-

-
-
[原创]FART正餐前甜点:ART下几个通用简单高效的dump内存中dex方法
- 47分钟前 177
-
[原创]FART正餐前甜点:ART下几个通用简单高效的dump内存中dex方法
本篇是对FART后续的补充,以及在实现FART过程中偶然发现的几个通用简单高效的脱壳方法,在FART后续的实现中,对内存中整体dex的dump也已经换成该方法来实现。该方法可以说简单高效并且实现也较为简单,可以很轻松通过xposed或者frida等hook框架通过很短的代码便能够实现对加固应用的脱壳。同时,该方法通用性较强。下面结合源码对该方案的原理和实现做简单的介绍。
1.ART类加载执行流程以及ArtMethod类
在上一篇《FART:ART环境下基于主动调用的自动化脱壳方案》文章中对当前ART环境下的通用脱壳方案进行了简单的总结,比如dexhunter、hook OpenMem方案,以及hook DexFile类函数方案等。最后,FART使用了通过classloader来实现对classloader中的dex的dump来脱壳的目的。该方法在获取到最终应用dex运行的classloader后,通过调用在框架层DexFile类中添加的相关jni函数来达到获取内存中整体dex的目的。整个实现过程可以说非常的繁琐,而且需要对Android系统有着非常清楚的认识。同时,该实现过程需要使用大量的反射进而带来了效率较低的问题。(当然,对于逆向来说。效率往往不是最重要的,达成目的才是关键)。在一次阅读源码的过程中,偶然发现了几处通用高效的dump内存中dex的方法。该方法主要涉及到ART环境下的类加载执行流程以及相关的类。
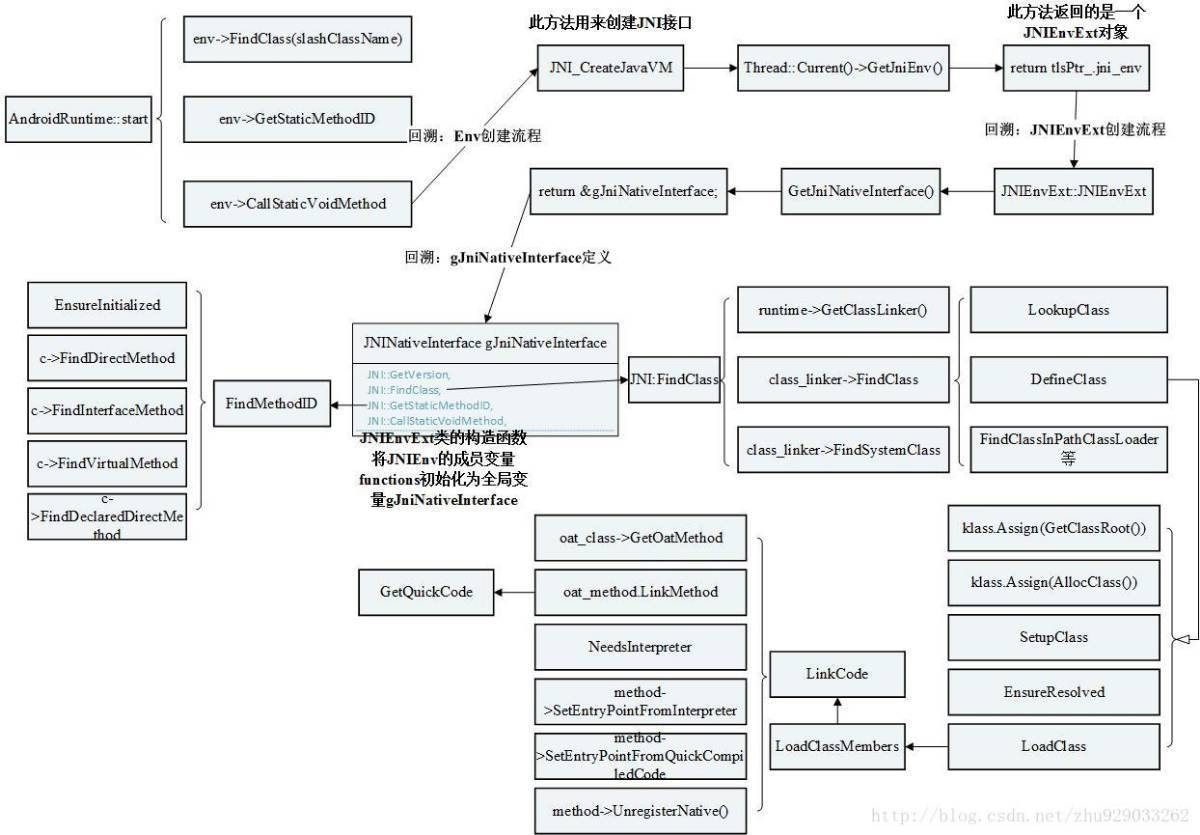
ART环境下函数执行过程中最关键的类便是ArtMethod类,这里以一张前辈绘制的图来说明ART环境下的类加载执行流程(详细内容可以参见文末的参考链接)。

从该图中的右下部分可以看到,当ART在调用函数前需要对函数所属的类完成加载链接,并最终准备好类中的每一个函数对应的ArtMethod对象以供接下来类的初始化以及函数的调用。整个流程可以简单概括为LoadClass->LoadClassMembers->LinkCode。LoadClassMembers函数负责准备接下来类函数执行过程中所需要的变量和函数。该函数首先是遍历内存中dex的相关field并初始化为ArtField对象;遍历类中所有的函数,并初始化函数对应的ArtMethod对象。我们主要看下LoadClassMembers函数:
void ClassLinker::LoadClassMembers(Thread* self, const DexFile& dex_file,
const uint8_t* class_data,
Handle<mirror::Class> klass,
const OatFile::OatClass* oat_class) {
{
// Note: We cannot have thread suspension until the field and method arrays are setup or else
// Class::VisitFieldRoots may miss some fields or methods.
ScopedAssertNoThreadSuspension nts(self, __FUNCTION__);
// Load static fields.
//遍历dex中的相关field
ClassDataItemIterator it(dex_file, class_data);
const size_t num_sfields = it.NumStaticFields();
ArtField* sfields = num_sfields != 0 ? AllocArtFieldArray(self, num_sfields) : nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; it.HasNextStaticField(); i++, it.Next()) {
CHECK_LT(i, num_sfields);
LoadField(it, klass, &sfields[i]);
}
klass->SetSFields(sfields);
klass->SetNumStaticFields(num_sfields);
DCHECK_EQ(klass->NumStaticFields(), num_sfields);
// Load instance fields.
const size_t num_ifields = it.NumInstanceFields();
ArtField* ifields = num_ifields != 0 ? AllocArtFieldArray(self, num_ifields) : nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; it.HasNextInstanceField(); i++, it.Next()) {
CHECK_LT(i, num_ifields);
LoadField(it, klass, &ifields[i]);
}
klass->SetIFields(ifields);
klass->SetNumInstanceFields(num_ifields);
DCHECK_EQ(klass->NumInstanceFields(), num_ifields);
// Load methods.
//遍历dex中的相关Method并初始化
if (it.NumDirectMethods() != 0) {
klass->SetDirectMethodsPtr(AllocArtMethodArray(self, it.NumDirectMethods()));
}
klass->SetNumDirectMethods(it.NumDirectMethods());
if (it.NumVirtualMethods() != 0) {
klass->SetVirtualMethodsPtr(AllocArtMethodArray(self, it.NumVirtualMethods()));
}
klass->SetNumVirtualMethods(it.NumVirtualMethods());
size_t class_def_method_index = 0;
uint32_t last_dex_method_index = DexFile::kDexNoIndex;
size_t last_class_def_method_index = 0;
//首先遍历初始化DirectMethod
for (size_t i = 0; it.HasNextDirectMethod(); i++, it.Next()) {
ArtMethod* method = klass->GetDirectMethodUnchecked(i, image_pointer_size_);
LoadMethod(self, dex_file, it, klass, method);
LinkCode(method, oat_class, class_def_method_index);
uint32_t it_method_index = it.GetMemberIndex();
if (last_dex_method_index == it_method_index) {
// duplicate case
method->SetMethodIndex(last_class_def_method_index);
} else {
method->SetMethodIndex(class_def_method_index);
last_dex_method_index = it_method_index;
last_class_def_method_index = class_def_method_index;
}
class_def_method_index++;
}
//然后遍历初始化VirtualMethod
for (size_t i = 0; it.HasNextVirtualMethod(); i++, it.Next()) {
ArtMethod* method = klass->GetVirtualMethodUnchecked(i, image_pointer_size_);
LoadMethod(self, dex_file, it, klass, method);
DCHECK_EQ(class_def_method_index, it.NumDirectMethods() + i);
LinkCode(method, oat_class, class_def_method_index);
class_def_method_index++;
}
DCHECK(!it.HasNext());
}
self->AllowThreadSuspension();
}有dump整体dex经验比如dalvik下通过hook dexparse或者dvmDexFileOpenPartial来达成定位内存中dex起始地址并dump的方法的人或许在这里便一眼看出该函数是一个脱壳点。该函数的第二个参数 const DexFile& dex_file包含了对当前处理的dex的DexFile对象的引用,通过该引用,我们便可以定位到该dex在内存中的起始地址并达成dump脱壳。同时,也可以看到,在对类中的函数进行遍历并初始化ArtMethod过程中的LoadMethod(self, dex_file, it, klass, method)函数也包含了对DexFile对象的引用,因此这也是一个脱壳点。接下来具体看LoadMethod函数:
void ClassLinker::LoadMethod(Thread* self, const DexFile& dex_file, const ClassDataItemIterator& it,
Handle<mirror::Class> klass, ArtMethod* dst) {
uint32_t dex_method_idx = it.GetMemberIndex();
const DexFile::MethodId& method_id = dex_file.GetMethodId(dex_method_idx);
const char* method_name = dex_file.StringDataByIdx(method_id.name_idx_);
ScopedAssertNoThreadSuspension ants(self, "LoadMethod");
//初始化相关变量
dst->SetDexMethodIndex(dex_method_idx);
dst->SetDeclaringClass(klass.Get());
//初始化CodeItem指针
dst->SetCodeItemOffset(it.GetMethodCodeItemOffset());
dst->SetDexCacheResolvedMethods(klass->GetDexCache()->GetResolvedMethods());
dst->SetDexCacheResolvedTypes(klass->GetDexCache()->GetResolvedTypes());
uint32_t access_flags = it.GetMethodAccessFlags();
if (UNLIKELY(strcmp("finalize", method_name) == 0)) {
// Set finalizable flag on declaring class.
if (strcmp("V", dex_file.GetShorty(method_id.proto_idx_)) == 0) {
// Void return type.
if (klass->GetClassLoader() != nullptr) { // All non-boot finalizer methods are flagged.
klass->SetFinalizable();
} else {
std::string temp;
const char* klass_descriptor = klass->GetDescriptor(&temp);
// The Enum class declares a "final" finalize() method to prevent subclasses from
// introducing a finalizer. We don't want to set the finalizable flag for Enum or its
// subclasses, so we exclude it here.
// We also want to avoid setting the flag on Object, where we know that finalize() is
// empty.
if (strcmp(klass_descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Object;") != 0 &&
strcmp(klass_descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Enum;") != 0) {
klass->SetFinalizable();
}
}
}
} else if (method_name[0] == '<') {
// Fix broken access flags for initializers. Bug 11157540.
bool is_init = (strcmp("<init>", method_name) == 0);
bool is_clinit = !is_init && (strcmp("<clinit>", method_name) == 0);
if (UNLIKELY(!is_init && !is_clinit)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Unexpected '<' at start of method name " << method_name;
} else {
if (UNLIKELY((access_flags & kAccConstructor) == 0)) {
LOG(WARNING) << method_name << " didn't have expected constructor access flag in class "
<< PrettyDescriptor(klass.Get()) << " in dex file " << dex_file.GetLocation();
access_flags |= kAccConstructor;
}
}
}
dst->SetAccessFlags(access_flags);
}该函数主要是通过指针对内存中的dex文件进行访问,获取到ArtMethod所需的相关内容后完成对ArtMethod的初始化工作,如
dst->SetDexMethodIndex(dex_method_idx);
dst->SetDeclaringClass(klass.Get());
dst->SetCodeItemOffset(it.GetMethodCodeItemOffset());
dst->SetDexCacheResolvedMethods(klass->GetDexCache()->GetResolvedMethods());
dst->SetDexCacheResolvedTypes(klass->GetDexCache()->GetResolvedTypes());
这几个赋值语句。在FART的实现中如何来确定被修复的函数属于哪一个类哪一个方法呢?事实上区分函数的唯一性可以靠该函数的相关属性如类型名+函数名+函数签名的形式来区分。而在FART中我直接使用了函数的method_idx属性来确定(对于一个dex中的所有函数都由method_idx来编号,这也是单个dex文件能包含的最大方法数为65536的原因)。其中,可以看到最关键的一个变量的初始化:dst->SetCodeItemOffset(it.GetMethodCodeItemOffset());该语句对当前函数所指向的内存中的smali指令的地址进行了初始化。当前一些函数抽取类壳一般有两种策略来处理,第一种属于占坑型,提前将dex中的函数体部分进行加密或者直接置为无效,在函数执行前再进行该部分空间的解密从而供函数调用执行;第二种则在加固过程中对dex进行了重构,导致原有的函数体的空间已经无效,在函数执行前直接修改该ArtMethod对象中的CodeItemOffse指向来达成函数的调用执行。接下来再看LinkCode源码:
void ClassLinker::LinkCode(ArtMethod* method, const OatFile::OatClass* oat_class,
uint32_t class_def_method_index) {
Runtime* const runtime = Runtime::Current();
if (runtime->IsAotCompiler()) {
// The following code only applies to a non-compiler runtime.
return;
}
// Method shouldn't have already been linked.
DCHECK(method->GetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode() == nullptr);
if (oat_class != nullptr) {
// Every kind of method should at least get an invoke stub from the oat_method.
// non-abstract methods also get their code pointers.
const OatFile::OatMethod oat_method = oat_class->GetOatMethod(class_def_method_index);
oat_method.LinkMethod(method);
}
// Install entry point from interpreter.
bool enter_interpreter = NeedsInterpreter(method, method->GetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode());
if (enter_interpreter && !method->IsNative()) {
method->SetEntryPointFromInterpreter(artInterpreterToInterpreterBridge);
} else {
method->SetEntryPointFromInterpreter(artInterpreterToCompiledCodeBridge);
}
if (method->IsAbstract()) {
method->SetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode(GetQuickToInterpreterBridge());
return;
}
if (method->IsStatic() && !method->IsConstructor()) {
// For static methods excluding the class initializer, install the trampoline.
// It will be replaced by the proper entry point by ClassLinker::FixupStaticTrampolines
// after initializing class (see ClassLinker::InitializeClass method).
method->SetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode(GetQuickResolutionStub());
} else if (enter_interpreter) {
if (!method->IsNative()) {
// Set entry point from compiled code if there's no code or in interpreter only mode.
method->SetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode(GetQuickToInterpreterBridge());
} else {
method->SetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode(GetQuickGenericJniStub());
}
}
if (method->IsNative()) {
// Unregistering restores the dlsym lookup stub.
method->UnregisterNative();
if (enter_interpreter) {
// We have a native method here without code. Then it should have either the generic JNI
// trampoline as entrypoint (non-static), or the resolution trampoline (static).
// TODO: this doesn't handle all the cases where trampolines may be installed.
const void* entry_point = method->GetEntryPointFromQuickCompiledCode();
DCHECK(IsQuickGenericJniStub(entry_point) || IsQuickResolutionStub(entry_point));
}
}
}
LinkCode函数对不同函数类型进行了不同的处理,进而完成对ArtMethod中相关变量的初始化工作,如针对native函数进行method->UnregisterNative(),针对以quick模式或interpreter模式执行的函数的不同的初始化工作。当然,ArtMethod类提供了一个函数:GetDexFile(),该函数也可以获取到当前ArtMethod对象所在的DexFile对象引用,在获得了当前DexFile对象引用后,也依然可以dump得到当前内存中的dex。
2.实现及实验验证
上面对ART环境下的类加载执行流程简单做了介绍,从而说明这几种通用dump方案的原理。实现部分就不在这里贴了,具体可以看上一篇文章《FART:ART环境下基于主动调用的自动化脱壳方案》,最终FART使用的是通过运行过程中ArtMethod来使用GetDexFile()函数从而获取到DexFile对象引用进而达成dex的dump。这里同时给出四种实现思路(具体的dump时机和方法上一节部分已经给出):
① 通过修改Android系统源代码,在这些dump点插入dump整体dex的代码
② 使用frida来hook这些函数,然后通过指针对这些对象中的变量进行访问,最终定位到内存中的dex的起始点并完成dump
③ 使用ida在过掉前期的反调试之后,对这些函数下断即可(过反调试是个繁琐的任务)
④ 使用xposed或者virtualxposed结合native层函数的hook技术实现
参考链接:
最后于 28分钟前 被hanbingle编辑 ,原因:
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh