2021-10-21 17:38:20 Author: hakin9.org(查看原文) 阅读量:118 收藏
$ bluescan -h
bluescan
A powerful Bluetooth scanner.
Author: Sourcell Xu from DBAPP Security HatLab.
License: GPL-3.0
Usage:
bluescan (-h | --help)
bluescan (-v | --version)
bluescan [-i <hci>] --clean BD_ADDR
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m br [--inquiry-len=<n>]
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m br --lmp-feature BD_ADDR
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m le [--scan-type=<type>] [--timeout=<sec>] [--sort=<key>]
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m le [--ll-feature|--smp-feature] [--timeout=<sec>] --addr-type=<type> BD_ADDR
bluescan -m le --adv [--channel=<num>]
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m sdp BD_ADDR
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m gatt [--include-descriptor] [--io-capability=<name>] --addr-type=<type> BD_ADDR
bluescan [-i <hci>] -m vuln [--addr-type=<type>] BD_ADDR
Arguments:
BD_ADDR Target Bluetooth device address. FF:FF:FF:00:00:00 means local
device.
Options:
-h, --help Display this help.
-v, --version Show the version.
-i <hci> HCI device used for subsequent scans. [default: The first HCI device]
-m <mode> Scan mode, support BR, LE, SDP, GATT and vuln.
--inquiry-len=<n> Inquiry_Length parameter of HCI_Inquiry command. [default: 8]
--lmp-feature Scan LMP features of the remote BR/EDR device.
--scan-type=<type> Scan type used for scanning LE devices, active or
passive. [default: active]
--timeout=<sec> Duration of the LE scanning, but may not be precise. [default: 10]
--sort=<key> Sort the discovered devices by key, only support
RSSI now. [default: rssi]
--adv Sniff advertising physical channel PDU. Need at
least one micro:bit.
--ll-feature Scan LL features of the remote LE device.
--smp-feature Detect pairing features of the remote LE device.
--channel=<num> LE advertising physical channel, 37, 38 or 39). [default: 37,38,39]
--include-descriptor Fetch descriptor information.
--addr-type=<type> Type of the LE address, public or random.
--io-capability=<name> Set IO capability of the agent. Available value: DisplayOnly, DisplayYesNo,
KeyboardOnly, NoInputNoOutput, KeyboardDisplay (KeyboardOnly) [default: NoInputNoOutput]
--clean Clean the cached data of a remote device.
Scan BR devices -m br
Classic Bluetooth devices may use three technologies: BR (Basic Rate), EDR (Enhanced Data Rate), and AMP (Alternate MAC/PHY). Since they all belong to the Basic Rate system, so when scanning these devices we call them BR device scanning:
As shown above, through BR device scanning, we can get the address, page scan repetition mode, class of device, clock offset, RSSI, and the extended inquiry response (Name, TX power, and so on) of the surrounding classic Bluetooth devices.
Scan LE devices -m le
Bluetooth technology, in addition to the Basic Rate system, is Low Energy (LE) system. When scanning Bluetooth low energy devices, it is called LE device scanning:
As shown above, through LE device scanning, we can get the address, address type, connection status, RSSI, and GAP data of the surrounding LE devices.
Scan BR LMP features -m br --lmp-feature
Detecting the LMP features of classic Bluetooth devices allows us to judge their underlying security features:
Scan LE LL features -m le --ll-feature
Detecting the LL (Link Layer) features for the LE devices:
Detect SMP Pairing features -m le --smp-feature
Detecting the SMP Pairing features of the remote LE device:
Sniffing advertising physical channel PDU -m le --adv
Compared with scanning above the HCI, using micro:bit to sniff the advertising physical channel PDU at the link layer, you can get richer LE device activity information:
💡 The scan mode has a hidden function.
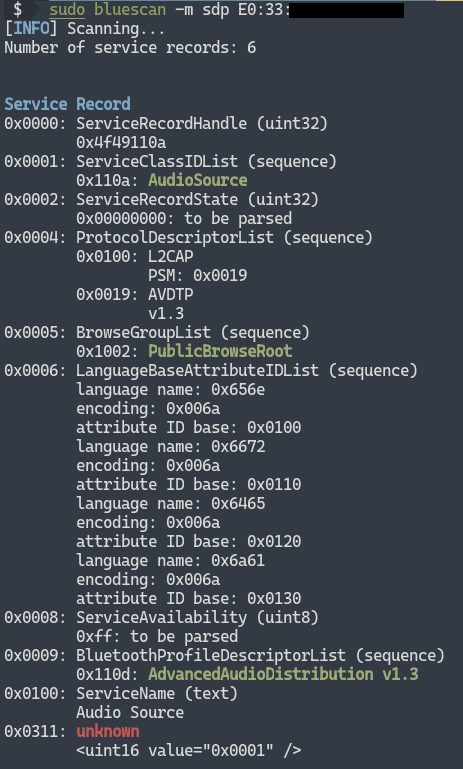
Scan SDP services -m sdp
Classic Bluetooth devices tell the outside world about their open services through SDP. After SDP scanning, we can get service records of them:
You can try to connect to these services for further hacking.
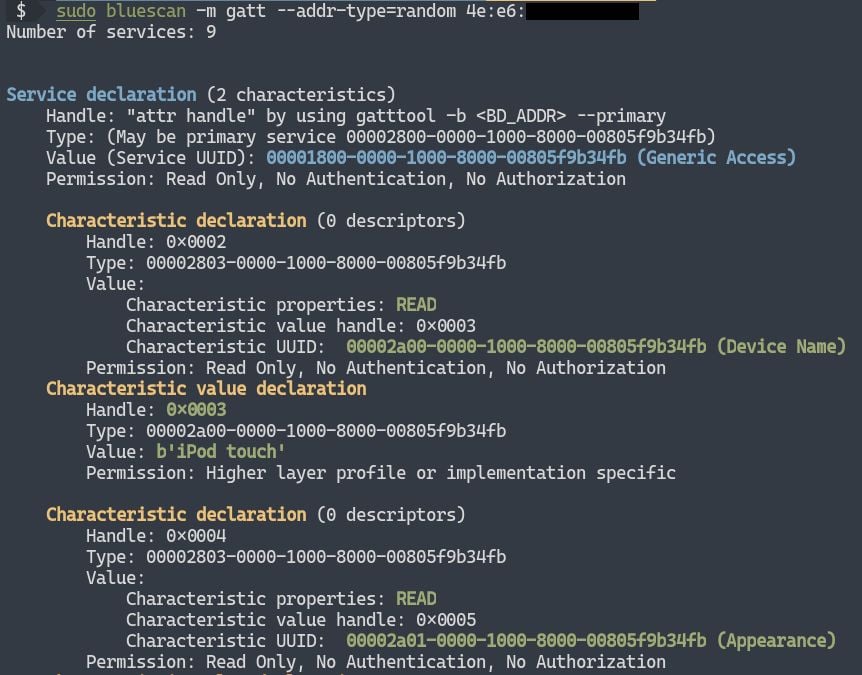
Scan GATT services -m gatt
LE devices tell the outside world about their open services through GATT. After GATT scanning, we can get the GATT service of them. You can try to read and write these GATT data for further hacking:
Vulnerabilities scanning -m vuln (demo)
Vulnerability scanning is still in the demo stage, and currently only supports CVE-2017-0785:
$ sudo bluescan -m vuln --addr-type=br ??:??:??:??:??:??
... ...
CVE-2017-0785
FAQ
- Exception: "Can't find the ID of hci0 in rfkill"Some old versions of rfkill do not support
-rand-noptions, like:# Ubuntu 16.04.1 rfkill --version # rfkill 0.5-1ubuntu3 (Ubuntu)"Please upgrade rfkill or OS to solve this problem.
PS: My system is Kali, and the version of rfkill is:
# Kali rfkill --version # rfkill from util-linux 2.36.1
If you encounter the following error, restart Bluetooth service to recover (sudo systemctl restart bluetooth.service):
[ERROR] Failed to execute management command 'scanend' (code: 11, error: Rejected)
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh