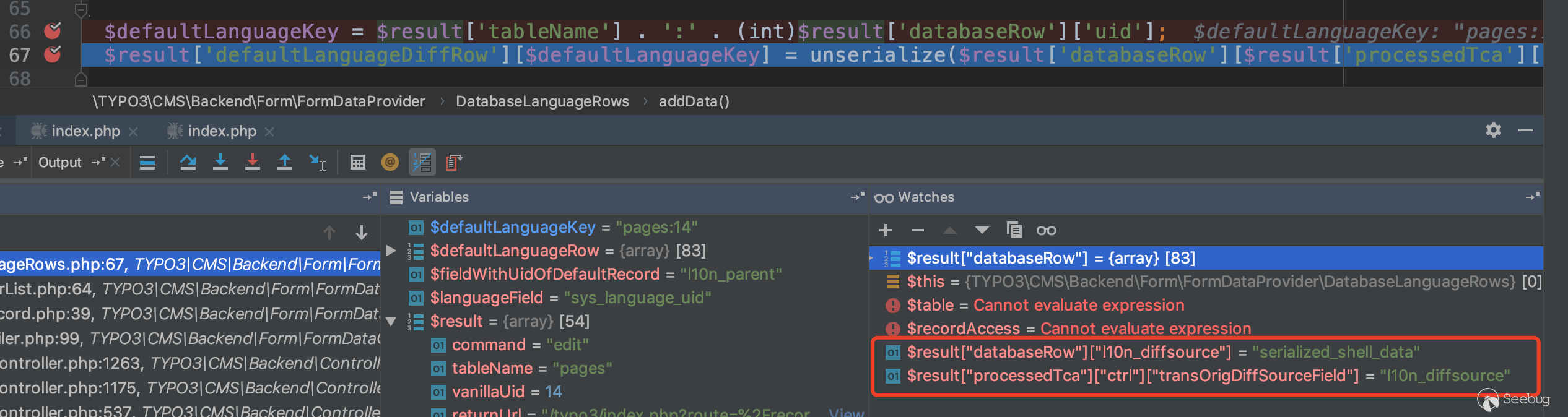
As you can see, our input successfully reached the deserialized position.
4.3 Core ext vulnerability point exploit process analysis
Let us then analyze the vulnerability point in Core.
Path: typo3/sysext/core/Classes/DataHandling/DataHandler.php:1453
public function fillInFieldArray($table, $id, $fieldArray, $incomingFieldArray, $realPid, $status, $tscPID)
{
// Initialize:
$originalLanguageRecord = null;
$originalLanguage_diffStorage = null;
$diffStorageFlag = false;
// Setting 'currentRecord' and 'checkValueRecord':
if (strpos($id, 'NEW') !== false) {
// Must have the 'current' array - not the values after processing below...
$checkValueRecord = $fieldArray;
if (is_array($incomingFieldArray) && is_array($checkValueRecord)) {
ArrayUtility::mergeRecursiveWithOverrule($checkValueRecord, $incomingFieldArray);
}
$currentRecord = $checkValueRecord;
} else {
// We must use the current values as basis for this!
$currentRecord = ($checkValueRecord = $this->recordInfo($table, $id, '*'));
// This is done to make the pid positive for offline versions; Necessary to have diff-view for page translations in workspaces.
BackendUtility::fixVersioningPid($table, $currentRecord);
}
// Get original language record if available:
if (is_array($currentRecord)
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['languageField']
&& $currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['languageField']] > 0
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField']
&& (int)$currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField']] > 0
) {
$originalLanguageRecord = $this->recordInfo($table, $currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField']], '*');
BackendUtility::workspaceOL($table, $originalLanguageRecord);
$originalLanguage_diffStorage = unserialize($currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']]);
}
//......If we want to go into the deserialized position, we need to satisfy the previous if condition.
if (is_array($currentRecord)
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigDiffSourceField']
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['languageField']
&& $currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['languageField']] > 0
&& $GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField']
&& (int)$currentRecord[$GLOBALS['TCA'][$table]['ctrl']['transOrigPointerField']] > 0
) That means the following conditions are required
$currentRecordis an array.- There are
transOrigDiffSourceField,languageField,transOrigPointerFieldfields in the table attribute of$tableinTCA. $table's attributeslanguageFieldandtransOrigPointerFieldhave corresponding values greater than0in$currentRecord.
Let's check the TCA table and there are six tables that meet the second condition.
sys_file_reference
sys_file_metadata
sys_file_collection
sys_collection
sys_category
pagesBut the value of the adminOnly attribute of all sys_* fields is 1, which can only be changed by the administrator. So the only table we can use is pages.
Its attribute value is
[languageField] => sys_language_uid
[transOrigPointerField] => l10n_parent
[transOrigDiffSourceField] => l10n_diffsourceIn the previous code, there is an if-else statement that processes the passed arguments.
From the comments, we can know about the function of each parameter passed in:
- The array
$fieldArrayis the default value, which generally is not we can control . - The array
$incomingFieldArrayis the field you want to set, it will be merged into$fieldArrayif allowed.
And if the if (strpos($id, 'NEW') !== false) condition is satisfied, which means$id is a string and there is a NEW string, it will enter the following operation to get merged.
$checkValueRecord = $fieldArray;
......
if (is_array($incomingFieldArray) && is_array($checkValueRecord)) {
ArrayUtility::mergeRecursiveWithOverrule($checkValueRecord, $incomingFieldArray);
}
$currentRecord = $checkValueRecord;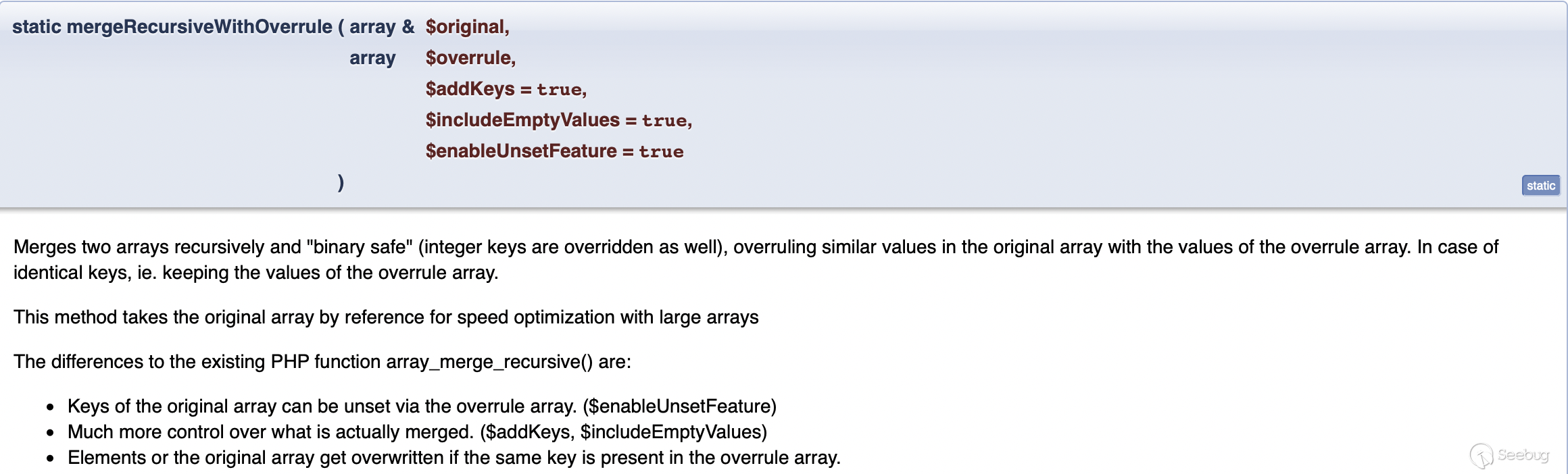
If the above if condition is not met, the value of $currentRecord will be retrieved directly from the database via the recordInfo method and we can't use it later.
To sum up, what we need are
$tableispages$idis a string and there is aNEWstringpayloadshould exist in$incomingFieldArray
Next we see where the function is called.
Through the global search, we only found one place, which was called in the process_datamap method at typo3/sysext/core/Classes/DataHandling/DataHandler.php:954.
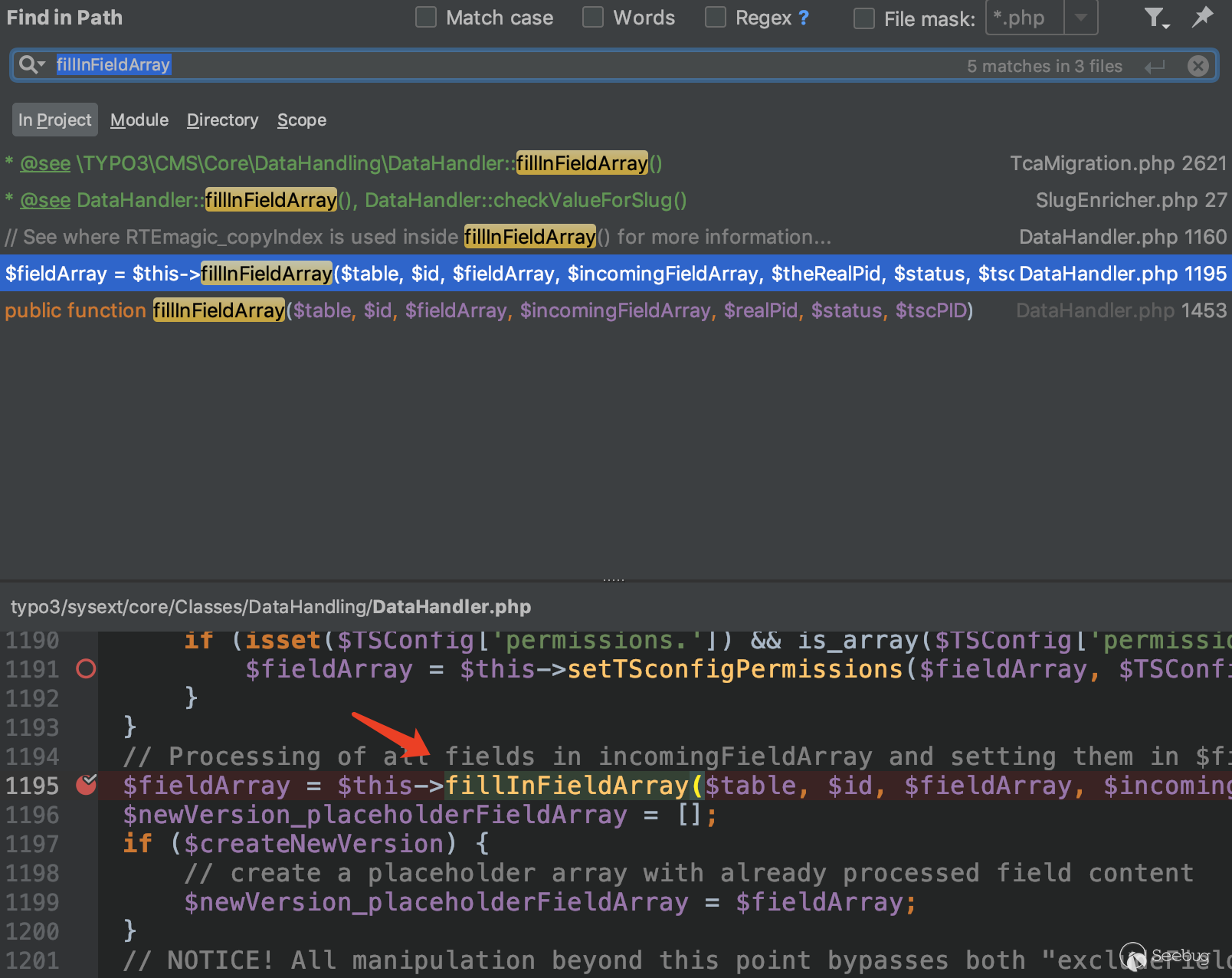
In the whole project, there are too many places to call process_datamap. Try to use xdebug dynamic debugging to find the call chain. From the analysis article of the RIPS team combined with the above analysis of the table name, we can know that the vulnerability point is in the function of creating page.
The next step is to find the mainAction method from EditDocumentController.php to the call chain of the fillInFieldArray method we analyzed earlier.
Try to create a new page in the website, then set a breakpoint at the location of the call fillInFieldArray. After sending the request, we get the call chain.
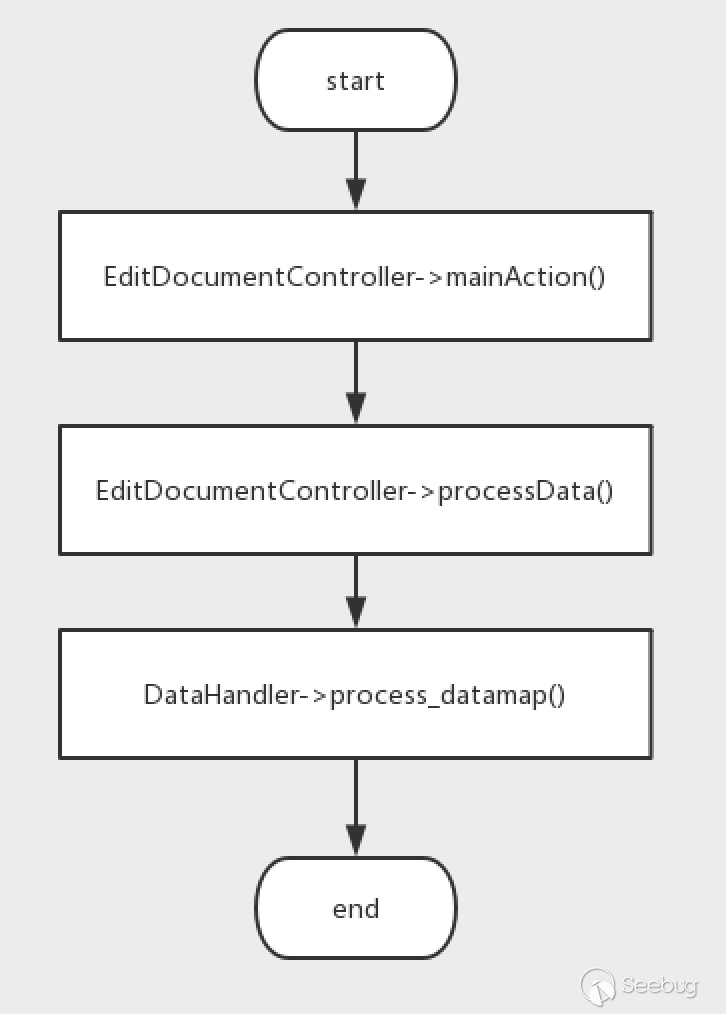
Take a look at the code for the mainAction method.
public function mainAction(ServerRequestInterface $request): ResponseInterface
{
// Unlock all locked records
BackendUtility::lockRecords();
if ($response = $this->preInit($request)) {
return $response;
}
// Process incoming data via DataHandler?
$parsedBody = $request->getParsedBody();
if ($this->doSave
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedok'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_saveandclosedok'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedokview'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedoknew'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_duplicatedoc'])
) {
if ($response = $this->processData($request)) {
return $response;
}
}
//......
}Enter the target $response = $this->processData($request) when the if condition is met.
if ($this->doSave
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedok'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_saveandclosedok'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedokview'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_savedoknew'])
|| isset($parsedBody['_duplicatedoc'])
) When creating a new page, the normal form carries doSave == 1, and the value of doSave is obtained in the method preInit.
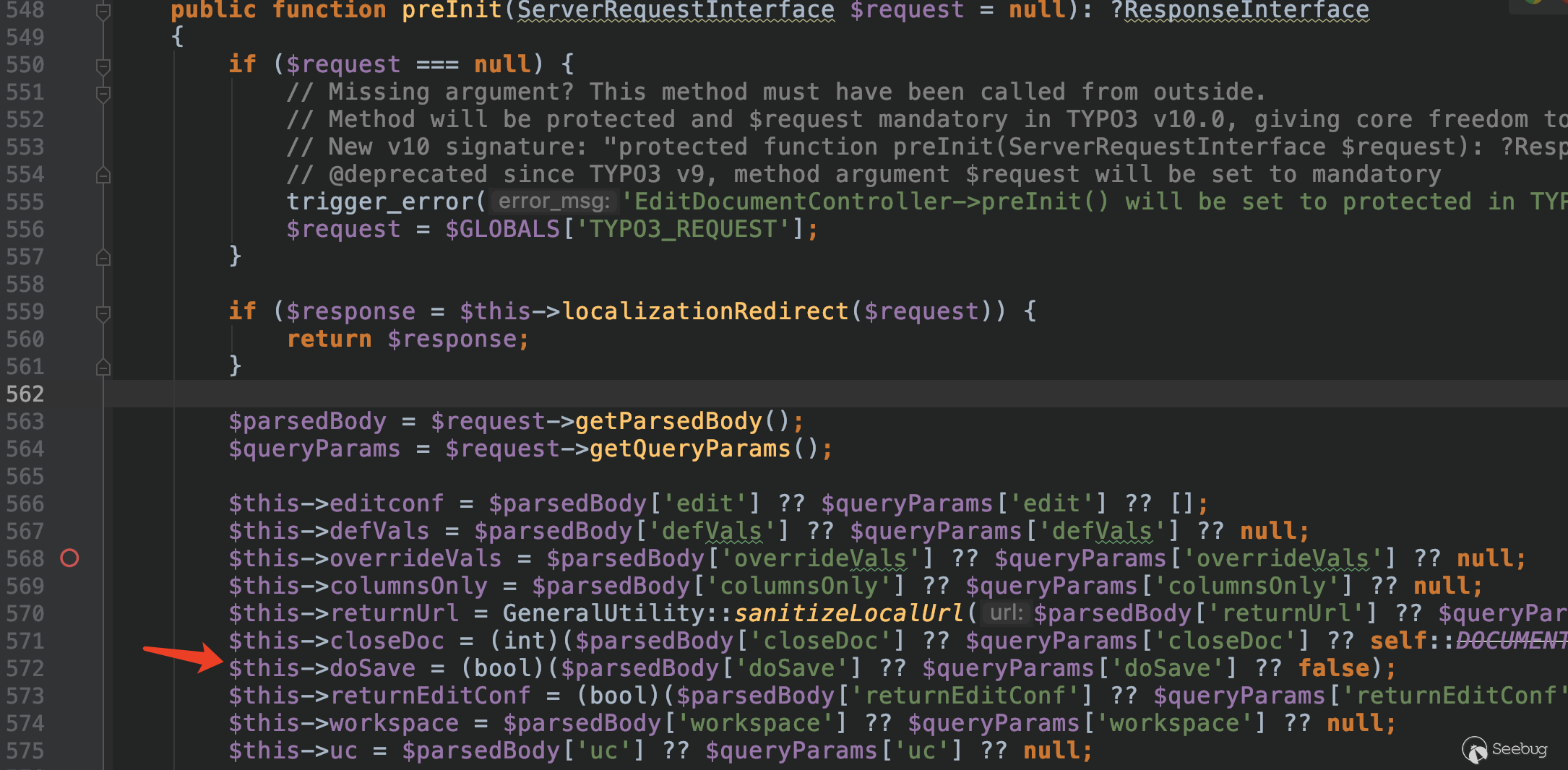
This condition is true by default, and then `request is passed to the processData method.
public function processData(ServerRequestInterface $request = null): ?ResponseInterface
{
// @deprecated Variable can be removed in TYPO3 v10.0
$deprecatedCaller = false;
//......
$parsedBody = $request->getParsedBody(); // Get Post request parameters
$queryParams = $request->getQueryParams(); // Get the Get request parameter
$beUser = $this->getBackendUser(); // Get user data
// Processing related GET / POST vars
$this->data = $parsedBody['data'] ?? $queryParams['data'] ?? [];
$this->cmd = $parsedBody['cmd'] ?? $queryParams['cmd'] ?? [];
$this->mirror = $parsedBody['mirror'] ?? $queryParams['mirror'] ?? [];
// @deprecated property cacheCmd is unused and can be removed in TYPO3 v10.0
$this->cacheCmd = $parsedBody['cacheCmd'] ?? $queryParams['cacheCmd'] ?? null;
// @deprecated property redirect is unused and can be removed in TYPO3 v10.0
$this->redirect = $parsedBody['redirect'] ?? $queryParams['redirect'] ?? null;
$this->returnNewPageId = (bool)($parsedBody['returnNewPageId'] ?? $queryParams['returnNewPageId'] ?? false);
// Only options related to $this->data submission are included here
$tce = GeneralUtility::makeInstance(DataHandler::class);
$tce->setControl($parsedBody['control'] ?? $queryParams['control'] ?? []);
// Set internal vars
if (isset($beUser->uc['neverHideAtCopy']) && $beUser->uc['neverHideAtCopy']) {
$tce->neverHideAtCopy = 1;
}
// Load DataHandler with data
$tce->start($this->data, $this->cmd);
if (is_array($this->mirror)) {
$tce->setMirror($this->mirror);
}
// Perform the saving operation with DataHandler:
if ($this->doSave === true) {
$tce->process_uploads($_FILES);
$tce->process_datamap();
$tce->process_cmdmap();
}
//......
}The code is easy to understand. The data parsed from $request is first stored in $this->data and $this->cmd, and then it instantiates the $tce, and call $ The tce->startmethod to store the incoming data in its own members datamap and cmdmap.
typo3/sysext/core/Classes/DataHandling/DataHandler.php:735
public function start($data, $cmd, $altUserObject = null)
{
//......
// Setting the data and cmd arrays
if (is_array($data)) {
reset($data);
$this->datamap = $data;
}
if (is_array($cmd)) {
reset($cmd);
$this->cmdmap = $cmd;
}
}And the if ($this->doSave === true) condition is also true. Enter the process_datamap method.
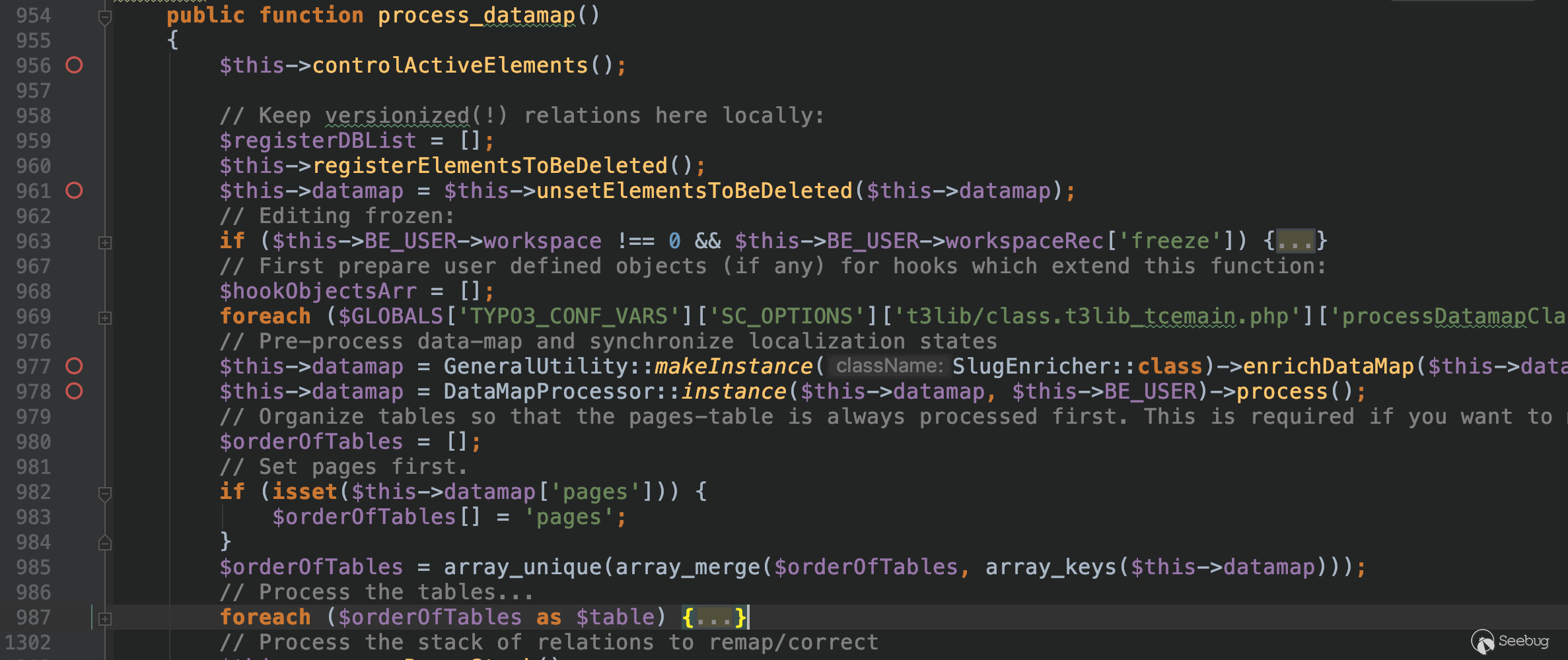
The code is commented for reading. In line 985 , all the key names in datamap are obtained and stored in $orderOfTables, and then into the foreach loop, and this $table is behind Pass in the fillInFieldArray method, so we only need to analyze the loop when $table == pages.
$fieldArray = $this->fillInFieldArray($table, $id, $fieldArray, $incomingFieldArray, $theRealPid, $status, $tscPID);Looking at the code in general, combined with the previous analysis, we need to meet the following conditions:
- The value of
$recordAccessshould betrue payloadin$incomingFieldArraywill not be deleted- The value of
$tableispages NEWstring exists in$id
Since the normal request can be directly called at the call to fillInFieldArray, the first, third, and fourth are valid in the normal request.
According to the previous analysis of the fillInFieldArray method, construct payload and add three key-value pairs to the submitted form.
data[pages][NEW5d3fa40cb5ac4065255421][l10n_diffsource] ==> serialized_shell_data
data[pages][NEW5d3fa40cb5ac4065255421][sys_language_uid] ==> 4
data[pages][NEW5d3fa40cb5ac4065255421][l10n_parent] ==> 4The NEW* string should be modified according to the value generated by the form.
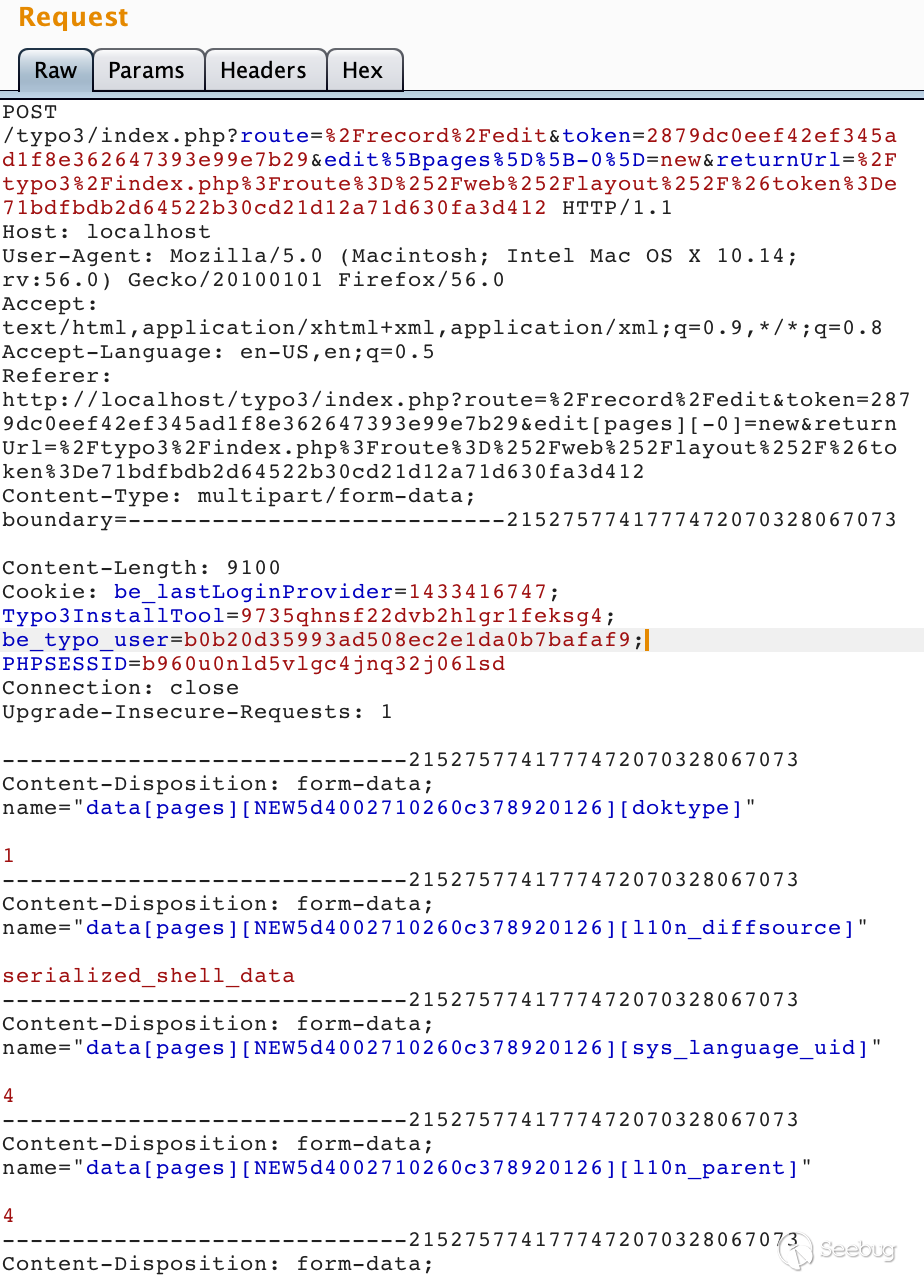
After sending the request, you can still enter fillInFieldArray, and in the $incomingFieldArray parameter, you can see the three key-value pairs we added.
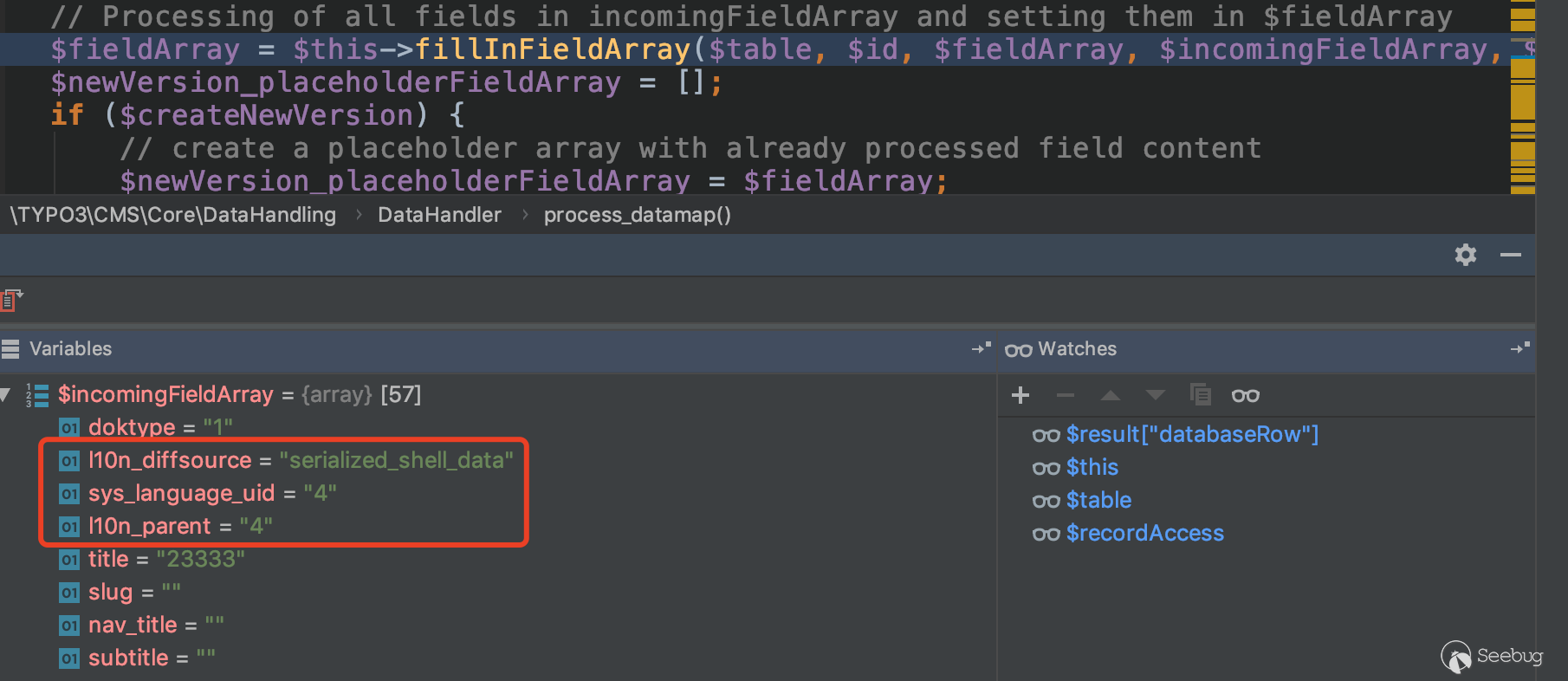
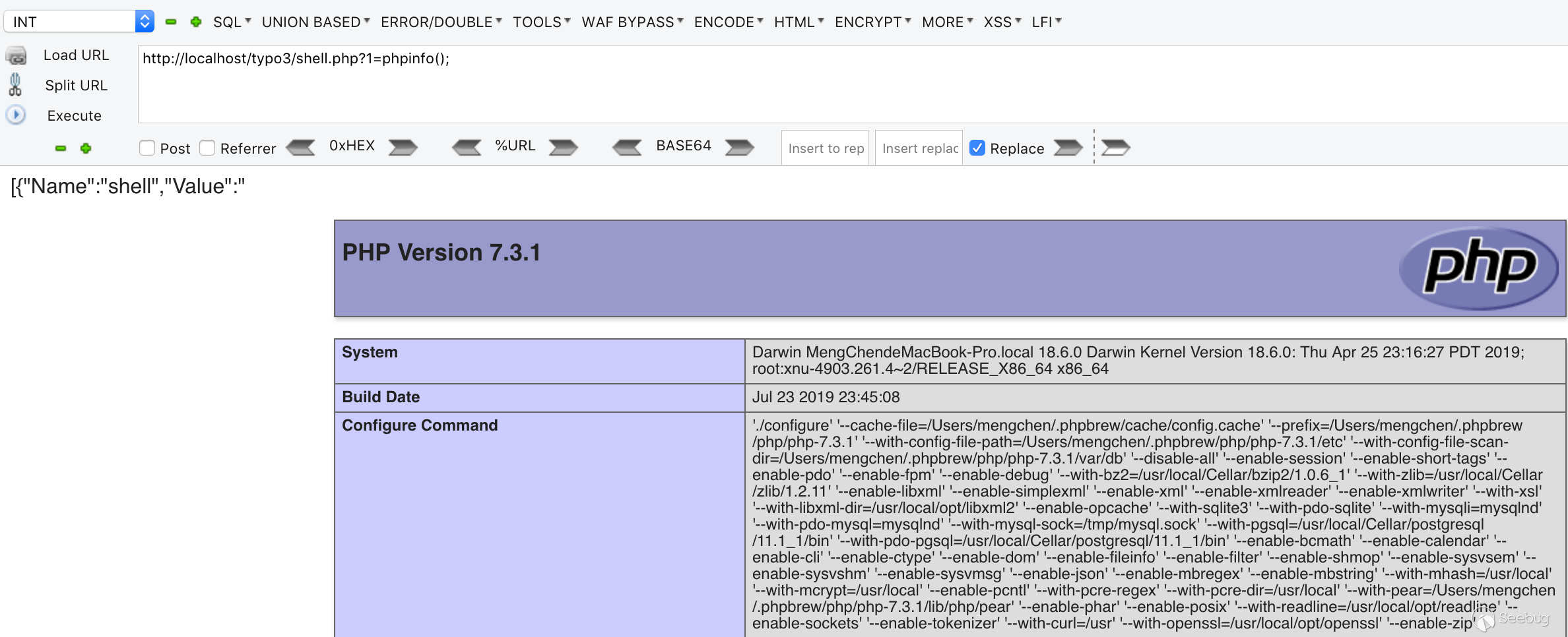
After entering fillInFieldArray, l10n_diffsource will be deserialized. At this point we change its l10n_diffsource to a constructed serialized string in the request, and resend the request to succeed getshell.
5. Conclusion
In fact, the exploitation conditions of this vulnerability is simple. You need to get a valid back end account of typo3, and have the right to edit page.
Moreover, analyzing Typo3 gives me a completely different feeling from other websites. In the process of analyzing the creating and modifying parameters of the page function, I did not find any filtering operations. All parameters in the back end are based on TCA. Only when the input does not meet the definition of TCA will the program throw an exception. The verification of TCA is not strict so it causes by the variable coverage.
The official patching method is not very good. It directly prohibits the deserialization operation, but I personally think the problem is in the previous variable coverage. Especially when using the Backend, we can directly cover the data from the database, and there may still be new problems in the future.
The above is just my view of this vulnerability. Please let me know if there is any mistake in this paper.
6. Reference
- https://blog.ripstech.com/2019/typo3-overriding-the-database/
- https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.unserialize.php
- https://docs.typo3.org/m/typo3/reference-tca/master/en-us/Introduction/Index.html
- https://typo3.org/security/advisory/typo3-core-sa-2019-020/
About Knownsec & 404 Team
Beijing Knownsec Information Technology Co., Ltd. was established by a group of high-profile international security experts. It has over a hundred frontier security talents nationwide as the core security research team to provide long-term internationally advanced network security solutions for the government and enterprises.
Knownsec's specialties include network attack and defense integrated technologies and product R&D under new situations. It provides visualization solutions that meet the world-class security technology standards and enhances the security monitoring, alarm and defense abilities of customer networks with its industry-leading capabilities in cloud computing and big data processing. The company's technical strength is strongly recognized by the State Ministry of Public Security, the Central Government Procurement Center, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China National Vulnerability Database of Information Security (CNNVD), the Central Bank, the Hong Kong Jockey Club, Microsoft, Zhejiang Satellite TV and other well-known clients.
404 Team, the core security team of Knownsec, is dedicated to the research of security vulnerability and offensive and defensive technology in the fields of Web, IoT, industrial control, blockchain, etc. 404 team has submitted vulnerability research to many well-known vendors such as Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, etc. And has received a high reputation in the industry.
The most well-known sharing of Knownsec 404 Team includes: KCon Hacking Conference, Seebug Vulnerability Database and ZoomEye Cyberspace Search Engine.
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/997/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/997/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh